| Citation: | Zhang L, Pan J, Zhang Z, Wu H, Yao N et al. Ultrasensitive skin‐like wearable optical sensors based on glass micro/nanofibers. Opto‐Electron Adv 3, 190022 (2020). doi: 10.29026/oea.2020.190022 |
Original Article Open Access
Ultrasensitive skin-like wearable optical sensors based on glass micro/nanofibers
-
Abstract
Electronic skin, a class of wearable electronic sensors that mimic the functionalities of human skin, has made remarkable success in applications including health monitoring, human-machine interaction and electronic-biological interfaces. While electronic skin continues to achieve higher sensitivity and faster response, its ultimate performance is fundamentally limited by the nature of low-frequency AC currents. Herein, highly sensitive skin-like wearable optical sensors are demonstrated by embedding glass micro/nanofibers (MNFs) in thin layers of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). Enabled by the transition from guided modes into radiation modes of the waveguiding MNFs upon external stimuli, the skin-like optical sensors show ultrahigh sensitivity (1870 kPa-1), low detection limit (7 mPa) and fast response (10 μs) for pressure sensing, significantly exceeding the performance metrics of state-of-the-art electronic skins. Electromagnetic interference (EMI)-free detection of high-frequency vibrations, wrist pulse and human voice are realized. Moreover, a five-sensor optical data glove and a 2×2-MNF tactile sensor are demonstrated. These initial results pave the way toward a new category of optical devices ranging from ultrasensitive wearable sensors to optical skins.-
Keywords:
- optical micro/nanofiber /
- pressure sensor /
- tactile sensor /
- wearable sensor
-

-
References
[1] Kim D H, Lu N S, Ma R, Kim Y S, Kim R H et al.Epidermal electronics.Science 333, 838-843(2011). doi: 10.1126/science.1206157 [2] Hammock M L, Chortos A, Tee B C K, Tok J B H, Bao Z N.25th anniversary article:the evolution of electronic skin (E-Skin):a brief history, design considerations, and recent progress.Adv Mater 25, 5997-6038(2013). doi: 10.1002/adma.201302240 [3] Mannsfeld S C B, Tee B C K, Stoltenberg R M, Chen C V H H, Barman S et al.Highly sensitive flexible pressure sensors with microstructured rubber dielectric layers.Nat Mater 9, 859-864(2010). doi: 10.1038/nmat2834 [4] Jason N N, Ho M D, Cheng W J.Resistive electronic skin.J Mater Chem C 5, 5845-5866(2017). doi: 10.1039/C7TC01169E [5] Wang X D, Zhou J, Song J H, Liu J, Xu N S et al.Piezoelectric field effect transistor and nanoforce sensor based on a single ZnO nanowire.Nano Lett 6, 2768-2772(2006). doi: 10.1021/nl061802g [6] Fan F R, Lin L, Zhu G, Wu W Z, Zhang R et al.Transparent triboelectric nanogenerators and self-powered pressure sensors based on micropatterned plastic films.Nano Lett 12, 3109-3114(2012). doi: 10.1021/nl300988z [7] Kang D, Pikhitsa P V, Choi Y W, Lee C, Shin S S et al.Ultrasensitive mechanical crack-based sensor inspired by the spider sensory system.Nature 516, 222-226(2014). doi: 10.1038/nature14002 [8] Yin D, Feng J, Ma R, Liu Y F, Zhang Y L et al.Efficient and mechanically robust stretchable organic light-emitting devices by a laser-programmable buckling process.Nat Commun 7, 11573(2016). doi: 10.1038/ncomms11573 [9] Miyamoto A, Lee S, Cooray N F, Lee S, Mori M et al.Inflammation-free, gas-permeable, lightweight, stretchable on-skin electronics with nanomeshes.Nat Nanotechnol 12, 907-913(2017). doi: 10.1038/nnano.2017.125 [10] Takei K, Takahashi T, Ho J C, Ko H, Gillies A G et al.Nanowire active-matrix circuitry for low-voltage macroscale artificial skin.Nat Mater 9, 821-826(2010). doi: 10.1038/nmat2835 [11] Larson C, Peele B, Li S, Robinson S, Totaro M et al.Highly stretchable electroluminescent skin for optical signaling and tactile sensing.Science 351, 1071-1074(2016). doi: 10.1126/science.aac5082 [12] Kim Y, Chortos A, Xu W T, Liu Y X, Oh J Y et al.A bioinspired flexible organic artificial afferent nerve.Science 360, 998-1003(2018). doi: 10.1126/science.aao0098 [13] Miller D A B.Rationale and challenges for optical interconnects to electronic chips.Proc IEEE 88, 728-749(2000). doi: 10.1109/5.867687 [14] Lee B.Review of the present status of optical fiber sensors.Opt Fiber Technol 9, 57-79(2003). doi: 10.1016/S1068-5200(02)00527-8 [15] Tong L M, Gattass R R, Ashcom J B, He S L, Lou J Y et al.Subwavelength-diameter silica wires for low-loss optical wave guiding.Nature 426, 816-819(2003). doi: 10.1038/nature02193 [16] Nagai R, Aoki T.Ultra-low-loss tapered optical fibers with minimal lengths.Opt Express 22, 28427-28436(2014). doi: 10.1364/OE.22.028427 [17] Brambilla G, Payne D N.The ultimate strength of glass silica nanowires.Nano Lett 9, 831-835(2019). [18] Rising A, Johansson J.Toward spinning artificial spider silk.Nat Chem Biol 11, 309-315(2015). doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1789 [19] Daly M, Sergides M, Nic Chormaic S.Optical trapping and manipulation of micrometer and submicrometer particles.Laser Photonics Rev 9, 309-329(2015). doi: 10.1002/lpor.201500006 [20] Sun D D, Guo T, Ran Y, Huang Y, Guan B O.In-situ DNA hybridization detection with a reflective microfiber grating biosensor.Biosens Bioelectron 61, 541-546(2014). doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2014.05.065 [21] Liu T, Liang L L, Xiao P, Sun L P, Huang Y Y et al.A label-free cardiac biomarker immunosensor based on phase-shifted microfiber Bragg grating. Biosens Bioelectron 100, 155-160(2018). doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2017.08.061 [22] Sumetsky M, Windeler R S, Dulashko Y, Fan X.Optical liquid ring resonator sensor.Opt Express 15, 14376-14381(2007). doi: 10.1364/OE.15.014376 [23] Wang C, Jin W, Liao C R, Ma J, Jin W et al.Highly birefringent suspended-core photonic microcells for refractive-index sensing.Appl Phys Lett 105, 061105(2014). doi: 10.1063/1.4892962 [24] Luo H P, Sun Q Z, Li X L, Yan Z J, Li Y P et al.Refractive index sensitivity characteristics near the dispersion turning point of the multimode microfiber-based Mach-Zehnder interferometer.Opt Lett 40, 5042-5045(2015). doi: 10.1364/OL.40.005042 [25] Gu F X, Wu G Q, Zeng H P.Hybrid photon-plasmon Mach-Zehnder interferometers for highly sensitive hydrogen sensing.Nanoscale 7, 924-929(2015). doi: 10.1039/C4NR06642A [26] Wu Y, Yao B C, Yu C B, Rao Y J.Optical graphene gas sensors based on microfibers:a review.Sensors 18, 941(2018). doi: 10.3390/s18040941 [27] Chen Y, Yan S C, Zheng X, Xu F, Lu Y Q.A miniature reflective micro-force sensor based on a microfiber coupler.Opt Express 22, 2443-2450(2014). doi: 10.1364/OE.22.002443 [28] Yang R, Yu Y S, Zhu C C, Xue Y, Chen C et al.PDMS-coated S-tapered fiber for highly sensitive measurements of transverse load and temperature.IEEE Sens J 15, 3429-3435(2015). doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2015.2388490 [29] Tong L M, Lou J Y, Mazur E.Single-mode guiding properties of subwavelength-diameter silica and silicon wire waveguides.Opt Express 12, 1025-1035(2004). doi: 10.1364/OPEX.12.001025 [30] Zhao X L, Hua Q L, Yu R M, Zhang Y, Pan C F.Flexible, stretchable and wearable multifunctional sensor array as artificial electronic skin for static and dynamic strain mapping.Adv Electron Mater 1, 1500142(2015). doi: 10.1002/aelm.201500142 [31] Persano L, Dagdeviren C, Su Y W, Zhang Y H, Girardo S et al.High performance piezoelectric devices based on aligned arrays of nanofibers of poly (vinylidenefluoride-co-trifluoroethylene).Nat Commun 4, 1633(2013). doi: 10.1038/ncomms2639 [32] Park J, Lee Y, Hong J, Ha M, Jung Y D et al.Giant tunneling piezoresistance of composite elastomers with interlocked microdome arrays for ultrasensitive and multimodal electronic skins.ACS Nano 8, 4689-4697(2014). doi: 10.1021/nn500441k [33] Zang Y P, Zhang F J, Huang D Z, Gao X K, Di C A et al.Flexible suspended gate organic thin-film transistors for ultra-sensitive pressure detection.Nat Commun 6, 6269(2015). doi: 10.1038/ncomms7269 [34] Zhou J, Gu Y D, Fei P, Mai W J, Gao Y F et al.Flexible piezotronic strain sensor.Nano Lett 8, 3035-3040(2008). doi: 10.1021/nl802367t [35] Wang X W, Gu Y, Xiong Z P, Cui Z, Zhang T.Silk‐molded flexible, ultrasensitive, and highly stable electronic skin for monitoring human physiological signals.Adv Mater 26, 1336-1342(2014). doi: 10.1002/adma.201304248 [36] Shin S H, Ji S, Choi S, Pyo K H, Wan A B et al.Integrated arrays of air-dielectric graphene transistors as transparent active-matrix pressure sensors for wide pressure ranges.Nat Commun 8, 14950(2017). doi: 10.1038/ncomms14950 [37] Nichols W W.Clinical measurement of arterial stiffness obtained from noninvasive pressure waveforms.Am J Hypertens 18, 3-10(2005). [38] Fujiwara E, dos Santos M F M, Suzuki C K.Flexible optical fiber bending transducer for application in glove-based sensors.IEEE Sens J, 14, 3631-3636(2014). doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2014.2330998 [39] Chen S, Lou Z, Chen D, Jiang K, Shen G Z.Polymer-enhanced highly stretchable conductive fiber strain sensor used for electronic data gloves.Adv Mater Technol 1, 1600136(2016). doi: 10.1002/admt.201600136 -
Supplementary Information
Supplementary information for Ultrasensitive skin‐like wearable optical sensors based on glass micro/nanofibers
Movie1.mp4 
Movie2.mp4 
Movie3.mp4 
-
Access History

Article Metrics
-
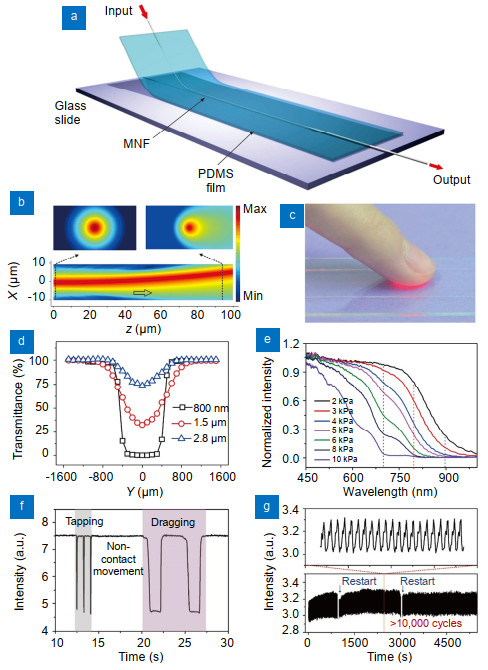
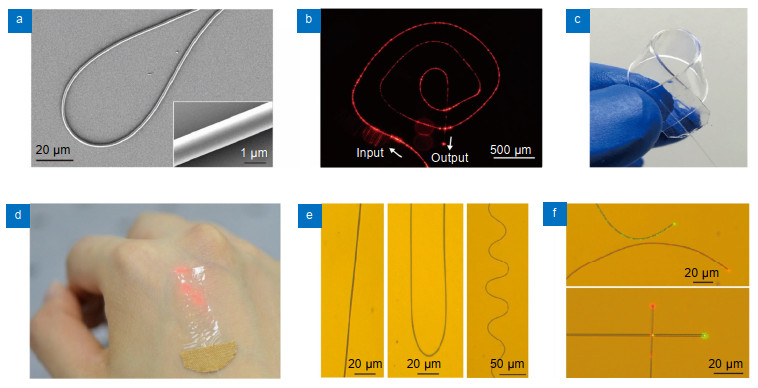
Figure 1.
Fabrication and characterization of MNF-embedded PDMS patches.
-
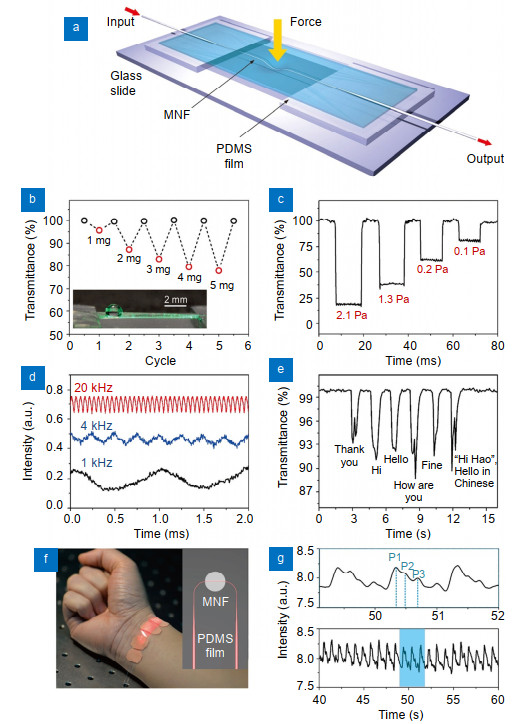
Figure 2.
Characterization of substrate supported SLWOSs.
-
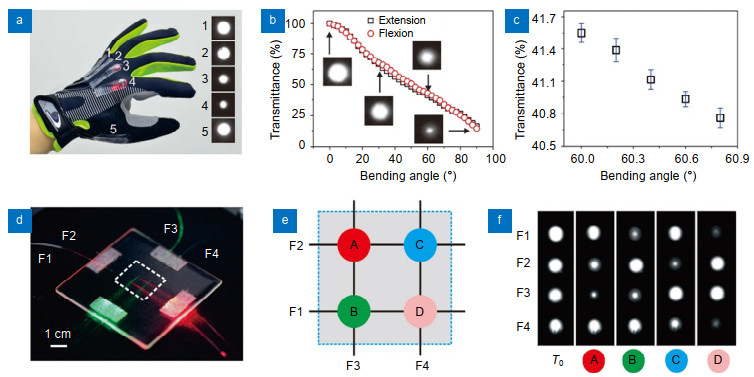
Figure 3.
Characterization of suspended SLWOSs.
-
Figure 4.
Optical data gloves and SLWOS with perpendicularly intersected 2×2 MNF arrays.

 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: