| Citation: | Wang Y Q, Ma X L, Li X, Pu M B, Luo X G. Perfect electromagnetic and sound absorption via subwavelength holes array. Opto-Electron Adv 1, 180013 (2018). doi: 10.29026/oea.2018.180013 |
Original Article Open Access
Perfect electromagnetic and sound absorption via subwavelength holes array
-
Abstract
Broadband sound absorption at low frequency is notoriously difficult because the thickness of the absorber should be proportional to the working wavelength. Here we report an acoustic metasurface absorber following the recent theory developed for electromagnetics. We first show that there is an intrinsic analogy between the impedance description of sound and electromagnetic metasurfaces. Subsequently, we demonstrated that the classic Salisbury and Jaumann absorbers can be realized for acoustic applications with the aid of micro-perforated plates. Finally, the concept of coherent perfect absorption is introduced to achieve ultrathin and ultra-broadband sound absorbers. We anticipate that the approach proposed here can provide helpful guidance for the design of future acoustic and electromagnetic devices.-
Keywords:
- metasurface /
- absorber /
- acoustic /
- electromagnetics
-

-
References
[1] Knott E F, Shaeffer J F, Tuley M T. Radar Cross Section 2nd ed (SciTech Publishing, Raleigh, North Carolina, 2004). [2] Hao J M, Wang J, Liu X L, Padilla W J, Zhou L et al. High performance optical absorber based on a plasmonic metamaterial. Appl Phys Lett 96, 251104 (2010). doi: 10.1063/1.3442904 [3] Feng Q, Pu M B, Hu C G, Luo X G. Engineering the dispersion of metamaterial surface for broadband infrared absorption. Opt Lett 37, 2133-2135 (2012). doi: 10.1364/OL.37.002133 [4] Mei J, Ma G C, Yang M, Yang Z Y, Wen W J et al. Dark acoustic metamaterials as super absorbers for low-frequency sound. Nat Commun 3, 756 (2012). doi: 10.1038/ncomms1758 [5] Vora A, Gwamuri J, Pala N, Kulkarni A, Pearce J M et al. Exchanging ohmic losses in metamaterial absorbers with useful optical absorption for photovoltaics. Sci Rep 4, 4901 (2014). [6] Song M W, Yu H L, Hu C G, Pu M B, Zhang Z J et al. Conversion of broadband energy to narrowband emission through double-sided metamaterials. Opt Express 21, 32207-32216 (2013). doi: 10.1364/OE.21.032207 [7] Cui Y X, He Y R, Jin Y, Ding F, Yang L et al. Plasmonic and metamaterial structures as electromagnetic absorbers. Laser Photonics Rev 8, 495-520 (2014). doi: 10.1002/lpor.v8.4 [8] Luo X G. Principles of electromagnetic waves in metasurfaces. Sci China Phys Mech Astron 58, 594201 (2015). doi: 10.1007/s11433-015-5688-1 [9] de Rosny J, Fink M. Overcoming the diffraction limit in wave physics using a time-reversal mirror and a novel acoustic sink. Phys Rev Lett 89, 124301 (2002). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.89.124301 [10] Lerosey G, de Rosny J, Tourin A, Fink M. Focusing beyond the diffraction limit with far-field time reversal. Science 315, 1120-1122 (2007). doi: 10.1126/science.1134824 [11] Chen L W, Zhou Y, Wu M X, Hong M H. Remote-mode microsphere nano-imaging: new boundaries for optical microscopes. Opto-Electron Adv 1, 170001 (2018). [12] Qin F, Hong M H. Breaking the diffraction limit in far field by planar metalens. Sci China Phys Mech Astron 60, 044231 (2017). doi: 10.1007/s11433-017-9005-8 [13] Jacob Z, Alekseyev L V, Narimanov E. Optical hyperlens: Far-field imaging beyond the diffraction limit. Opt Express 14, 8247-8256 (2006). [14] Li J, Fok L, Yin X B, Bartal G, Zhang X. Experimental demonstration of an acoustic magnifying hyperlens. Nat Mater 8, 931-934 (2009). doi: 10.1038/nmat2561 [15] Kildishev A V, Boltasseva A, Shalaev V M. Planar photonics with metasurfaces. Science 339, 1232009 (2013). doi: 10.1126/science.1232009 [16] Yu N F, Capasso F. Flat optics with designer metasurfaces. Nat Mater 13, 139-150 (2014). doi: 10.1038/nmat3839 [17] Ma G C, Yang M, Xiao S W, Yang Z Y, Sheng P. Acoustic metasurface with hybrid resonances. Nat Mater 13, 873-878 (2014). doi: 10.1038/nmat3994 [18] Luo X G. Subwavelength optical engineering with metasurface waves. Adv Opt Mater 6, 1701201 (2018). doi: 10.1002/adom.201701201 [19] Pu M B, Feng Q, Wang M, Hu C G, Huang C et al. Ultrathin broadband nearly perfect absorber with symmetrical coherent illumination. Opt Express 20, 2246-2254 (2012). doi: 10.1364/OE.20.002246 [20] Li S C, Luo J, Anwar S, Li S, Lu W X et al. Broadband perfect absorption of ultrathin conductive films with coherent illumination: Superabsorption of microwave radiation. Phys Rev B 91, 220301(R) (2015). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.91.220301 [21] Pu M B, Hu C G, Huang C, Wang C T, Zhao Z Y et al. Investigation of Fano resonance in planar metamaterial with perturbed periodicity. Opt Express 21, 992-1001 (2013). doi: 10.1364/OE.21.000992 [22] Maa D-Y. Potential of microperforated panel absorber. J Acoust Soc Am 104, 2861-2866 (1998). doi: 10.1121/1.423870 [23] Herdtle T, Bolton J S, Kim N N, Alexander J H, Gerdes R W. Transfer impedance of microperforated materials with tapered holes. J Acoust Soc Am 134, 4752 (2013). doi: 10.1121/1.4824968 [24] Qian Y J, Kong D Y, Liu S M, Sun S M, Zhao Z. Investigation on micro-perforated panel absorber with ultra-micro perforations. Appl Acoust 74, 931-935 (2013). doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2013.01.009 [25] Chambers B. Optimum design of a salisbury screen radar absorber. Electron Lett 30, 1353-1354 (1994). doi: 10.1049/el:19940896 [26] Knott E F, Langseth K. Performance degradation of Jaumann absorbers due to curvature. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag 28, 137-139 (1980). doi: 10.1109/TAP.1980.1142278 [27] Duan Y T, Luo J, Wang G H, Hang Z H, Hou B et al. Theoretical requirements for broadband perfect absorption of acoustic waves by ultra-thin elastic meta-films. Sci Rep 5, 12139 (2015). doi: 10.1038/srep12139 [28] Cheng Y, Zhou C, Yuan B G, Wu D J, Wei Q et al. Ultra-sparse metasurface for high reflection of low-frequency sound based on artificial Mie resonances. Nat Mater 14, 1013-1019 (2015). doi: 10.1038/nmat4393 [29] Smith F C. Design principles of broadband adaptive Salisbury screen absorber. Electron Lett 38, 1052-1054 (2002). doi: 10.1049/el:20020699 [30] Munk B A, Munk P, Pryor J. On designing Jaumann and circuit analog absorbers (CA absorbers) for oblique angle of incidence. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag 55, 186-193 (2007). doi: 10.1109/TAP.2006.888395 [31] Pu M B, Chen P, Wang Y Q, Zhao Z Y, Wang C T et al. Strong enhancement of light absorption and highly directive thermal emission in graphene. Opt Express 21, 11618-11627 (2013). doi: 10.1364/OE.21.011618 [32] Akselrod G M, Huang J N, Hoang T B, Bowen P T, Su L et al. Large-area metasurface perfect absorbers from visible to near-infrared. Adv Mater 27, 8028-8034 (2015). doi: 10.1002/adma.201503281 [33] Chong Y D, Ge L, Cao H, Stone A D. Coherent perfect absorbers: time-reversed lasers. Phys Rev Lett 105, 053901 (2010). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.105.053901 [34] Pu M B, Feng Q, Hu C G, Luo X G. Perfect absorption of light by coherently induced plasmon hybridization in ultrathin metamaterial film. Plasmonics 7, 733-738 (2012). doi: 10.1007/s11468-012-9365-1 [35] Li S C, Duan Q, Li S, Yin Q, Lu W X et al. Perfect electromagnetic absorption at one-atom-thick scale. Appl Phys Lett 107, 181112 (2015). doi: 10.1063/1.4935427 [36] Papaioannou M, Plum E, Valente J, Rogers E T F, Zheludev N I. Two-dimensional control of light with light on metasurfaces. Light Sci Appl 5, e16070 (2016). doi: 10.1038/lsa.2016.70 [37] Li X, Pu M B, Wang Y Q, Ma X L, Li Y et al. Dynamic control of the extraordinary optical scattering in semicontinuous 2D metamaterials. Adv Opt Mater 4, 659-663 (2016). doi: 10.1002/adom.v4.5 [38] Rozanov K N. Ultimate thickness to bandwidth ratio of radar absorbers. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag 48, 1230-1234 (2000). doi: 10.1109/8.884491 [39] Wang D C, Zhang L C, Gu Y H, Mehmood M Q, Gong Y D et al. Switchable ultrathin quarter-wave plate in terahertz using active phase-change metasurface. Sci Rep 5, 15020 (2015). doi: 10.1038/srep15020 [40] Wan W J, Chong Y D, Ge L, Noh H, Stone A D et al. Time-reversed lasing and interferometric control of absorption. Science 331, 889-892 (2011). doi: 10.1126/science.1200735 [41] Wei P J, Croenne C, Chu S T, Li J. Symmetrical and anti-symmetrical coherent perfect absorption for acoustic waves. Appl Phys Lett 104, 121902 (2014). doi: 10.1063/1.4869462 [42] Zhang J F, MacDonald K F, Zheludev N I. Controlling light-with-light without nonlinearity. Light Sci Appl 1, e18 (2012). doi: 10.1038/lsa.2012.18 [43] Ebbesen T W, Lezec H J, Ghaemi H F, Thio T, Wolff P A. Extraordinary optical transmission through sub-wavelength hole arrays. Nature 391, 667-669 (1998). doi: 10.1038/35570 [44] Munk B A. Frequency Selective Surfaces: Theory and Design (Wiley, New York, 2000). -
Access History

Article Metrics
-
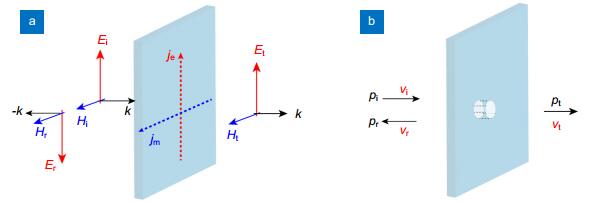
Figure 1.
Boundary conditions for the electromagnetic and acoustic waves on a thin plate.
-
Figure 2.
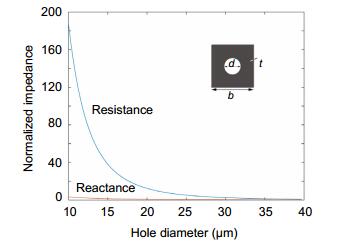
Normalized impedance versus the hole diameter d at a frequency of 10 kHz.
-
Figure 3.
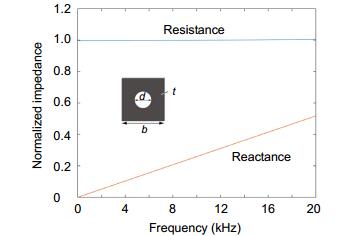
Normalized impedance of micro-perforated plate.
-
Figure 4.
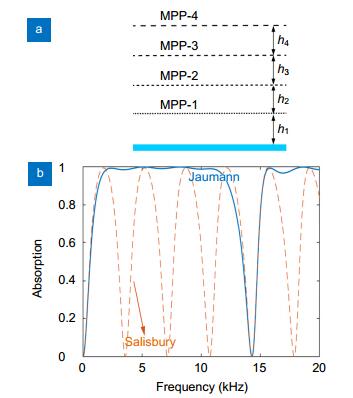
Acoustic Salisbury and Jaumann absorbers.
-
Figure 5.
Angular dependence of the Jaumann absorber.
-
Figure 6.
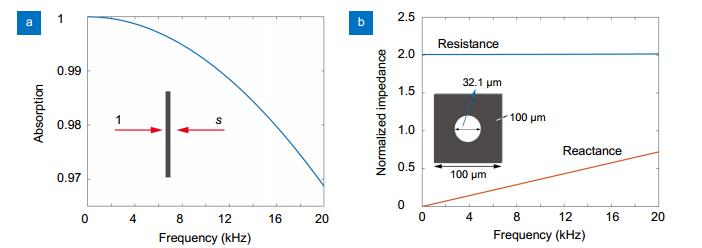
Acoustic coherent perfect absorber.
-
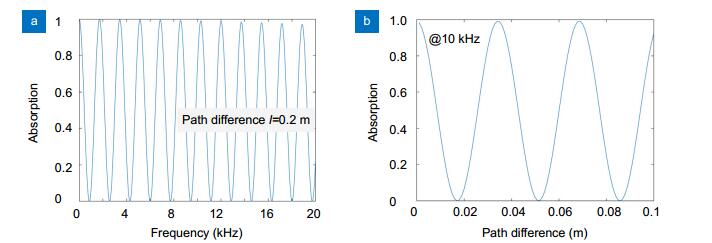
Figure 7.
Variation in the absorption under different coherent conditions.
-
Figure 8.
Schematic of the acoustic multilayer.

 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: