| Citation: | He P H , Zhang H C, Gao X X, Niu L Y, Tang W X et al. A novel spoof surface plasmon polariton structure to reach ultra-strong field confinements.Opto-Electron Adv 2, 190001 (2019). doi: 10.29026/oea.2019.190001 |
Original Article Open Access
A novel spoof surface plasmon polariton structure to reach ultra-strong field confinements
-
Abstract
Ultrathin corrugated metallic structures have been proved to support spoof surface plasmon polariton (SPP) modes on two-dimension (2D) planar microwave circuits. However, to provide stronger field confinement, larger width of strip is required to load deeper grooves, which is cumbersome in modern large-scale integrated circuits and chips. In this work, a new spoof SPP transmission line (TL) with zigzag grooves is proposed. This new structure can achieve stronger field confinement compared to conventional one with the same strip width. In other words, the proposed spoof SPP TL behaves equivalently to a conventional one with much larger size. Dispersion analysis theoretically indicates the negative correlation between the ability of field confinement and cutoff frequencies of spoof SPP TLs. Numerical simulations indicate that the cutoff frequency of the proposed TL is lower than the conventional one and can be easily modified with the fixed size. Furthermore, two samples of the new and conventional spoof SPP TLs are fabricated for experimental demonstration. Measured S-parameters and field distributions verify the ultra-strong ability of field confinement of the proposed spoof SPP TL. Hence, this novel spoof SPP structure with ultra-strong field confinement may find wide applications in microwave and terahertz engineering. -

-
References
[1] Barnes W L, Dereux A, Ebbesen T W. Surface plasmon subwavelength optics. Nature 424, 824-830 (2003). doi: 10.1038/nature01937 [2] Jones A C, Olmon R L, Skrabalak S E, Wiley B J, Xia Y N et al. Mid-IR plasmonics: near-field imaging of coherent plasmon modes of silver nanowires. Nano Lett 9, 2553-2558 (2009). doi: 10.1021/nl900638p [3] Fang N, Lee H, Sun C, Zhang X. Sub-diffraction-limited optical imaging with a silver superlens. Science 308, 534-537 (2005). doi: 10.1126/science.1108759 [4] Anker J N, Hall W P, Lyandres O, Shah N C, Zhao J et al. Biosensing with plasmonic nanosensors. Nat Mater 7, 442-453 (2008). doi: 10.1038/nmat2162 [5] Polman A, Atwater H A. Photonic design principles for ultrahigh-efficiency photovoltaics. Nat Mater 11, 174-177 (2012). doi: 10.1038/nmat3263 [6] Pendry J B, Martín-Moreno L, García-Vidal F J. Mimicking surface plasmons with structured surfaces. Science 305, 847-848 (2004). doi: 10.1126/science.1098999 [7] Goubau G. On the excitation of surface waves. Proc IRE 40, 865-868 (1952). doi: 10.1109/JRPROC.1952.273856 [8] Hibbins A P, Evans B R, Sambles J R. Experimental verification of designer surface plasmons. Science 308, 670-672 (2005). doi: 10.1126/science.1109043 [9] García-Vidal F J, Martín-Moreno L, Pendry J B. Surfaces with holes in them: new plasmonic metamaterials. J Opt A Pure Appl Opt 7, S97-S101 (2005). doi: 10.1088/1464-4258/7/2/013 [10] Juluri B K, Lin S C S, Walker T R, Jensen L, Huang T J. Propagation of designer surface plasmons in structured conductor surfaces with parabolic gradient index. Opt Express 17, 2997-3006 (2009). doi: 10.1364/OE.17.002997 [11] Elliott R. On the theory of corrugated plane surfaces. Trans IRE Prof Group Antennas Propag 2, 71-81 (1954). doi: 10.1109/T-AP.1954.27975 [12] Maier S A, Andrews S R, Martín-Moreno L, García-Vidal F J. Terahertz surface plasmon-polariton propagation and focusing on periodically corrugated metal wires. Phys Rev Lett 97, 176805 (2006). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.97.176805 [13] Nagpal P, Lindquist N C, Oh S H, Norris D J. Ultrasmooth patterned metals for plasmonics and metamaterials. Science 325, 594-597 (2009). doi: 10.1126/science.1174655 [14] Zhou Y J, Jiang Q, Cui T J. Bidirectional bending splitter of designer surface plasmons. Appl Phys Lett 99, 111904 (2011). doi: 10.1063/1.3639277 [15] Rivas J G. Terahertz: the art of confinement. Nat Photonics 2, 137-138 (2008). doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2008.12 [16] Gan Q Q, Fu Z, Ding Y J, Bartoli F J. Ultrawide-bandwidth slow-light system based on THz plasmonic graded metallic grating structures. Phys Rev Lett 100, 256803 (2008). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.100.256803 [17] Luo X G. Principles of electromagnetic waves in metasurfaces. Sci China Phys, Mech Astron 58, 594201 (2015). [18] Pors A, Moreno E, Martín-Moreno L, Pendry J B, García-Vidal F J. Localized spoof plasmons arise while texturing closed surfaces. Phys Rev Llett 108, 223905 (2012). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.108.223905 [19] Chen L W, Zheng X R, Du Z R, Jia B H, Gu M et al. A frozen matrix hybrid optical nonlinear system enhanced by a particle lens. Nanoscale7, 14982-14988 (2015). doi: 10.1039/C5NR03304G [20] Li X, Chen L W, Li Y, Zhang X H, Pu M B et al. Multicolor 3D meta-holography by broadband plasmonic modulation. Sci Adv 2, e1601102 (2016). doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1601102 [21] Qin F, Ding L, Zhang L, Monticone F, Chum C C et al. Hybrid bilayer plasmonic metasurface efficiently manipulates visible light. Sci Adv2, e1501168 (2016). doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1501168 [22] Gao H, Li Y, Chen L W, Jin J J, Pu M B et al. Quasi-Talbot effect of orbital angular momentum beams for generation of optical vortex arrays by multiplexing metasurface design. Nanoscale 10, 666-671 (2018). doi: 10.1039/C7NR07873K [23] Gan Q Q, Gao Y K, Wagner K, Vezenov D, Ding Y J et al. Experimental verification of the rainbow trapping effect in adiabatic plasmonic gratings. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108, 5169-5173 (2011). doi: 10.1073/pnas.1014963108 [24] Williams C R, Andrews S R, Maier S A, Fernández-Domínguez A I, Martín-Moreno L et al. Highly confined guiding of terahertz surface plasmon polaritons on structured metal surfaces. Nat Photonics 2, 175-179 (2008). doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2007.301 [25] Shen X P, Cui T J, Martin-Cano D, García-Vidal F J. Conformal surface plasmons propagating on ultrathin and flexible films. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA110, 40-45 (2013). doi: 10.1073/pnas.1210417110 [26] Kianinejad A, Chen Z N, Qiu C W. Spoof plasmon-based slow-wave excitation of dielectric resonator antenna. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag 64, 2094-2099 (2016). doi: 10.1109/TAP.2016.2545738 [27] Zhang H C, Tang W X, Xu J, Liu S, Liu J F et al. Reduction of shielding-box volume using SPP-like transmission lines. IEEE Trans Comp, Packag Manuf Technol 7, 1486-1492 (2017). doi: 10.1109/TCPMT.2017.2700950 [28] Zhang H C, Cui T J, Xu J, Tang W X, Liu J F. Real-time controls of designer surface plasmon polaritons using programmable plasmonic metamaterial. Adv Mater Technol 2, 1600202 (2017). doi: 10.1002/admt.v2.1 [29] He P H, Zhang H C, Tang W X, Wang Z X, Yan R T et al. A multi-layer spoof surface plasmon polariton waveguide with corrugated ground. IEEE Access 5, 25306-25311 (2017). doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2768481 [30] Kianinejad A, Chen Z N, Qiu C W. Design and modeling of spoof surface plasmon modes-based microwave slow-wave transmission line. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech 63, 1817-1825 (2015). doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2015.2422694 [31] Zhang D W, Zhang K, Wu Q, Yang G H, Sha X J. High-efficiency broadband excitation and propagation of second-mode spoof surface plasmon polaritons by a complementary structure. Opt Lett 42, 2766-2769 (2017). doi: 10.1364/OL.42.002766 [32] Zhang D W, Zhang K, Wu Q, Dai R W, Sha X J. Broadband high-order mode of spoof surface plasmon polaritons supported by compact complementary structure with high efficiency. Opt Lett 43, 3176-3179 (2018). doi: 10.1364/OL.43.003176 [33] Zhang H C, Zhang Q, Liu J F, Tang W X, Fan Y F et al. Smaller-loss planar SPP transmission line than conventional microstrip in microwave frequencies. Sci Rep 6, 23396 (2016). doi: 10.1038/srep23396 [34] Zhang H C, Cui T J, Zhang Q, Fan Y F, Fu X J. Breaking the challenge of signal integrity using time-domain spoof surface plasmon polaritons. ACS Photonics 2, 1333-1340 (2015). doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.5b00316 [35] Ma H F, Shen X P, Cheng Q, Jiang W X, Cui T J. Broadband and high-efficiency conversion from guided waves to spoof surface plasmon polaritons. Laser Photon Rev 8, 146-151 (2014). doi: 10.1002/lpor.201300118 [36] Pan B C, Liao Z, Zhao J, Cui T J. Controlling rejections of spoof surface plasmon polaritons using metamaterial particles. Opt Express 22, 13940-13950 (2014). doi: 10.1364/OE.22.013940 -
Access History

Article Metrics
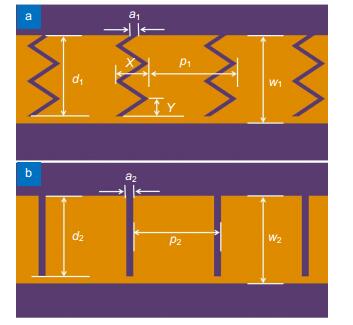
- Figure 1. The detailed geometric configuration of the new spoof SPP TL and conventional spoof SPP TL.
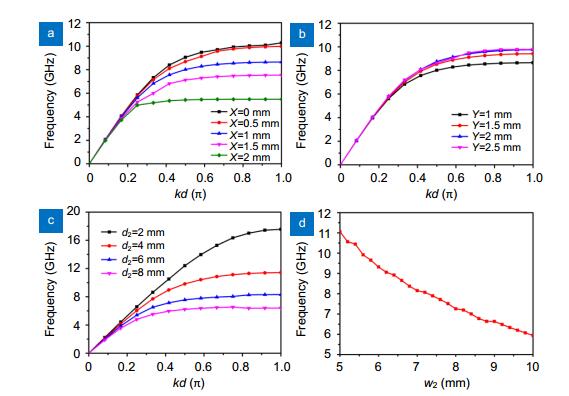
- Figure 2. The simulated dispersion curves for the two kinds of spoof SPP TLs with different geometric parameters and the plot of the relationship between depth of grooves and cutoff frequency.
- Figure 3. Schematic diagram of the conversion structures between CPW and the new spoof SPP TLs, which is composed of tapered strip, gradient zigzag corrugations and flaring ground.
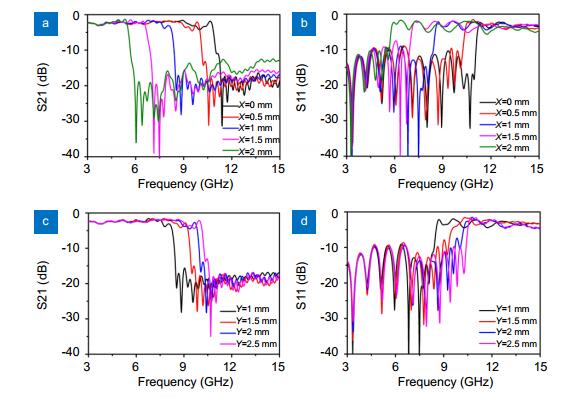
- Figure 4. Simulated S-parameters of the whole structures with different X and Y.
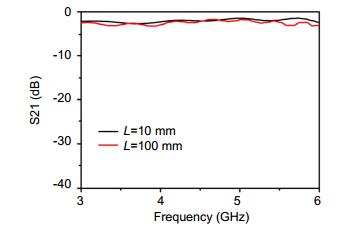
- Figure 5. The simulated transmission coefficients of the two samples with different lengths of spoof SPP TL.
- Figure 6. The simulated amplitude distributions of electric field on the cross sections of the typical spoof SPP TL with straight grooves and the new spoof SPP TL with undulant grooves at 6 GHz.
- Figure 7. Two samples of the typical spoof SPP TL with straight grooves and the new spoof SPP TL with undulant grooves.
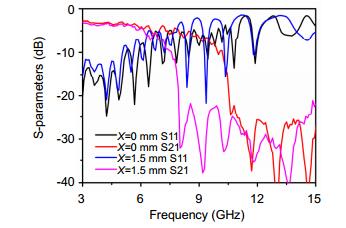
- Figure 8. The measured S-parameters of the two samples with straight grooves (X=0 mm) and zigzag grooves (X=1.5 mm).
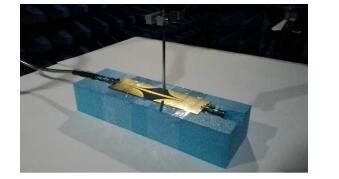
- Figure 9. The photograph of the electromagnetic measurement system which is composed of a electromagnetic shielding chamber, a VNA and a monopole antenna (as a probe) installed in a mechanical platform which can scan the plane or space under the control of stepper motor.
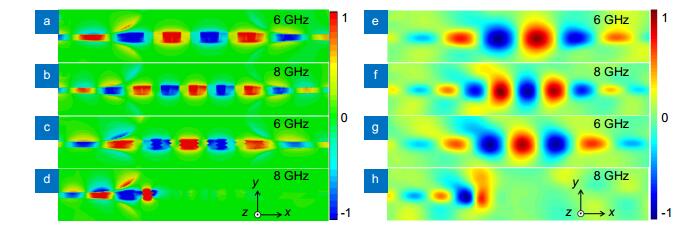
- Figure 10. Simulated (a, b, c, d) and measured (e, f, g, h) near-field distributions of z-component of electric fields of the conventional (a, b, e, f) and proposed (c, d, g, h) spoof SPP structures at 6 GHz and 8 GHz.

 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: