| Citation: | Yang QX, Liu HL, He S, Tian QY, Xu B et al. Circular cladding waveguides in Pr:YAG fabricated by femtosecond laser inscription: Raman, luminescence properties and guiding performance. Opto-Electron Adv 4, 200005 (2021).. doi: 10.29026/oea.2021.200005 |
Circular cladding waveguides in Pr:YAG fabricated by femtosecond laser inscription: Raman, luminescence properties and guiding performance
-
Abstract
We report on the fabrication of circular cladding waveguides with cross-section diameters of 60−120 μm in Pr:YAG crystal by applying femtosecond laser inscription. The fabricated waveguides present 2D guidance on the cross-section and fairly low propagation losses. Multiple high-order guiding modes are observed in waveguides with different diameters. Corresponding simulation results reveal the origin of a specific kind of guiding modes. Confocal micro-Raman (μ-Raman) experiments demonstrate the modification effects in femtosecond laser affected areas and ascertain the refractive index induced guiding mechanism. In addition, luminescence emission properties of Pr3+ ions at waveguide volume are well preserved during the femtosecond laser inscription process, which may result in a potential high-power visible waveguide laser. -

-
References
[1] Zhang D, Sugioka K. Hierarchical microstructures with high spatial frequency laser induced periodic surface structures possessing different orientations created by femtosecond laser ablation of silicon in liquids. Opto-Electron Adv 2, 190002 (2019). doi: 10.29026/oea.2019.190002 [2] Liu X, Bai B, Chen Q, Sun H. Etching-assisted femtosecond laser modification of hard materials. Opto-Electron Adv 2, 190021 (2019). doi: 10.29026/oea.2019.190021 [3] Zhang LM, Guo TY, Ren YY, Cai YJ, Mackenzie MD et al. Cooperative up-converted luminescence in Yb, Na:CaF2 cladding waveguides by femtosecond laser inscription. Opt Commun 441, 8–13 (2019). doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2019.01.032 [4] Bharadwaj V, Courvoisier A, Fernandez TT, Ramponi R, Galzerano G et al. Femtosecond laser inscription of Bragg grating waveguides in bulk diamond. Opt Lett 42, 3451–3453 (2017). doi: 10.1364/OL.42.003451 [5] Sotillo B, Bharadwaj V, Hadden JP, Sakakura M, Chiappini A et al. Diamond photonics platform enabled by femtosecond laser writing. Sci Rep 6, 35566 (2016). doi: 10.1038/srep35566 [6] Li SL, Deng FM, Huang ZP. Femtosecond laser inscription waveguides in Nd:GdVO4 crystal. Opt Eng 55, 107104 (2016). doi: 10.1117/1.OE.55.10.107104 [7] Chandrahalim H, Rand SC, Fan XD. Fusion of renewable ring resonator lasers and ultrafast laser inscribed photonic waveguides. Sci Rep 6, 32668 (2016). doi: 10.1038/srep32668 [8] Vázquez MR, Sotillo B, Rampini S, Bharadwaj V, Gholipour B et al. Femtosecond laser inscription of nonlinear photonic circuits in Gallium Lanthanum Sulphide glass. J Phys Photonics 1, 015006 (2018). doi: 10.1088/2515-7647/aade60 [9] Li SL, Ye YK, Shen CY, Wang HL. Femtosecond laser inscribed cladding waveguide structures in LiNbO3 crystal for beam splitters. Opt Eng 57, 117103 (2018). doi: 10.1117/1.OE.57.11.117103 [10] Piromjitpong T, Dubov M, Boscolo S. High-repetition-rate femtosecond-laser inscription of low-loss thermally stable waveguides in lithium niobate. Appl Phys A 125, 302 (2019). doi: 10.1007/s00339-019-2609-6 [11] Lv JM, Cheng YZ, Lu QM, Vázquez de Aldana JR, Hao XT et al. Femtosecond laser written optical waveguides in z-cut MgO:LiNbO3 crystal: Fabrication and optical damage investigation. Opt Mater 57, 169–173 (2016). doi: 10.1016/j.optmat.2016.05.003 [12] Chen F, Vázquez de Aldana JRV. Optical waveguides in crystalline dielectric materials produced by femtosecond-laser micromachining. Laser Photonics Rev 8, 251–275 (2014). doi: 10.1002/lpor.201300025 [13] Jia Y, Wang S, Chen F. Femtosecond laser direct writing of flexibly configured waveguide geometries in optical crystals: fabrication and application. Opto-Electron Adv 3, 190042 (2020). doi: 10.29026/oea.2020.19004 [14] Skryabin N, Kalinkin A, Dyakonov I, Kulik S. Femtosecond laser written depressed-cladding waveguide 2 × 2, 1 × 2 and 3 × 3 directional couplers in Tm(3+):YAG crystal. Micromachines (Basel) 11, 1 (2019). doi: 10.3390/mi11010001 [15] Ren YY, Jiao Y, Vázquez de Aldana JR, Chen F. Ti:Sapphire micro-structures by femtosecond laser inscription: Guiding and luminescence properties. Opt Mater 58, 61–66 (2016). doi: 10.1016/j.optmat.2016.05.023 [16] Bérubé JP, Lapointe J, Dupont A, Bernier M, Vallée R. Femtosecond laser inscription of depressed cladding single-mode mid-infrared waveguides in sapphire. Opt Lett 44, 37–40 (2019). doi: 10.1364/OL.44.000037 [17] Li SL, Huang ZP, Ye YK, Wang HL. Femtosecond laser inscribed cladding waveguide lasers in Nd:LiYF4 crystals. Opt Laser Technol 102, 247–253 (2018). doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2018.01.003 [18] Romero C, García Ajates J, Chen F, Vázquez de Aldana JR. Fabrication of tapered circular depressed-cladding waveguides in Nd:YAG crystal by femtosecond-laser direct inscription. Micromachines (Basel) 11, 10 (2019). doi: 10.3390/mi11010010 [19] Nie WJ, He RY, Cheng C, Rocha U, Vázquez de Aldana JR et al. Optical lattice-like cladding waveguides by direct laser writing: fabrication, luminescence, and lasing. Opt Lett 41, 2169–2172 (2016). doi: 10.1364/OL.41.002169 [20] Liu HL, Luo SY, Xu B, Xu HY, Cai ZP et al. Femtosecond-laser micromachined Pr:YLF depressed cladding waveguide: Raman, fluorescence, and laser performance. Opt Mater Express 7, 3990–3997 (2017). doi: 10.1364/OME.7.003990 [21] Okhrimchuk AG, Butvina LN, Dianov EM, Lichkova NV, Zagorodnev VN et al. New laser transition in a Pr3+:RbPb2Cl5crystal in the 2.3—2.5-μm range. Quantum Electron 36, 41–44 (2006). doi: 10.1070/QE2006v036n01ABEH013101 [22] Nie HK, Zhang PX, Zhang BT, Yang KJ, Zhang LH et al. Diode-end-pumped Ho, Pr:LiLuF4 bulk laser at 2.95 μm. Opt Lett 42, 699–702 (2017). doi: 10.1364/OL.42.000699 [23] Fan MQ, Li T, Li GQ, Zhao SZ, Yang KJ et al. Passively Q-switched Ho, Pr:LiLuF4 laser with graphitic carbon nitride nanosheet film. Opt Express 25, 12796–12803 (2017). doi: 10.1364/OE.25.012796 [24] Cheng YJ, Peng J, Xu B, Yang H, Luo ZQ et al. Passive Q-switching of a diode-pumped Pr:LiYF4 visible laser using WS2 as saturable absorber. IEEE Photonics J 8, 1–6 (2016). [25] Fibrich M, Šulc J, Zavadilová A, Jelínková H. Nonlinear mirror mode-locked Pr:YAlO3 laser. Laser Phys 27, 055801 (2017). doi: 10.1088/1555-6611/aa66f5 [26] Sattayaporn S, Loiseau P, Aka G, Marzahl DT, Kränkel C. Crystal growth, spectroscopy and laser performances of Pr(3+):Sr0.7La0.3Mg0.3Al11.7O19 (Pr:ASL). Opt Express 26, 1278–1289 (2018). doi: 10.1364/OE.26.001278 [27] Wu PF, He S, Liu HL. Annular waveguide lasers at 1064 nm in Nd:YAG crystal produced by femtosecond laser inscription. Appl Opt 57, 5420–5424 (2018). doi: 10.1364/AO.57.005420 [28] Liu HL, Vázquez de Aldana JR, Hong MH, Chen F. Femtosecond laser inscribed Y-branch waveguide in Nd:YAG crystal: Fabrication and continuous-wave lasing. IEEE J Sel Top Quantum Electron 22, 227–230 (2016). doi: 10.1109/JSTQE.2015.2439191 [29] McDaniel S, Thorburn F, Lancaster A, Stites R, Cook G et al. Operation of Ho:YAG ultrafast laser inscribed waveguide lasers. Appl Opt 56, 3251–3256 (2017). doi: 10.1364/AO.56.003251 [30] Kim MH, Calmano T, Choi SY, Lee BJ, Baek IH et al. Monolayer graphene coated Yb:YAG channel waveguides for Q-switched laser operation. Opt Mater Express 6, 2468–2474 (2016). doi: 10.1364/OME.6.002468 [31] Gómez-Castellanos I, Rodriguez-Dagnino RM. Intensity distributions and cutoff frequencies of linearly polarized modes for a step-index elliptical optical fiber. Opt Eng 46, 045003 (2007). doi: 10.1117/1.2719698 -
Access History

Article Metrics
-
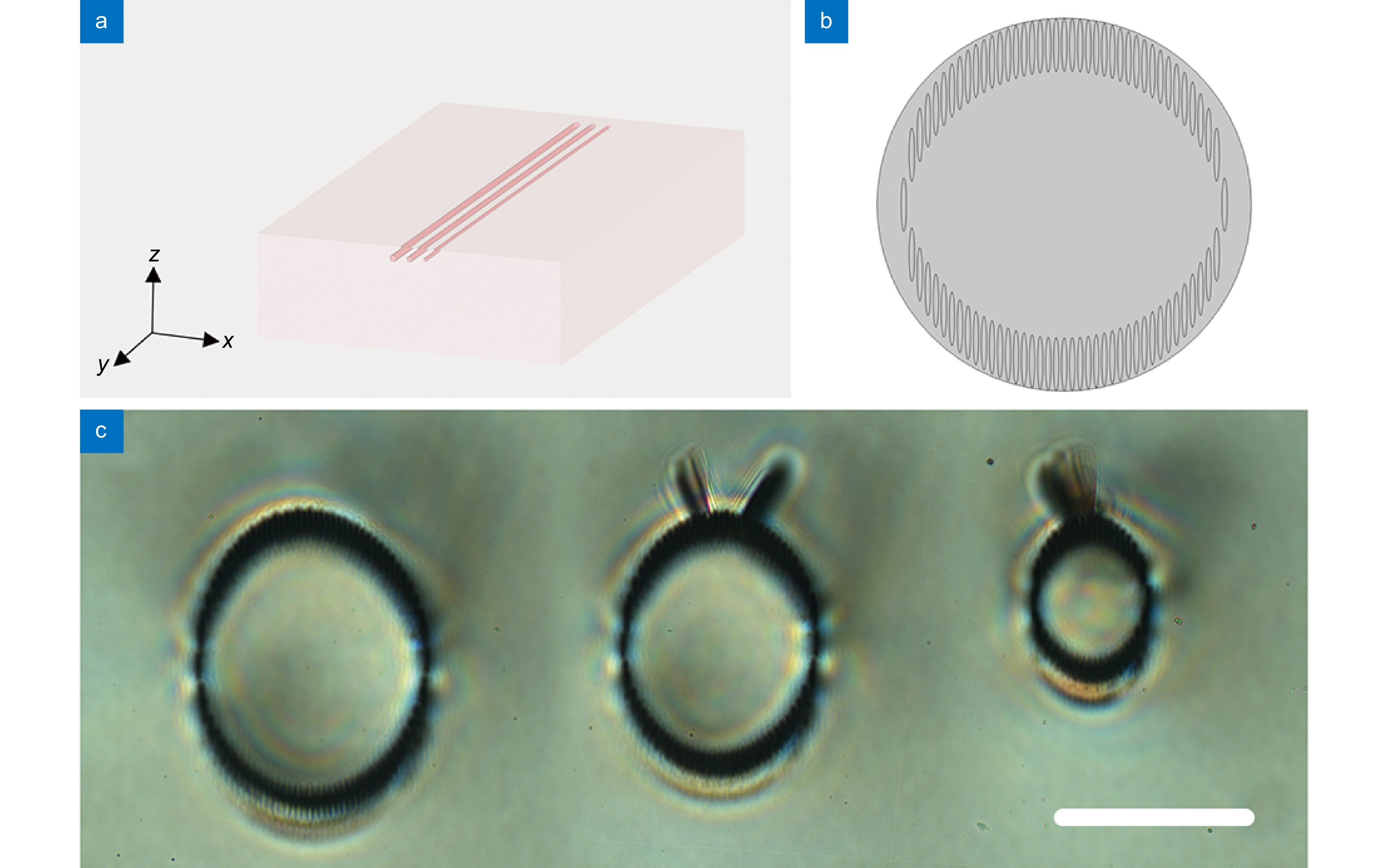
Figure 1.
(a) The 3D schematic diagram of waveguides. Coordinate axes are defined. (b) The 2D geometry structure (corresponding to the 120 μm waveguide), which is also used in the guiding mode simulation process. (c) The cross-section microscope images of the circular cladding waveguides with different diameters: 120 μm, 100 μm, and 60 μm, respectively. The scale bar in the figure is 100 μm.
-
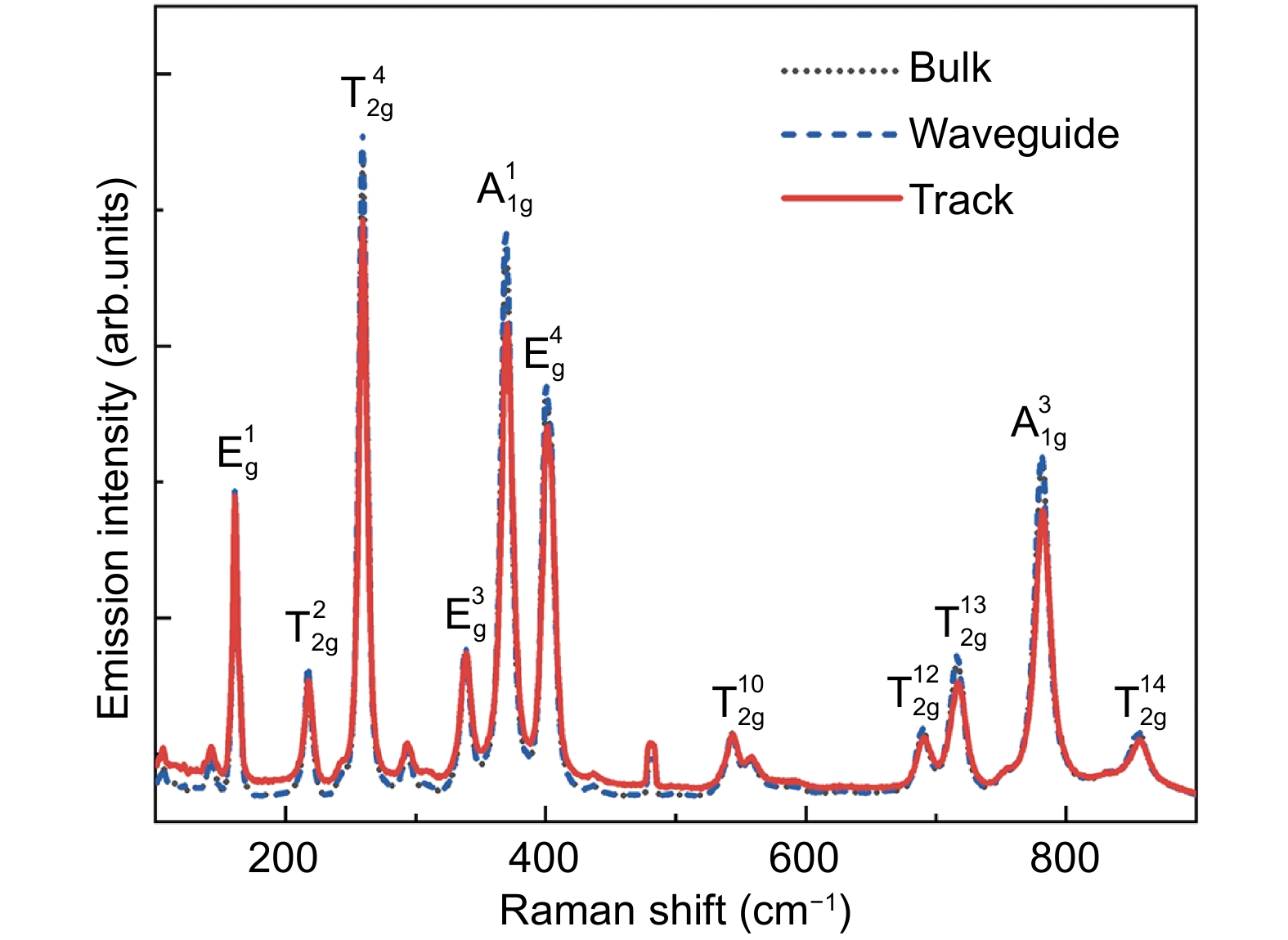
Figure 2.
Raman spectra collected from non-processed bulk area (black dotted line, covered by almost identical blue dashed line), waveguide volume (blue dashed line), and damage track (red solid line) excited by a 532 nm laser. Corresponding molecular vibration modes are marked out on every peak.
-
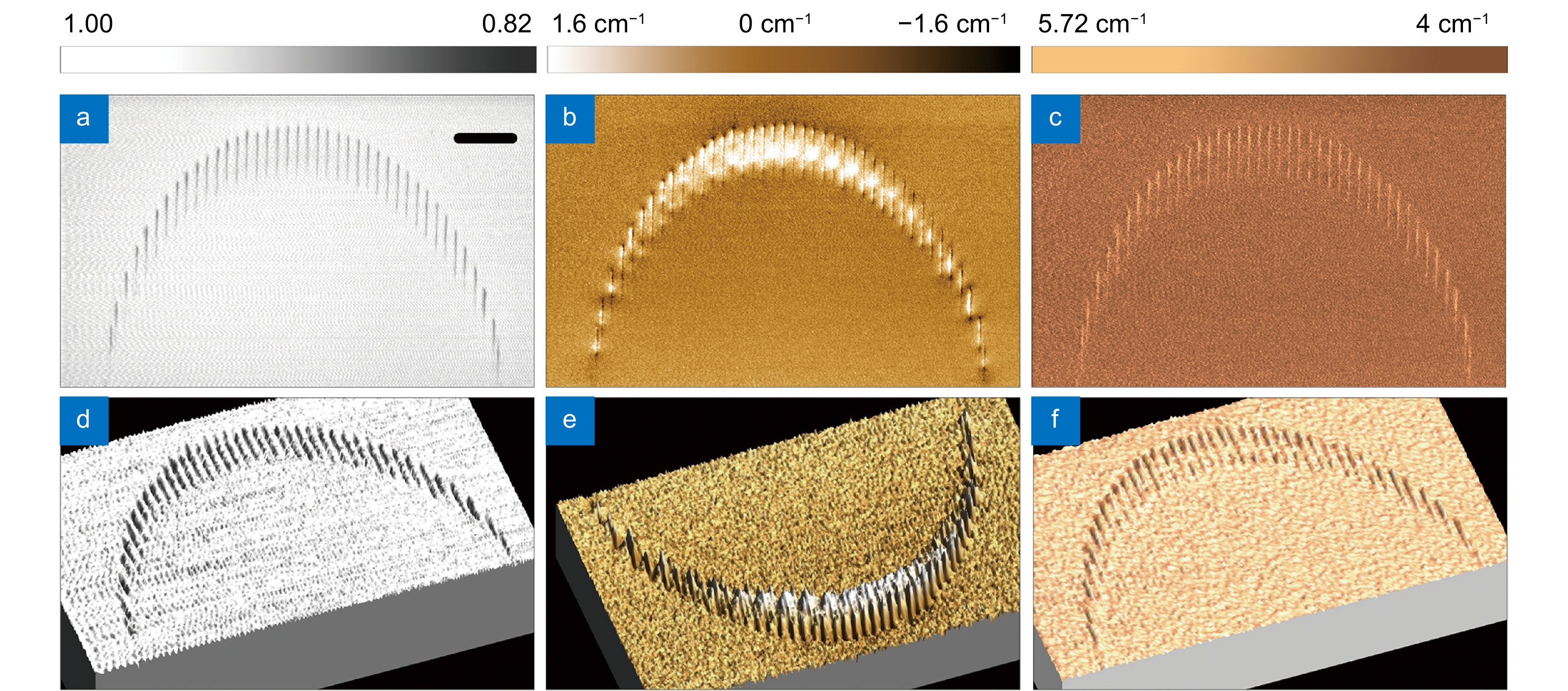
Figure 3.
Confocal μ-Raman 2D mapping results are exhibited as 2D and 3D images with imaging channels. (a) and (d) Intensity (normalized); (b) and (e) Shift; (c) and (f) FWHM of the characteristic peak at 259 cm-1, respectively. The scale bar in the figure is 20 μm.
-
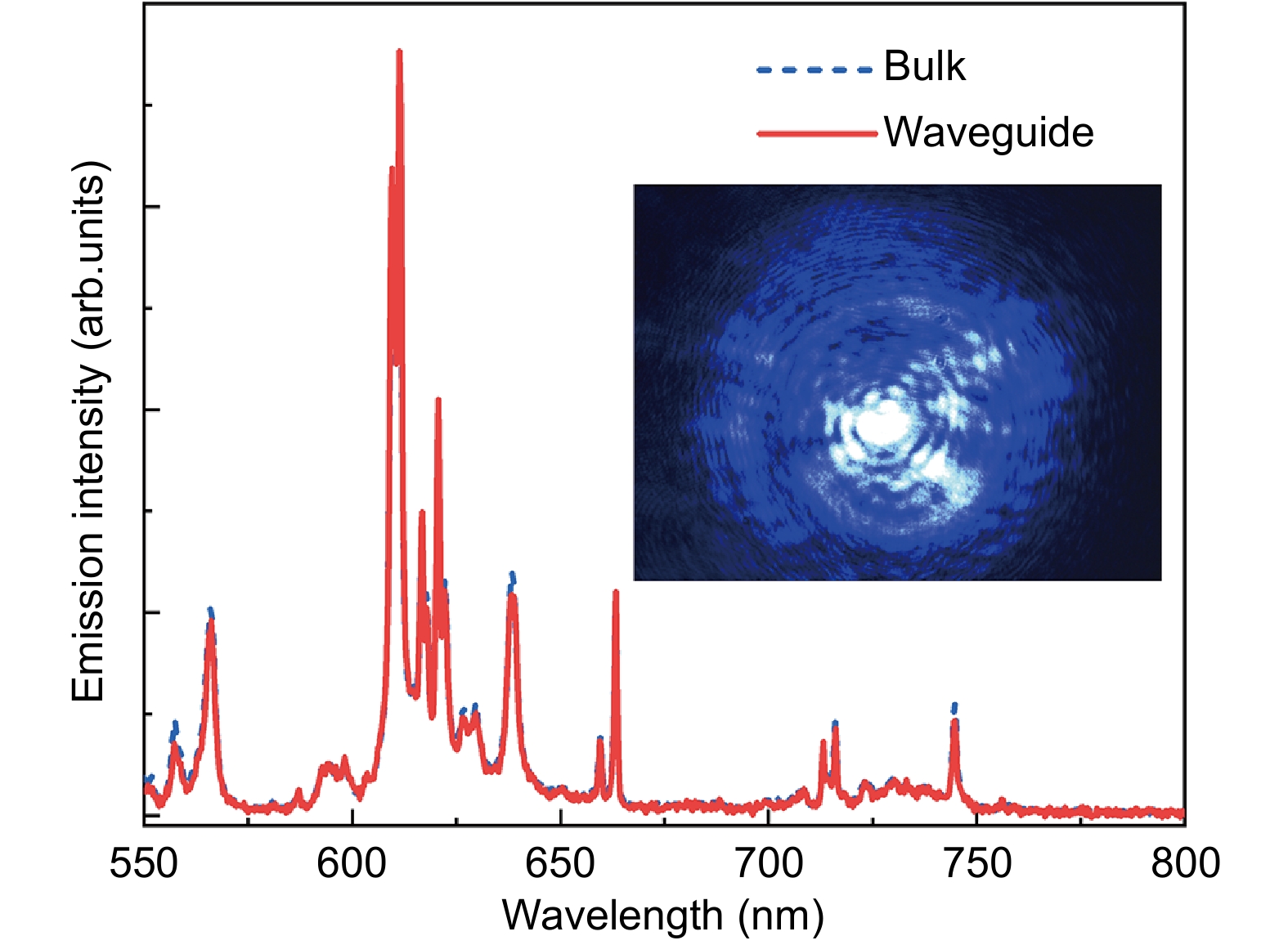
Figure 4.
Luminescence emission spectra of waveguide volume (blue dashed line) and non-processed bulk area (red solid line). Inset shows the output end-face image captured by a color CCD camera while a laser beam at 400 nm has been coupled into the waveguide through another end-face.
-
Figure 5.
A specific kind of modes with an intensity distribution of horizontal fringes in waveguides with different diameters. (a) and (d) 120 μm; (b) and (e) 100 μm; (c) and (f) 60 μm. (a−c) Experimental mode intensity distributions gained by the end-face coupling system using a laser beam at 632.8 nm. (d−f) Corresponding simulation results. The effective refractive indexes are 1.8392, 1.8390 and 1.8389, respectively. Red arrows point to the directions of electric field. The scale bar in the figure is 20 μm.
-
Figure 6.
Simulated mode profiles and corresponding horizontally polarized electric field distributions of (a) and (c) the circularly symmetric fiber model; (b) and (d) the elliptical fiber model. The effective refractive indexes are 1.8395 and 1.8394, respectively. Red arrows point to the directions of electric field.

 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: