-
摘要:
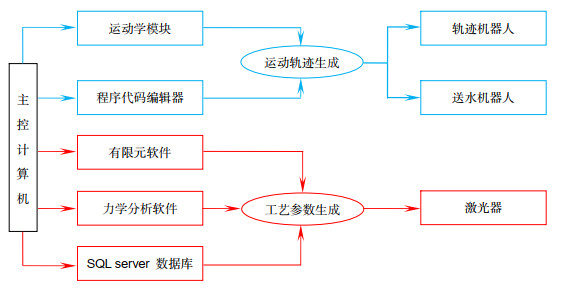
针对复杂曲面类零件,研发一种新型表面激光冲击强化的控制系统,该系统是一套全自动可控操作系统,通过工控机/PLC集成控制,实现自动化、数字化控制,并完成实时在线监控和信息交互反馈,属于开放式分布系统。该系统用于激光冲击强化核心设备(包括激光器、机器人、辅助控制、质量检测装置与辅助系统等),实现各环节的信息交互和系统的协同工作,通过实时监控系统,远程观察加工状态,有效避免重大事故的发生。同时,该控制系统添加激光冲击强化工艺试验数据记录功能,可根据实际需求调用后台工艺参数数据库,实现高效工艺参数优化。除此之外,该系统还能够实现激光冲击强化模型建立、加工过程有限元模拟、复杂曲面加工轨迹自动规划、加工策略制定等功能,从而实现激光冲击强化自动化生产,目前已经处于工程应用阶段。
 Abstract:
Abstract:This paper introduced control system for complex curved surface laser shock processing, which was a set of automatic and digital control system operation, and controlled by the industrial PC/PLC. And it completed the real-time online monitoring and information interaction feedback, belonging to the open distributed system, by the fact that the remote monitoring and control system status of processing effectively avoid the occurrence of major accidents. This system was laser shock processing core device (including laser, robot, auxiliary control, quality testing device and auxiliary system, etc.), that implemented each link of information interaction and systems work together. By the remote monitoring, control system status of processing effectively avoided the occurrence of major accidents. At the same time, the control system added process of laser shock processing test data record function. According to actual demand parameters database called the background, parameter optimization was processed effectively. In addition, the system also could realize laser shock processing model established in this paper, complex surface machining trajectory planning automatically and processing strategy. The system can realize the automatic production of the whole blade laser impact of aero engine, and it is already in the engineering application stage.
-
Key words:
- laser shock peening(LSP) /
- automation /
- simulation /
- trajectory planning /
- process parameters
-

-
-
[1] Dai K, Villegas J, Stone Z, et al. Finite element modeling of the surface roughness of 5052 Al alloy subjected to a surface severe plastic deformation process[J]. Acta Materialia, 2004, 52(20): 5771-5782. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2004.08.031
[2] Spanrad S, Tong J. Characterisation of foreign object damage (FOD) and early fatigue crack growth in laser shock peened Ti-6Al-4V aerofoil specimens[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2011, 528(4-5): 2128-2136. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2010.11.045
[3] See D W, Dulaney J L, Clauer A H, et al. The air force manufacturing technology laser peening initiative[J]. Surface Engineering, 2002, 18(1): 32-36. doi: 10.1179/026708401225001264
[4] King A, Steuwer A, Woodward C, et al. Effects of fatigue and fretting on residual stresses introduced by laser shock peening[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2006, 435-436: 12-18. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2006.07.020
[5] Zhou J Z, Huang S, Zuo L D, et al. Effects of laser peening on residual stresses and fatigue crack growth properties of Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2014, 52: 189-194. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2013.06.011
[6] Ocaña J L, Morales M, García-Ballesteros J J, et al. Laser shock microforming of thin metal sheets[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2009, 255(10): 5633-5636. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2008.10.084
[7] 李伟, 李应红, 何卫锋, 等. 激光冲击强化技术的发展和应用[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2008, 45(12): 15-19. doi: 10.3788/LOP20084512.0015
Li Wei, Li Yinghong, He Weifeng, et al. Development and application of laser shock processing[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2008, 45(12): 15-19. doi: 10.3788/LOP20084512.0015
[8] Sathyajith S, S Kalainathan. Effect of laser shot peening on precipitation hardened aluminum alloy 6061-T6 using low energy laser[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2012, 50(3): 345-348. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2011.11.002
[9] 石朝阳, 刘赤荣, 应才苏. 激光冲击强化技术研究与应用现状[J]. 机械设计与制造, 2010, (4): 61-63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3997.2010.04.025
Shi Chaoyang, Liu Chirong, Ying Caisu. Research and application of laser shock processing[J]. Machinery Design & Manufacture, 2010, (4): 61-63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3997.2010.04.025
[10] Nie Xiangfan, He Weifeng, Zang Shunlai, et al. Effect study and application to improve high cycle fatigue resistance of TC11 titanium alloy by laser shock peening with multiple impacts[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2014, 253: 68-75. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2014.05.015
[11] 聂祥樊, 何卫锋, 李启鹏, 等. 激光喷丸改善TC6钛合金组织和力学性能[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2013, 25(5): 1115-1119. doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20132505.1115
Nie Xiangfan, He Weifeng, Li Qipeng, et al. Improvement of structure and mechanical properties of TC6 titanium alloy with laser shock peening[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2013, 25(5): 1115-1119. doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20132505.1115
[12] Peyre P, Fabbro R, Merrien P, et al. Laser shock processing of aluminium alloys. Application to high cycle fatigue behaviour[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 1996, 210(1-2): 102-113. doi: 10.1016/0921-5093(95)10084-9
[13] Liu K K, Hill M R. The effects of laser peening and shot peening on fretting fatigue in Ti-6Al-4V coupons[J]. Tribology International, 2009, 42(9): 1250-1262. doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2009.04.005
[14] DeWald A T, Rankin J E, Hill M R, et al. Assessment of tensile residual stress mitigation in alloy 22 welds due to laser peening[J]. Journal of Engineering Materials and Technology, 2004, 126(4): 465-473. doi: 10.1115/1.1789957
[15] Montross C S, Wei Tao, Ye Lin, et al. Laser shock processing and its effects on microstructure and properties of metal alloys: a review[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2002, 24(10): 1021-1036. doi: 10.1016/S0142-1123(02)00022-1
[16] Chai Lihua, Chen Yuyong, Zhang Laiqi, et al. Effect of spark plasma sintering temperature on microstructure and mechanical properties of melt-spun TiAl alloys[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(3): 528-533. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61209-0
[17] 陶春虎, 刘庆瑔, 曹春晓, 等. 航空用钛合金的失效及其预防[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2002: 5-10.
Tao Chunhu, Liu Qingquan, Cao Chunxiao, et al. Failure and prevention of aeronautical titanium alloyAerospace titanium alloys failure and its prevention[M]. Beijing: Defense Press, 2002: 5-10.
[18] 胡太友, 乔红超, 赵吉宾, 等. 激光冲击强化设备的开发[J]. 光电工程, 2017, 44(7): 732-737. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.07.010
Hu Taiyou, Qiao Hongchao, Zhao Jibin, et al. Develop of Laser Shock Peening Device[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2017, 44(7): 732-737. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.07.010
[19] 李松夏, 乔红超, 赵吉宾, 等. 激光冲击强化技术原理及研究发展[J]. 光电工程, 2017, 44(6): 569-576. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.06.001
Li Songxia, Qiao Hongchao, Zhao Jibin, et al. Laser shock peening technology principle and research development[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2017, 44(6): 569-576. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.06.001
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS

 下载:
下载: