-
摘要:
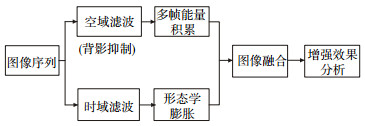
在对点像的探测中,无论采用空域还是时域处理,都只利用了点像元的部分信息,它们都具有一定的局限性。为此,本文提出一种融合多帧时空域滤波的点像元增强算法。首先利用改进后的Top-hat变换对多帧图像做空域处理,然后将具有较好频率分析优势的小波变换引入多帧图像中进行时域处理,最后利用联合分布概率把时空域两种处理方法所得到的灰度图进行融合。实验表明,增强后对具有空天背景的多帧图像平均灰度值和平均信噪比增益得到有效增强。
 Abstract:
Abstract:Both the spatial or time domain processing all have certain limitations by using only the partial information of the target. Therefore, this paper proposes an enhancement algorithm for low signal noise ratio point pixel based on time and spatial correlation. First, the improved Top-hat transform is used for image spatial processing, and then the wavelet transform, which has a good advantage of frequency analysis into the image, is introduced into the time domain processing. Finally, the joint probability distribution is adopted to integrate gray image obtained by the two processing methods. The experimental results show that the average grey value and SNR gain of target are enhanced effectively after enhancement.
-
Key words:
- point pixel /
- background modeling /
- wavelet transform /
- image enhance
-

Abstract: Point pixel enhancement algorithm is an important preprocessing technique in automatic point recognition and detection systems. The point pixel in the image of the pixels are small, lacking information such as shape and texture, of low signal noise ratio, and easily submerged in the complex background, which is extremely unfavorable for subsequent extraction and detection. So point enhancement is necessary.
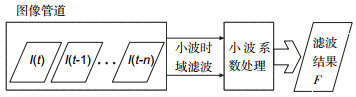
In recent years, lots of papers have been published about the use of spatial domain or time domain on single-frame image enhancement method. Spatial domain is processed to achieve background prediction and the purpose of enhancing the point by filtering or spatial correlation, such as top-hat background suppression, local adaptive filtering and two-dimensional least mean square filtering method (TDLMS). At present, some researchers have proposed a background modeling of anisotropy method from the perspective of image "singularity" for large span background. And time domain processing mainly uses wavelet transform to realize point pixel enhancement, calculate the normalized correlation coefficient among the point pixel coefficient, the background edge coefficient and the noise figure, and enhance the point pixel by distinguishing the correlation coefficient difference, suppressing the background.
The above-mentioned enhancement methods, whether they are spatial domain or time domain processing, use only part of the information of the point pixels. Thus they all have limitations: The spatial processing focuses on the use of gray features of the pixel, and the disadvantage is to ignore the point pixel like the continuity of gray in the time domain. The time domain processing focuses on the continuity of the point pixel gray scale in the time domain, but does not fully consider the gray-scale distribution of the point pixel in the spatial domain. The interference of the noise may introduce more false information. At present, the multi-frame point pixel enhancement method of joint space-time domain is paid more and more attention to. Based on the difference among the point pixel, the background and the noise in the space-time characteristics, we fully consider the spatial and temporal characteristics of the point pixel and uses the joint distribution probability to fuse the gray-scale graphs obtained by the two methods of space-time domain, to improve the image signal-to-noise ratio.
-

-
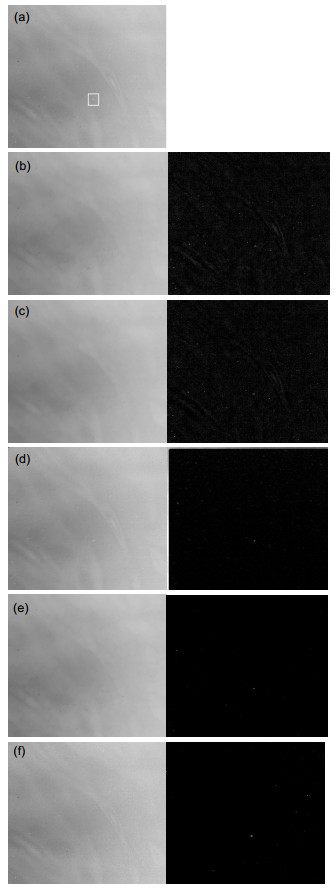
图 4 不同背景预测法得到的背景预测及背景抑制图. (a)原图像. (b) Top-hat背景预测及背景抑制. (c)形态学滤波背景预测及背景抑制. (d) TDLMS背景预测及背景抑制. (e)多尺度形态学背景预测及背景抑制. (f)本文方法背景预测及背景抑制.
Figure 4. Background prediction and background suppression obtained by different background prediction methods. (a) Background. (b) Top-hat background suppression and background prediction. (c) Morphological filter method. (d) TDLMS filter method. (e) Multiscale morphological filter method. (f) Applying our method.
表 1 5帧不同信噪比图像情况.
Table 1. 5 signal to noise ratio of frame image.
帧数 1 2 3 4 5 信噪比 1.73 1.96 1.85 1.82 1.60 表 2 各背景预测法MSE值比较.
Table 2. Comparison of MSE values in different background prediction methods.
表 3 各背景预测方法值SSIM比较.
Table 3. Comparison of SSIM values in different background prediction methods.
表 4 各背景预测方法GSNR值比较.
Table 4. Comparison of GSNR values in different background prediction methods.
表 5 对比分析累积前后的增强效果.
Table 5. Analysis before and after the cumulative effect.
表 6 对比分析时域处理前后的增强效果.
Table 6. Analysis before and after the time domain processing enhancement effect.
算法 时域处理前(原图) 时域处理后 平均灰度 平均信噪比 平均灰度 平均信噪比 小波变换 134 1.23 154 2.47 -
[1] Bai Xiangzhi, Zhou Fugen. Infrared small target enhancement and detection based on modified top-hat transformations[J]. Computers and Electrical Engineering, 2010, 36(10): 1193‒1201. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/222383883_Infrared_small_target_enhancement_and_detection_based_on_modified_top-hat_transformations
[2] 张耀, 雍杨, 张启衡, 等.低对比度小目标检测[J].强激光与粒子束, 2010, 22(11): 2566‒2570. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/ac465d197cd184254b35356d.html
Zhang Yao, Yong Yang, Zhang Qiheng, et al. Detection of dim point target with low contrast[J]. Laser and Particle Beams, 2010, 22(11): 2566‒2570. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/ac465d197cd184254b35356d.html
[3] 张路, 张志勇, 肖山竹, 等.基于多向背景预测的红外弱小目标检测[J].信号处理, 2010, 26(11): 1646‒1651. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2010.11.008
Zhang Lu, Zhang Zhiyong, Xiao Shanzhu, et al. Detection of dim infrared targets by multi-direction prediction of background[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2010, 26 (11): 1646‒1651. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2010.11.008
[4] Fan Xiangsuo, Xu Zhiyong, Zhang Jianlin, et al. Infrared dim and small targets detection method based on local energy center of sequential image[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2017, 2007: 4572147. doi: 10.1155/2017/4572147.
[5] 景亮, 彭真明, 何艳敏, 等.各向异性SUSAN滤波红外弱小目标检测[J].强激光与粒子束, 2013, 25(9): 124‒129. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/jt/Detail/Periodical?id=Periodical_qjgylzs201309008
Jiang Liang, Peng Zhenming, He Yanmin, et al. Infrared dim target detection based on anisotropic SUSAN filtering[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2013, 25(9): 124‒129. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/jt/Detail/Periodical?id=Periodical_qjgylzs201309008
[6] Fan Xiangsuo, Xu Zhiyong, Zhang Jianlin, et al. Dim small targets detection based on self-adaptive caliber temporal-spatial filtering[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2017, 85: 465‒477. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1350449517300786
[7] 荣健, 申金娥, 钟晓春.基于小波和SVR的红外弱小目标检测方法[J].西南交通大学学报, 2008, 43(5): 555‒560. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=xnjt200805002&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
Rong Jian, Shen Jine, Zhong Xiaochun. New method for infrared dim target detection based on wavelet and SVR[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2008, 43(5): 555‒560. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=xnjt200805002&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
[8] Liu Gang, Liang Xiaogeng. Detection of aerial small target in infrared image based on wavelet transform and pipe-line filter[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2011, 47(30): 198‒201.
[9] 李大伟. 复杂背景下红外弱小目标检测[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2013.
Li Dawei. Small dim targets detection in infrared video with complex background [D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2013.
[10] Bae T W, Kim Y C, Ahn S H, et al. An efficient two-dimensional least mean square (TDLMS) based on block statistics for small target detection[J]. Journal of Infrared, Millimeter, and Tera-hertz Waves, 2009, 30(10): 1092–1101. doi: 10.1007/s10762-009-9530-6
[11] 佟雨兵, 张其善, 祁云平, 等.基于PSNR与SSIM联合的图像质量评价模型[J].中国图象图形学报, 2010, 11(12): 1758–1763. http://doi.wanfangdata.com.cn/10.3969/j.issn.1006-8961.2006.12.003
Tong Yubing, Zhang Qishan, Qi Yunping, et al. Image quality assessing by combining PSNR with SSIM[J]. Chinese Journal of Image and Graphics, 2010, 11(12): 1758–1763. http://doi.wanfangdata.com.cn/10.3969/j.issn.1006-8961.2006.12.003
[12] Wang Zhou, Bovik A C, Sheikh H R, et al. Image quality as-sessment: from error visibility to structural similarity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2004, 13(4): 600–612.
[13] 曹琦, 毕笃彦.红外弱小目标检测中的特征选择性滤波方法[J].光学学报, 2011, 29(9): 2048‒2412. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_gxxb200909012.aspx
Cao Qi, Bi Duyan. Characteristic-selecting filtering in infrared small target detection[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2011, 29(9): 2048–2412. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_gxxb200909012.aspx
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS

 下载:
下载: