-
摘要:
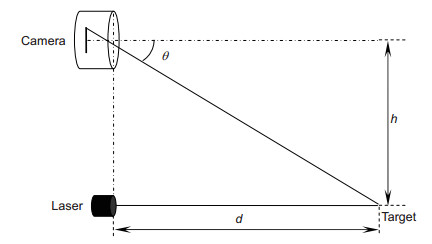
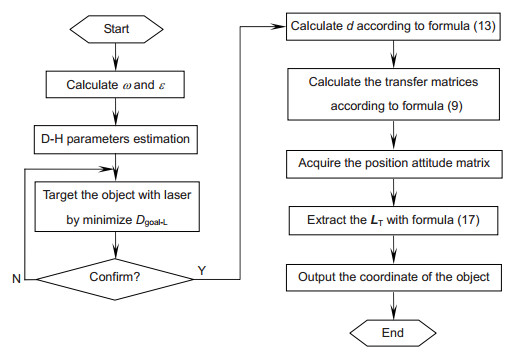
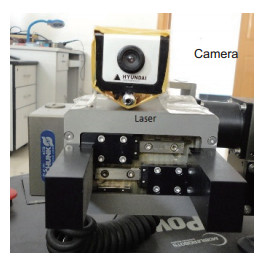
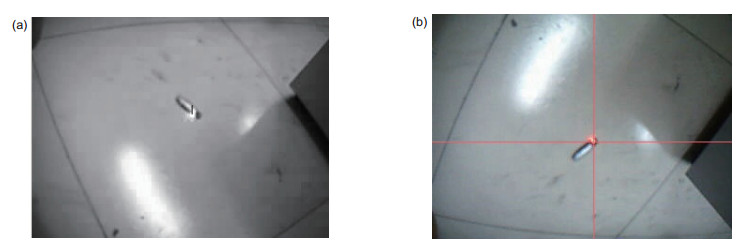
机械臂末端安装双目视觉,会降低其在障碍环境下的可通过性。针对此问题,本文构建了一种单目手眼与激光结合的位置测量方法,先通过手眼获取光斑,利用投射位置、投射点与手眼光轴的相对位置关系构建测量方法,然后采用D-H模型构建坐标转换系统,计算目标点的位置。目标测量精度与距离负相关,适用于中短距离的位置测量。与目前常用的双目测量方法相比,本方法减少了摄像机使用个数,降低了机械臂末端测量系统的宽度,更适用于狭窄空间作业,同时也提高了机械臂的有效载荷能力。
 Abstract:
Abstract:The installation of binocular vision at the end of a manipulator reduces its availability in environments with obstacles. To deal with the problem, this study puts forward a target localization method using a laser and the monocular hand-eye vision. In the proposed method, the centre of the laser spot is obtained by the hand-eye vision, and the geometric relations among the laser emission point, light-spot and the optical axis of the camera are used to calculate the distance. Then, the D-H method is employed to construct the coordinate conversion system, so that the location of the target can be calculated. The measuring precision is negatively correlated with the distance, and it is suitable for the measurement in medium or short distance. Compared with the commonly used binocular measurement methods, the proposed method uses fewer cameras, which reduces the width of the measurement system on manipulators, and makes it more applicable to narrow workspace. Moreover, it also improves the effective load capacity of manipulators.
-
Key words:
- machine vision /
- manipulator /
- 3D-localization /
- robot applications
-

Overview: Over the past decade, vision-based positioning technology has attracted more and more attentions, and has been widely used in robotics. Binocular vision is often installed at the end of a manipulator, which is used to get the position and the orientation information of targets. However, the installation of binocular vision reduces the flexibility and the load capacity of a manipulator. This problem becomes more obvious, when the load capacity of a manipulator is low or the working space is narrow. Moreover, the price of binocular vision is still relatively high. To deal with the problem above, this study puts forward a target localization method using a laser and a monocular hand-eye vision. The lower priced laser equipment used in this study can only send out a light beam, and cannot measure the distance independently. The hand-eye vision system is used to obtain the centre of the laser spot. The geometric relations among the laser emission point, light-spot and the optical axis of the camera are applied to calculate the distance from the target point to the laser emitter. The Denavit–Hartenberg convention (D–H) is often used to calculate the position and the orientation of links and joints in robotics. The distance from the target point to the laser emitter can be considered as an extended link of the manipulator. Under this assumption, the D-H method can be employed to construct the coordinate conversion system, which contains the beam of the laser and the mechanical manipulator. With this coordinate conversion system, the location of the target can be calculated. The coordinate measuring precision is negatively correlated with the distance, and it is suitable for the position measurement of medium and short distance. When a target is far away, the error is too large that it cannot work effectively. The light illuminations in the working environment have an impact on the laser spot taken by the camera. Compared with the commonly used binocular measurement methods, the proposed method uses only one camera, which reduces the width of the measurement system on manipulators, and makes it more suitable for working in narrow workspace. When searching for an object with a mobile robot, the arm is often required to enter a hole or a narrow gap. The method proposed in this paper is especially suitable for the above case. Moreover, this design also reduces the weight of the sensor on the manipulator that improves the effective load capacity of manipulators.
-

-
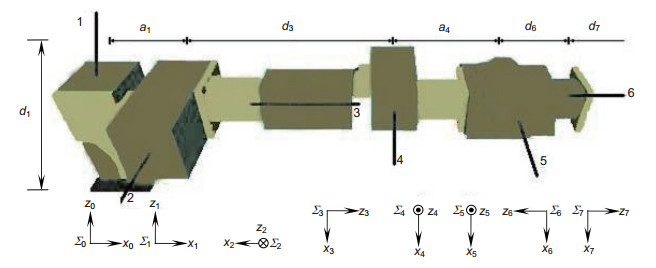
表 1 Powercube机械手的运动学参数
Table 1. Kinematic parameters of the Powercube manipulator
Frame θi/(°) ai/m di/m Ψi/(°) ∑0/∑1 θ1 a1=0.125 d1=0.135 -90 ∑1/∑2 θ2+90 0 0 -90 ∑2/∑3 θ3+180 0 d3=0.339 -90 ∑3/∑4 θ4-90 a4=0.175 0 0 ∑4/∑5 θ5+90 0 0 -90 ∑5/∑6 θ6 0 d6=0.195 180 ∑6/∑7 θ7 0 d7=0.05 0 表 2 测量系统的误差
Table 2. Errors in this measurement system
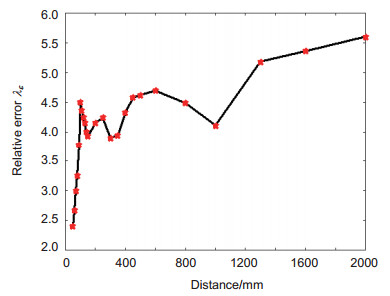
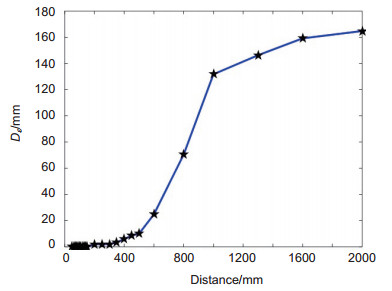
Distance/mm εmargin/mm λε/% Dε/mm 50 1.2 2.40 0.08 60 1.6 2.67 0.11 70 2.1 3.00 0.15 80 2.6 3.25 0.19 90 3.4 3.78 0.28 100 4.5 4.50 0.52 110 4.8 4.36 0.37 120 5.1 4.25 0.38 130 5.4 4.15 0.47 140 5.6 4.00 0.51 150 5.9 3.93 0.33 200 8.3 4.15 1.85 250 10.6 4.24 1.94 300 11.7 3.90 2.04 350 13.8 3.94 3.47 400 17.3 4.33 5.89 450 20.6 4.58 8.56 500 23.1 4.62 10.08 600 28.2 4.70 24.81 800 35.9 4.49 70.46 1000 41.1 4.11 131.73 1300 67. 4 5.18 146.28 1600 85.7 5.36 159.16 2000 112 5.60 164.75 10000 \ \ \ 表 3 本文所提方法与双目定位的对比
Table 3. Comparison between the method and binocular location
Binocular method This method Device width/mm > 150 70 Price/RMB 3000 200 Weight/g > 400 160 Applicability Broad space Narrow space Error for 300 mm 0.49 11.7 Error for 500 mm 0.80 23.1 Error for 700 mm 0.98 28.6 Error for 1000 mm 1.20 41.1 -
[1] Siegwart R, Nourbakhsh I R. Introduction to autonomous mobile robots[M]. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 2004: 3-45.
[2] Chaudhury A, Ward C, Talasaz A, et al. Computer vision based autonomous robotic system for 3D plant growth measurement[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE 12th Conference on Computer and Robot Vision (CRV), Halifax, Canada, 2015: 290-296.
[3] Iguchi Y, Yamaguchi J. Omni-directional 3D measurement using double fish-eye stereo vision[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE 21st Korea-Japan Joint Workshop on Frontiers of Computer Vision (FCV), Mokpo, Korea, 2015: 1-6.
[4] 黄文有, 徐向民, 吴凤岐, 等.核环境水下双目视觉立体定位技术研究[J].光电工程, 2016, 43(12): 28-33. http://www.oee.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract1840.shtml
Huang W Y, Xu X M, Wu F Q, et al. Research of underwater binocular vision stereo positioning technology in nuclear condition[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2016, 43(12): 28-33. http://www.oee.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract1840.shtml
[5] He T, Chen J Y, Hu X, et al. A study of 3D coordinate measuring based on binocular stereo vision[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2015, 740: 531-534. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.740
[6] 魏少鹏, 严惠民, 张秀达.一种深度相机与双目视觉结合的视差估计技术[J].光电工程, 2015, 42(7): 72-77. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=gdgc201507014&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
Wei S P, Yan H M, Zhang X D. Disparity estimation based on the combination of depth camera and stereo vision[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2015, 42(7): 72-77. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=gdgc201507014&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
[7] An X C, Hong W, Xia H. Research on binocular vision absolute localization method for indoor robots based on natural landmarks[C]//Proceedings of 2015 IEEE Chinese Automation Congress (CAC), Wuhan, 2015: 604-609.
[8] Nefti-Meziani S, Manzoor U, Davis S, et al. 3D Perception from binocular vision for a low cost humanoid robot NAO[J]. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2015, 68: 129-139. doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2014.12.016
[9] Li H, Li B, Xu W F. Development of a remote-controlled mobile robot with binocular vision for environment monitoring[C]//Proceedings of 2015 IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation, Lijiang, 2015: 737-742.
[10] Urmson C, Anhalt J, Bagnell D, et al. Autonomous driving in urban environments: boss and the urban challenge[J]. Journal of Field Robotics, 2008, 25(8): 425-466. doi: 10.1002/rob.v25:8
[11] Fanello S R, Pattacini U, Gori I, et al. 3D stereo estimation and fully automated learning of eye-hand coordination in humanoid robots[C]//Proceedings of the 14th IEEE-RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots (Humanoids), Madrid, Spain, 2014: 1028-1035.
[12] Chao F, Lee M H, Jiang M, et al. An infant development-inspired approach to robot hand-eye coordination[J]. International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems, 2014, 11(2): 15. doi: 10.5772/57555
[13] Henry P, Krainin M, Herbst E, et al. RGB-D mapping: using Kinect-style depth cameras for dense 3D modeling of indoor environments[J]. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2012, 31(5): 647-663. doi: 10.1177/0278364911434148
[14] 黄风山. 光笔式单摄像机三维坐标视觉测量系统关键技术的研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2005.
Huang F S. Study on the key technique of single camera 3D coordinate vision measurement system using a light pen[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2005.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10056-2007078600.htm [15] Aroca R V, Burlamaqui A F, Gon alves L M G. Method for reading sensors and controlling actuators using audio interfaces of mobile devices[J]. Sensors, 2012, 12(2): 1572-1593. doi: 10.3390/s120201572
[16] Xu D, Calderon C A A, Gan J Q, et al. An analysis of the Inverse Kinematics for a 5-DOF manipulator[J]. International Journal of Automation and Computing, 2005, 2(2): 114-124. doi: 10.1007/s11633-005-0114-1
[17] Craig J J. Introduction to robotics: mechanics and control[M]. 3rd ed. London: Pearson Education, 2005: 62-120.
[18] da Graça Marcos M, Machado J A T, Azevedo-Perdicoulis T P. An evolutionary approach for the motion planning of redundant and hyper-redundant manipulators[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2010, 60(1-2): 115-129. doi: 10.1007/s11071-009-9584-y
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: