-
摘要:
针对水下环境中传统算法对双目图像匹配时存在速度慢、误匹配较多等问题,提出一种基于ORB(的特征检测和曲线极线约束相结合的水下立体匹配方法。先检测图像的特征点,生成描述子,并进行特征匹配;然后根据折射定律,结合双目相机的内外参数,推导出水下曲线极线;最后结合水下曲线极线约束,剔除误匹配点。实验结果表明,相比传统的SIFT算法与曲线约束,论文提出的立体匹配方法在有效控制误匹配的情况下,显著提高了运算速度,对提升水下双目视觉系统的快速处理能力具有实践意义。
 Abstract:
Abstract:Since the traditional algorithm may cause problems such as slow running speed and more mismatching points when perform stereo matching on underwater environment, the ORB characteristics detection and curve restriction has been applied in this paper. Firstly the image should be detected so as to find out the characteristics, generate the descriptor, and match the feature points. Then the underwater curve restriction can be deduced according to the law of refraction combining internal and external parameters of camera. Finally the mismatching points can be decreased by means of underwater curve restriction. The experimental results have shown that in the case of effectively controlling mismatches, the speed of this algorithm are faster than traditional SIFT algorithm combined with curve restriction. As a result, it is of practical significance to improve the speed of underwater binocular vision system.
-

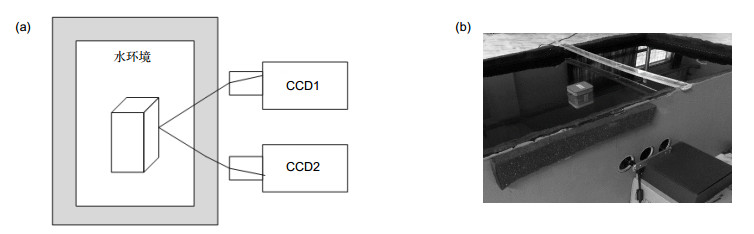
Overview: With the exploration of Marine resources, the underwater vision technology has a very broad application prospect. As a main branch of computer vision, binocular stereo vision has become a common realization form of underwater vision technology due to its relatively simple structure and high efficiency. Among the realization steps of image acquisition, camera calibration, image preprocessing, stereo matching and 3D reconstruction, stereo matching is a key technology and a hot spot in binocular vision field. How to get a matching algorithm with high precision and high speed is more difficult to study. At present, the underwater stereo matching method adopts adaptive search, determines the optimal search domain, and is based on color segmentation, but only takes into account the calculation accuracy. For example, in previous literature, SIFT feature matching and curve constraint were adopted to further improve accuracy, but the calculation speed was not discussed. In this paper, a matching method is proposed to improve the operation speed under the premise of ensuring accuracy.
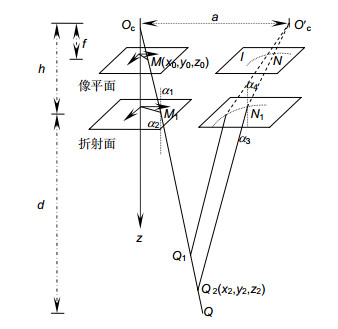
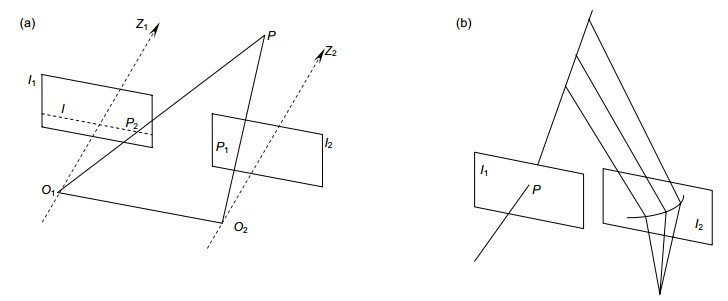
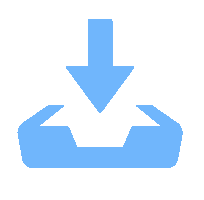
According to different matching primitives, stereo matching is mainly divided into regional matching and feature matching. The region-based matching algorithm takes parallax for each pixel, and finally gets the dense parallax map. While the feature-based matching algorithm extracts feature points for matching, and finally gets the sparse parallax map. Due to problems such as low illumination and high noise in underwater images, which will cause large errors in solving dense parallax plan. Thus, feature matching algorithm that is insensitive to noise and environment is selected in this paper. Commonly used feature matching algorithms include SURF, KAZA, SIFT, ORB, etc., among which SIFT algorithm is the most classic one. This algorithm has many advantages, such as good stability, high precision and strong robustness, which are widely used in many scenes. But at the same time, there are problems such as large calculation and long time. After SIFT, an ORB algorithm is also proposed. ORB is an algorithm for rapid feature extraction and matching. Although there are some problems such as low accuracy and many mismatches in complex scenes with large changes such as scale and illumination, the computing speed is greatly improved compared with the previous algorithm, and some scenes can be two orders of magnitude higher than the SIFT algorithm. Although the velocity of ORB algorithm is improved, there are a series of factors affecting the image quality, such as refraction, lens distortion, etc., in the underwater environment. If it is used directly, there will be many mismatches. For the accuracy problem, the curvilinear polar constraint commonly used in underwater stereo matching is derived under the circumstance that underwater environment does not meet the polar constraint in air, which is applicable to underwater curve polar constraint, so as to eliminate the mismatched points and ensure the matching accuracy.
This paper adopts underwater stereo matching method combining ORB feature detection and curve polar line constraint. Firstly, it used ORB feature detection algorithm to match feature points of underwater image, and then reduced mismatched points according to curve polar line constraint, so as to achieve the goal of improving speed under the premise of ensuring accuracy.
-

-
表 1 相机参数
Table 1. Camera parameters
左相机 右相机 (fx, fy) (352.5668,354.5694) (352.5668,354.5694) (cx, cy) (334.734,191.319) (345.472, 190.423) k (-0.15670,-0.03325,-0.07572) (-0.17060,0.02663,0.00513) R (1,-0.000188,0.013209,0.000177,1,0.000857,-0.013209,-0.000855) T (-119.7177,-0.16548,0.79235) 表 2 匹配对数与时间比较
Table 2. Comparison of time and matching pairs
表 3 三种算法匹配对数
Table 3. The number of matched pairs of the three algorithms
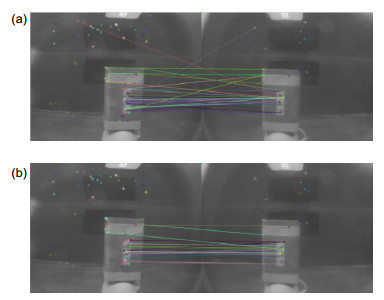
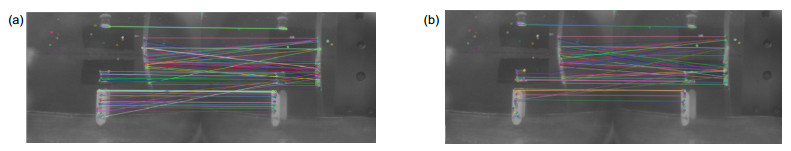
图像编号 11 45 93 97 99 106 SIFT加曲线约束 317 450 340 372 364 413 ORB算法 132 162 206 158 145 173 本文算法 105 114 117 123 106 124 -
[1] 曹之乐, 严中红, 王洪.双目立体视觉匹配技术综述[J].重庆理工大学学报(自然科学), 2015, 29(2):70-75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8425(z).2015.02.014
Cao Z L, Yan Z H, Wang H. Summary of binocular stereo vision matching technology[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Technology (Natural Science), 2015, 29(2):70-75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8425(z).2015.02.014
[2] 张强, 郝凯, 李海滨.水下环境中基于曲线约束的SIFT特征匹配算法研究[J].光学学报, 2014, 34(2):0215003. doi: 10.3788/aos201434.0215003
Zhang Q, Hao K, Li H B. Research on scale invariant feature transform feature matching based on underwater curve constraint[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2014, 34(2):0215003. doi: 10.3788/aos201434.0215003
[3] 张强, 卢士强, 李海滨, 等.基于色彩分割的水下立体匹配算法的研究[J].光学学报, 2016, 36(8):0815001. doi: 10.3788/aos201636.0815001
Zhang Q, Lu S Q, Li H B, et al. Research on underwater stereo matching method based on color segmentation[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2016, 36(8):0815001. doi: 10.3788/aos201636.0815001
[4] 赵鹏.机器视觉研究与发展[M].北京:科学出版社, 2012.
[5] Sanchez-Ferreira C, Mori J Y, Llanos C H, et al.Development of a stereo vision measurement architecture for an underwater robot[C]//2013 IEEE 4th Latin American Symposium on Circuits and Systems, 2013: 1-4.
[6] Lowe D G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2004, 60(2):91-110. doi: 10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94
[7] Lowe D G. Object recognition from local scale-invariant features[C]//Proceedings of the Seventh IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 1999, 2: 1150-1157.
[8] Rublee E, Rabaud V, Konolige K, et al. ORB: An efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF[C]//2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2011: 2564-2571.
[9] 彭辉, 文友先, 翟瑞芳, 等.结合SURF算子和极线约束的柑橘立体图像对匹配[J].计算机工程与应用, 2011, 47(8):157-160. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2011.08.046
Peng H, Wen Y X, Zhai R F, et al. Stereo matching for binocular citrus images using SURF operator and epipolar constraint[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2011, 47(8):157-160. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2011.08.046
[10] Gedge J, Gong M L, Yang Y H. Refractive epipolar geometry for underwater stereo matching[C]//2011 Canadian Conference on Computer and Robot Vision, 2011: 146-152.
[11] Li J, Pan T S, Tseng K K, et al. Design of a monocular simultaneous localisation and mapping system with ORB feature[C]//2013 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, 2013: 1-4.
[12] 张文明, 邓茜雪, 张强, 等.基于非平行系统的水下图像转化模型[J].光子学报, 2015, 44(2):211002. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20154402.0211002
Zhang W M, Deng X X, Zhang Q, et al. Non-parallel system underwater image transformation model[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2015, 44(2):211002. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20154402.0211002
[13] Wang H B, Sun H Y, Shen J, et al. A research on stereo matching algorithm for underwater image[C]//2014 4th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, 2011: 850-854.
[14] 李雅倩, 张岩松, 李海滨, 等.基于深度约束的水下稠密立体匹配[J].光子学报, 2017, 46(7):0715001. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20174607.0715001
Li Y Q, Zhang Y S, Li H B, et al. Underwater dense stereo matching based on depth constraint[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2017, 46(7):0715001. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20174607.0715001
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: