Modeling and inverse compensation control of hysteresis nonlinear characteristics of piezoelectric steering mirror
-
摘要:
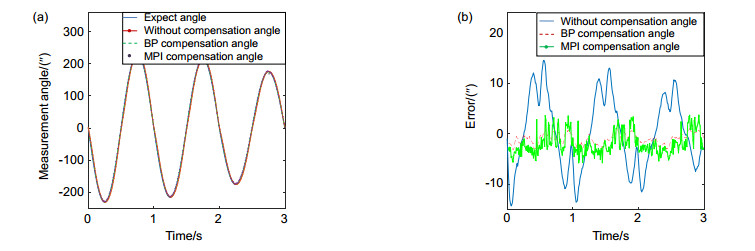
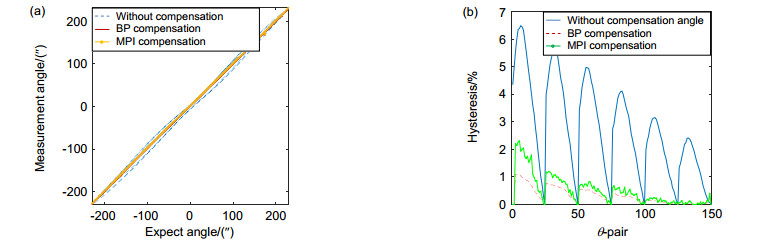
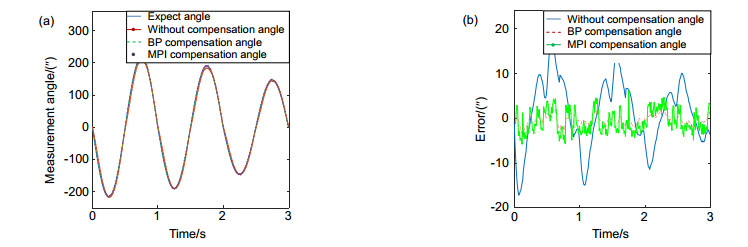
自适应光学系统中的压电倾斜镜通常是用来实时校正大气湍流引起的波前畸变,但压电倾斜镜的响应都有较大的非线性迟滞效应,大大降低了倾斜镜的到位精度,并且影响系统稳定性,制约了倾斜校正系统的带宽,因此需要对迟滞现象进行建模,通过建立的模型进行补偿。本文通过引入迟滞算子,使用贝叶斯正则化训练算法训练BP神经网络来构建压电倾斜镜迟滞模型,以中国科学院光电技术研究所自主研制的压电倾斜镜为对象开展了实验研究。最后的实验结果表明,通过BP神经网络构建的压电倾斜镜迟滞模型具有较准确的辨识能力,其中,X方向的迟滞大小由6.5%降低到了1.3%,Y方向的迟滞大小由7.1%降低到了1.6%。
 Abstract:
Abstract:In the adaptive optics system, the piezoelectric steering mirror(tip/tilt mirror, TTM) is usually used to correct the wavefront aberration caused by atmospheric turbulence in real time. However, the response of the piezoelectric tilting mirror has large nonlinear hysteresis effect, which greatly reduces the precision of the tilting mirror in place, affects the stability of the system, and restricts the bandwidth of the skew correction system. Therefore, the hysteresis phenomenon needs to be modeled and compensated by the established model. In this paper, hysteresis operator is introduced and using Bayesian regularization training algorithm to train BP (back propagation) neural network to construct hysteresis model of piezoelectric steering mirror. Then experimental study was conducted on a piezoelectric steering mirror developed by Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences. The final experimental results show that the hysteresis model of piezoelectric steering mirror constructed by BP neural network has more accurate identification capability, the hysteresis size in the X direction decreased from 6.5% to 1.3% and that in the Y direction decreased from 7.1% to 1.6%.
-
Key words:
- adaptive optics /
- piezoelectric steering mirror /
- hysteresis /
- neural network /
- hysteresis operator
-

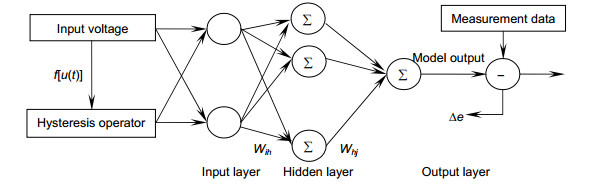
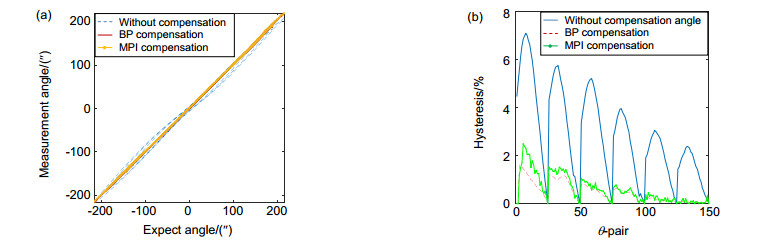
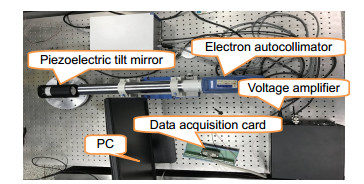
Overview: Piezoelectric tilt mirror in adaptive optics system is usually used to correct the wavefront distortion caused by atmospheric turbulence in real time. However, piezoelectric ceramic materials often have inherent hysteretic characteristics. In practical application, such hysteresis makes the control of piezoelectric tilt mirror difficult. The hysteretic characteristic of piezoelectric ceramics is that two displacement curves of piezoelectric ceramics do not coincide with each other in the process of pressure rise and pressure fall. The main characteristic is that the output displacement of the piezoelectric actuator at the next moment depends not only on the input voltage and output displacement at the current moment, but also on the input voltage at the previous moment. The results show that the nonlinear tracking error caused by the asymmetry of hysteresis curve is more than 15% in the case of uncontrolled open loop. Therefore, non-linear hysteresis compensation is essential to achieve high accuracy control of tip/tilt mirror (TTM), so the hysteresis phenomenon needs to be modeled and compensated by the established model. Many scholars have studied the hysteresis and non-linearity of piezoelectric tilt mirror. The traditional hysteresis and non-linearity models include Preisach model, KP model, PI model, etc. However, the parameters of these models are difficult to solve and the calculation is complex, which is not conducive to the application in engineering practice. In this paper, the hysteresis model of piezoelectric tilt mirror is constructed by introducing the hysteresis operator and using the Bayesian regularization training algorithm to train BP neural network. The final experimental results show that the hysteresis model of piezoelectric tilt mirror constructed by BP neural network has a relatively accurate identification capability, where the hysteresis size in the X direction is reduced from 6.5% to 1.3%, the identification error range of positive model is between -0.048 arcmin to +0.048 arcmin, the minimum root-mean-square error (RMSE) is 0.0106 arcmin, and the relative error is 0.0119. The model identification error range of the inverse hysteresis operator used in the experiment is -0.035 V to +0.03 V, the minimum RMSE is 0.0132 V, and the relative error is 0.0124. The hysteresis in the Y direction was reduced from 7.1% to 1.6%. The positive model identification error range of BP hysteresis operator adopted in the experiment was -0.048 arcmin to +0.05 arcmin, the minimum RMSE was 0.0112 arcmin, and the relative error was 0.0134. The model identification error range of the adopted inverse hysteresis operator is -0.04 V to +0.04 V, the minimum RMSE is 0.0148 V, and the relative error is 0.0142. For the piezoelectric tilt mirror developed by Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, the model established has relatively accurate identification ability.
-

-
表 1 迟滞补偿结果
Table 1. The results of hysteresis compensation
Hysteresis model Hysteresis size in X direction/% Hysteresis size in Y direction/% Without compensation 6.5 7.1 BP compensation 1.3 1.6 MPI compensation 2.21 2.89 -
[1] Tyson R K. Introduction to Adaptive Optics[M]. Bellingham, Washington: SPIE Press, 2000.
[2] 王玉坤, 胡立发, 王冲冲, 等.液晶自适应光学系统中倾斜镜的建模与控制[J].光学精密工程, 2016, 24(4): 771-779. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201604012
Wang Y K, Hu L F, Wang C C, et al. Modeling and control of Tip/Tilt Mirror in liquid crystal adaptive optical system[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2016, 24(4): 771-779. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201604012
[3] 王冲冲, 胡立发, 何斌, 等.基于神经网络的压电倾斜镜磁滞补偿方法研究[J].中国激光, 2013, 40(11): 1113001. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgjg201311042
Wang C C, Hu L F, He B, et al. Hysteresis compensation method of piezoelectric steering mirror based on neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2013, 40(11): 1113001. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgjg201311042
[4] Perez Arancibia N O, Chen N, Gibson J S, et al. Variable-order adaptive control of a microelectromechanical steering mirror for suppression of laser beam jitter[J]. Optical Engineering, 2006, 45(10): 104206. doi: 10.1117/1.2363189
[5] 谭逢富, 陈修涛, 姚佰栋, 等.激光大气传输倾斜校正系统[J].红外与激光工程, 2011, 40(3): 429-432. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2011.03.010
Tan F F, Chen X T, Yao B D, et al. Tilt correction system for laser atmospheric propagation[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2011, 40(3): 429-432. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2011.03.010
[6] 王红红, 陈方斌, 寿少峻, 等.基于FSM的高精度光电复合轴跟踪系统研究[J].应用光学, 2010, 31(6): 909-913. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2082.2010.06.008
Wang H H, Chen F B, Shou S J, et al. High precision electro-optical tracking system based on fast steering mirror[J]. Journal of Applied Optics, 2010, 31(6): 909-913. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2082.2010.06.008
[7] Kluk D J, Boulet M T, Trumper D L. A high-bandwidth, high-precision, two-axis steering mirror with moving iron actuator[J]. Mechatronics, 2012, 22(3): 257-270. doi: 10.1016/j.mechatronics.2012.01.008
[8] 徐飞飞, 纪明, 赵创社.快速偏转反射镜研究现状及关键技术[J].应用光学, 2010, 31(5): 847-850. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2082.2010.05.036
Xu F F, Ji M, Zhao C S. Status of fast steering mirror[J]. Journal of Applied Optics, 2010, 31(5): 847-850. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2082.2010.05.036
[9] Mayergoyz I D. Mathematical Models of Hysteresis[M]. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1991.
[10] Hu H, Mrad R B. On the classical Preisach model for hysteresis in piezoceramic actuators[J]. Mechatronics, 2003, 13(2): 85-94. doi: 10.1016/S0957-4158(01)00043-5
[11] Banks H T, Kurdila A J. Hysteretic control influence operators representing smart material actuators: identification and approximation[C]//Proceedings of the 35th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Kobe, Japan, 1996: 3711-3716.
[12] Su C Y, Wang Q Q, Chen X K, et al. Adaptive variable structure control of a class of nonlinear systems with unknown Prandtl-Ishlinskii hysteresis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2005, 50(12): 2069-2074. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2005.860260
[13] 赵新龙.基于迟滞算子的迟滞非线性系统建模与控制研究[D].上海: 上海交通大学, 2006.
Zhao X L. Modeling and control for hysteresis systems based on hysteretic operator[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2006.
http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y1812272 [14] 马连伟.三明治迟滞非线性系统的建模与控制研究[D].上海: 上海交通大学, 2007.
Ma L W. Modeling and control for sandwich hysteresis systems[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2007.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10248-2008052008.htm [15] Kuhnen K. Modeling, identification and compensation of complex hysteretic nonlinearities: a modified Prandtl-Ishlinskii approach[J]. European Journal of Control, 2003, 9(4): 407-418. doi: 10.3166/ejc.9.407-418
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: