| Citation: | Ren D Q, Zhang T Y, Wang G. An optimized high-performance technique for adaptive optics static aberration correction[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2022, 49(3): 210319. doi: 10.12086/oee.2022.210319 |
An optimized high-performance technique for adaptive optics static aberration correction
-
Abstract
For adaptive optics (AO) systems, Non-Common Path Aberration (NCPA) is considered as a critical issue to limit its diffraction-limited imaging performance and the static aberration will inevitably be introduced in the common path of the AO system inevitably at the same time, especially when it is coupled to telescopes intended for scientific observation. This paper presents an optimized focal-plane-based static aberration correction technique, which can copy a perfect point-spread function (PSF) generated by a single-mode fiber to the AO system via iteration optimization algorithm and static aberration in the AO system can be rapidly corrected. Compared with the focal-plane approach we proposed before, this optimized approach can achieve a global optimization result rapidly and deliver better performance when the AO system has a large initial static wavefront error. This technique can be implemented more conveniently in the AO system than other traditional correction methods for achieving an extremely high imaging performance in astronomy or other fields.-
Keywords:
- adaptive optics /
- aberration correction /
- high angular resolution
-

-
References
[1] Baudoz P, Mas M, Galicher R, et al. Focal plane wavefront sensor sensitivity for ELT planet finder[J]. Proc SPIE, 2010, 7736: 77365S. doi: 10.1117/12.858272 [2] Wallace J K, Rao S, Jensen-Clem R M, et al. Phase-shifting Zernike interferometer wavefront sensor[J]. Proc SPIE, 2011, 8126: 81260F. doi: 10.1117/12.892843 [3] Campbell E W, Bauman B J, Sweider D R, et al. High-accuracy calibration of an adaptive optics system using a phase-shifting diffraction interferometer[J]. Proc SPIE, 1999, 3762: 237−244. doi: 10.1117/12.363579 [4] Gonsalves R A. Phase retrieval and diversity in adaptive optics[J]. Opt Eng, 1982, 21(5): 215829. [5] Lamb M, Correia C, Sauvage J F, et al. Exploring the operational effects of phase diversity for the calibration of non-common path errors on NFIRAOS[J]. Proc SPIE, 2016, 9909: 99096E. [6] Wallace J K, Burruss R S, Bartos R D, et al. The Gemini Planet Imager calibration wavefront sensor instrument[J]. Proc SPIE, 2010, 7736: 77365D. [7] Hinkley S, Oppenheimer B R, Zimmerman N, et al. A new high contrast imaging program at Palomar observatory[J]. Publ Astron Soc Pac, 2011, 123(899): 74−86. doi: 10.1086/658163 [8] Ren D Q, Penn M, Wang H M, et al. A portable solar adaptive optics system[J]. Proc SPIE, 2009, 7438: 74380P. doi: 10.1117/12.824457 [9] Ren D Q, Dong B. Demonstration of portable solar adaptive optics system[J]. Opt Eng, 2012, 51(10): 101705. doi: OptEng [10] Yamamoto S. Development of inspection robot for nuclear power plant[C]//Proceedings 1992 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Nice, 1992, 2: 1559‒1566. [11] Ren D Q, Dong B, Zhu Y T, et al. Correction of non–common-path error for extreme adaptive optics[J]. Publ Astron Soc Pac, 2012, 124(913): 247−253. doi: 10.1086/664947 [12] Vorontsov M A, Carhart G W, Ricklin J C. Adaptive phase-distortion correction based on parallel gradient-descent optimization[J]. Opt Lett, 1997, 22(12): 907−909. doi: 10.1364/OL.22.000907 [13] Vorontsov M A, Sivokon V P. Stochastic parallel-gradient-descent technique for high-resolution wave-front phase-distortion correction[J]. J Opt Soc Am A, 1998, 15(10): 2745−2758. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.15.002745 [14] Vorontsov M A, Yu M. Compensation of distant phase-distorting layers. II. Extended-field-of-view adaptive receiver system[J]. J Opt Soc Am A, 2004, 21(9): 1659−1668. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.21.001659 [15] Petit C, Sauvage J F, Costille A, et al. SAXO: the extreme adaptive optics system of SPHERE (I) system overview and global laboratory performance[J]. J Astron Telesc Instrum Syst, 2016, 2(2): 025003. doi: 10.1117/1.JATIS.2.2.025003 [16] Fusco T, Sauvage J F, Petit C, et al. Final performance and lesson-learned of SAXO, the VLT-SPHERE extreme AO: from early design to on-sky results[J]. Proc SPIE, 2014, 9148: 91481U. [17] Liu Y, Ma J Q, He T, et al. Hybrid simulated annealing-hill climbing algorithm for fast aberration correction without wavefront sensor[J]. Opt Precis Eng, 2012, 20(2): 213−219. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20122002.0213 [18] Burke D, Patton B, Huang F, et al. Adaptive optics correction of specimen-induced aberrations in single-molecule switching microscopy[J]. Optica, 2015, 2(2): 177−185. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.2.000177 [19] Sauvage J F, Fusco T, Rousset G, et al. Fine calibration and pre-compensation of non-common path aberrations for high performance AO system[J]. Proc SPIE, 2005, 5903: 59030B. -
Access History

-
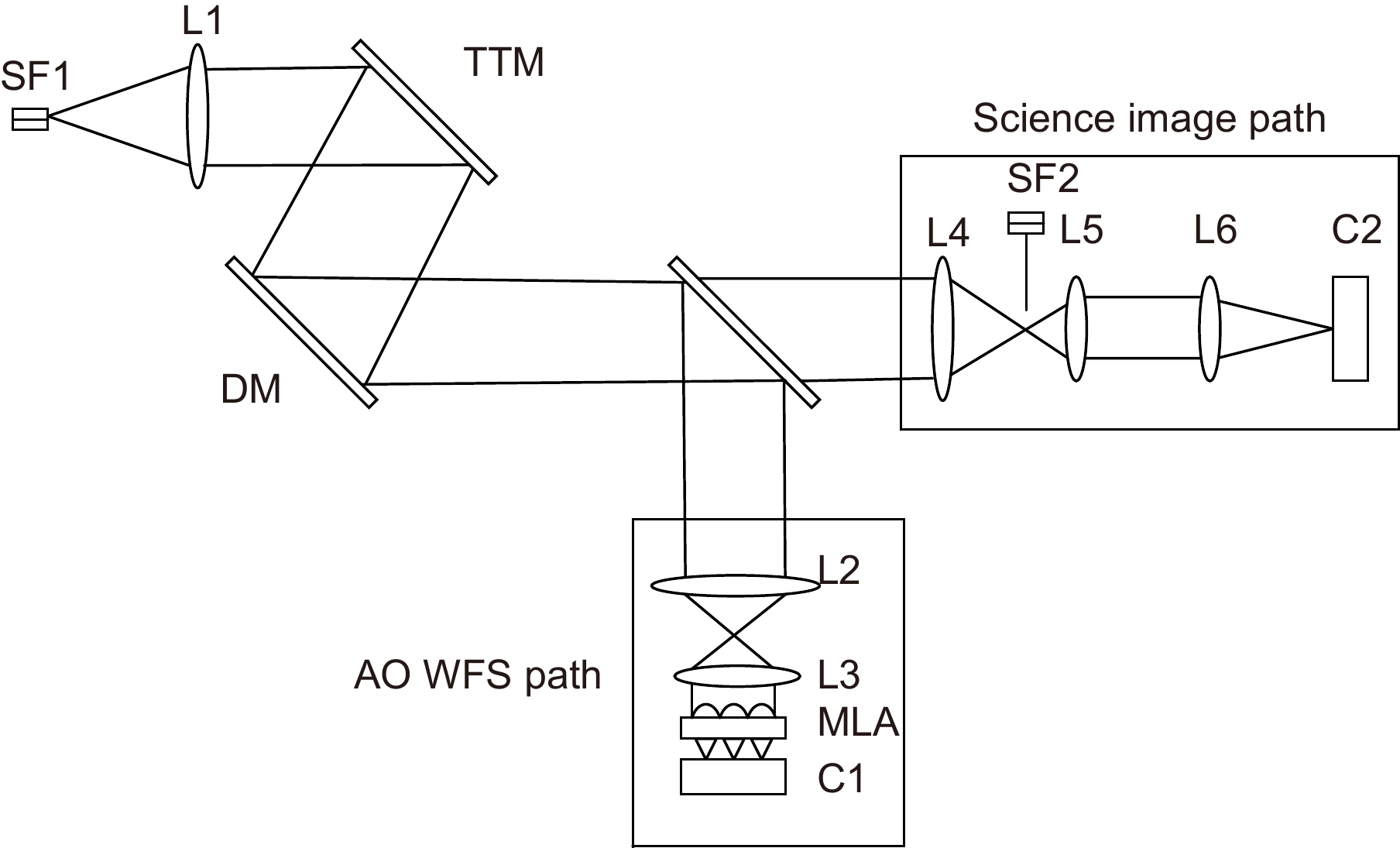
Figure 1.
The schematic diagram of AO system for correction
-
Figure 2.
The real experimental optical path of AO system for the NCPA measurement and correction
-
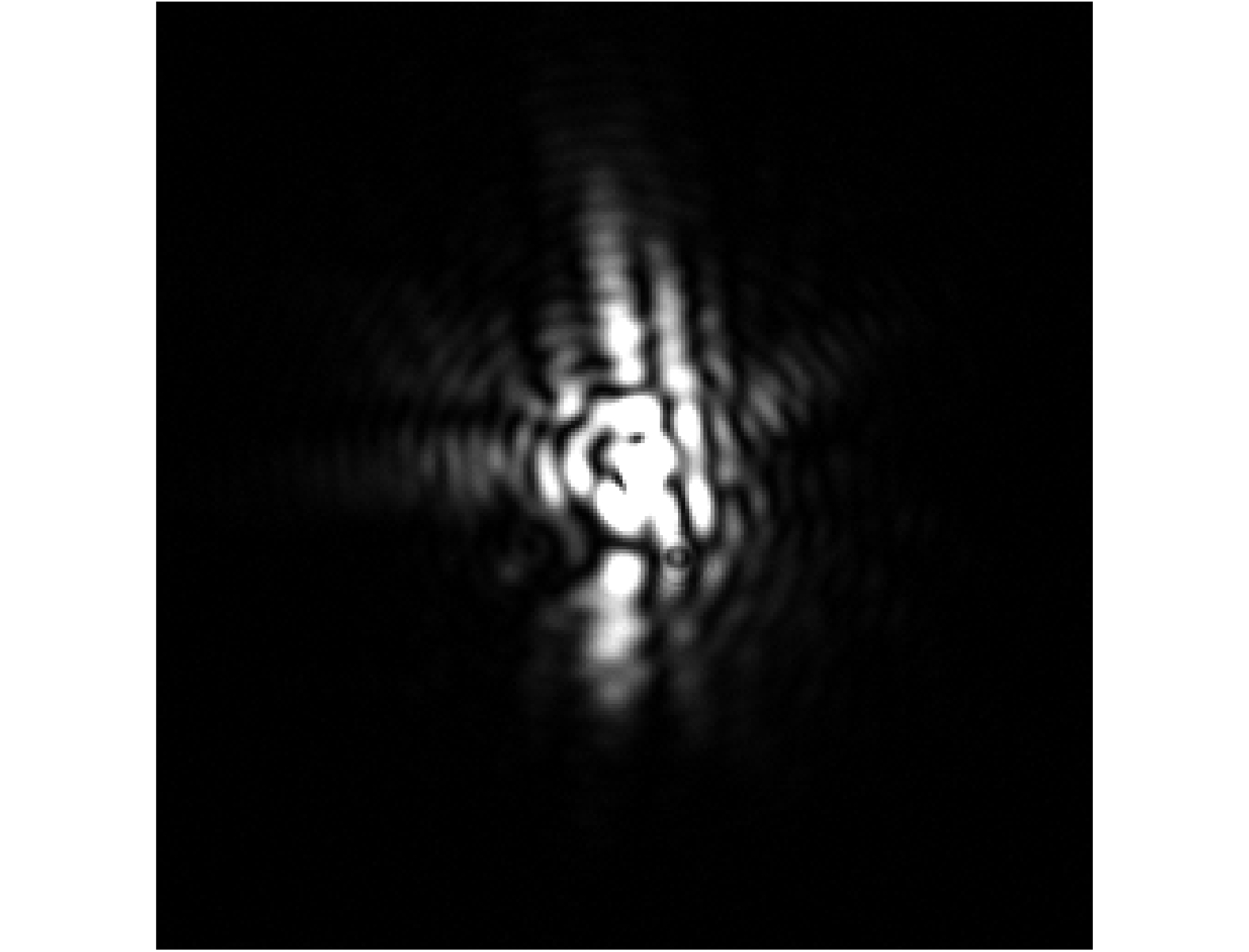
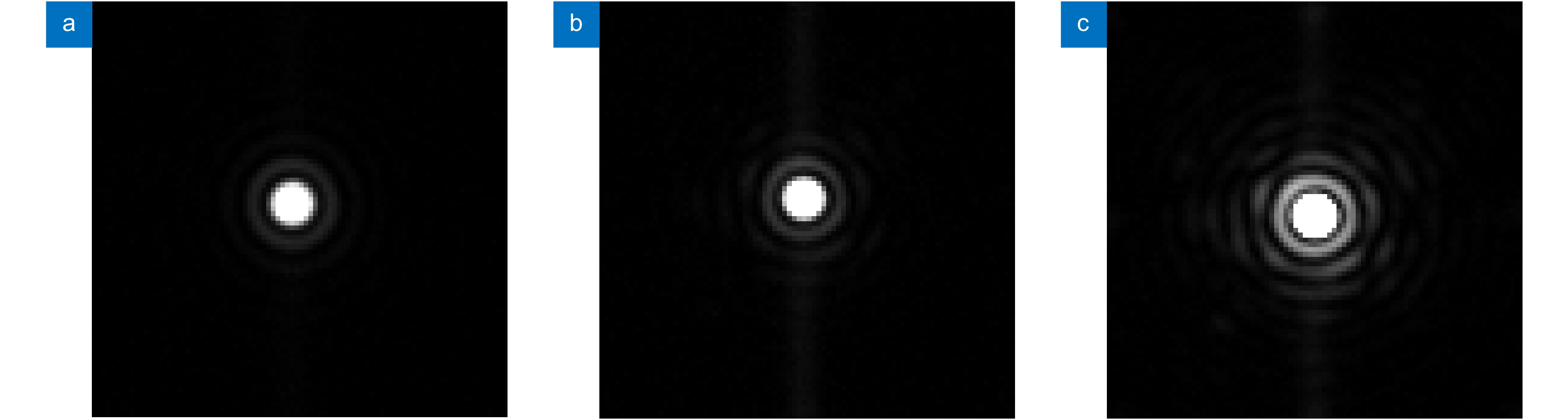
Figure 3.
Initial focal plane PSF
-
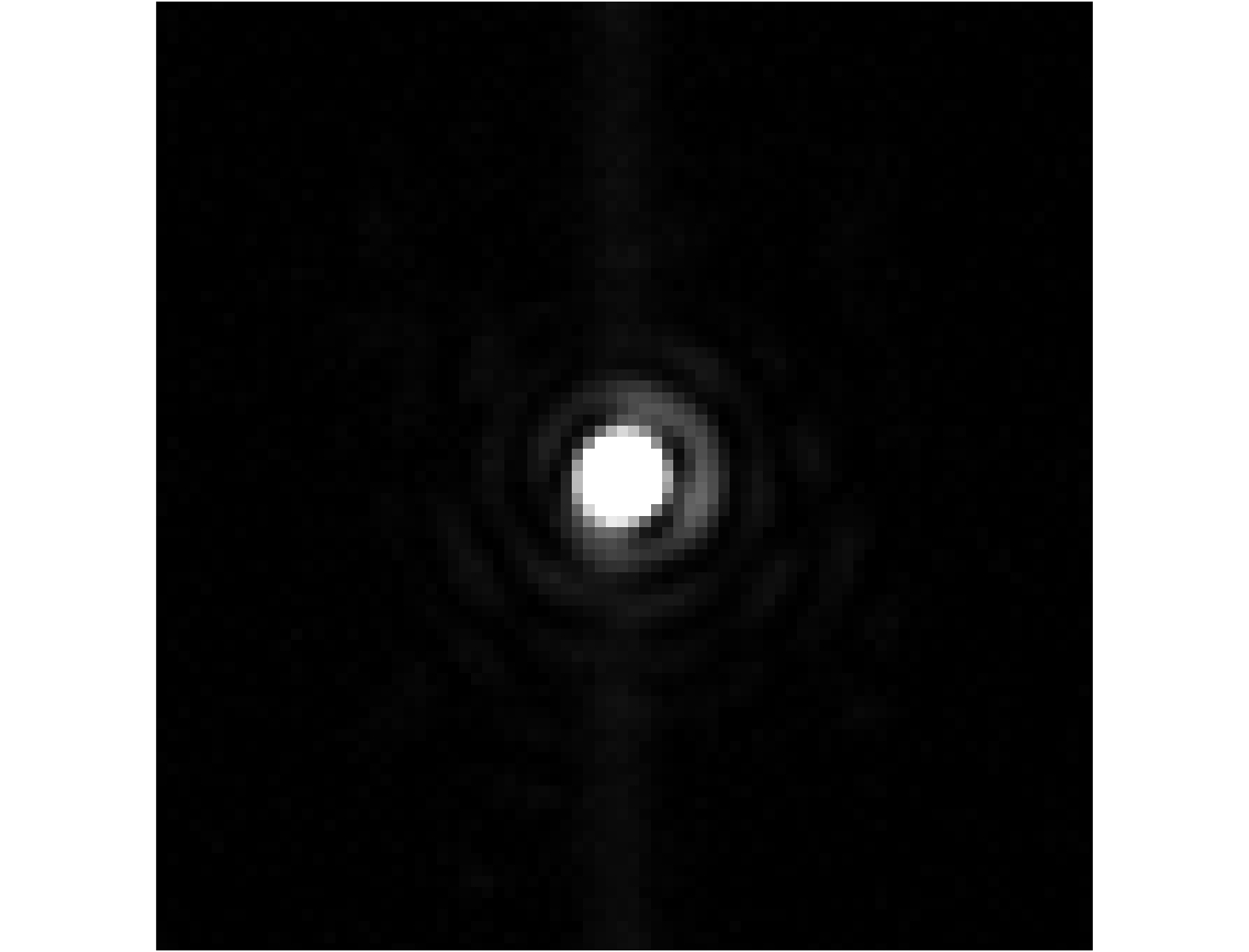
Figure 4.
Reference PSF and PSFs after correction.
-
Figure 5.
Metric function evolution as a function of iteration steps
-
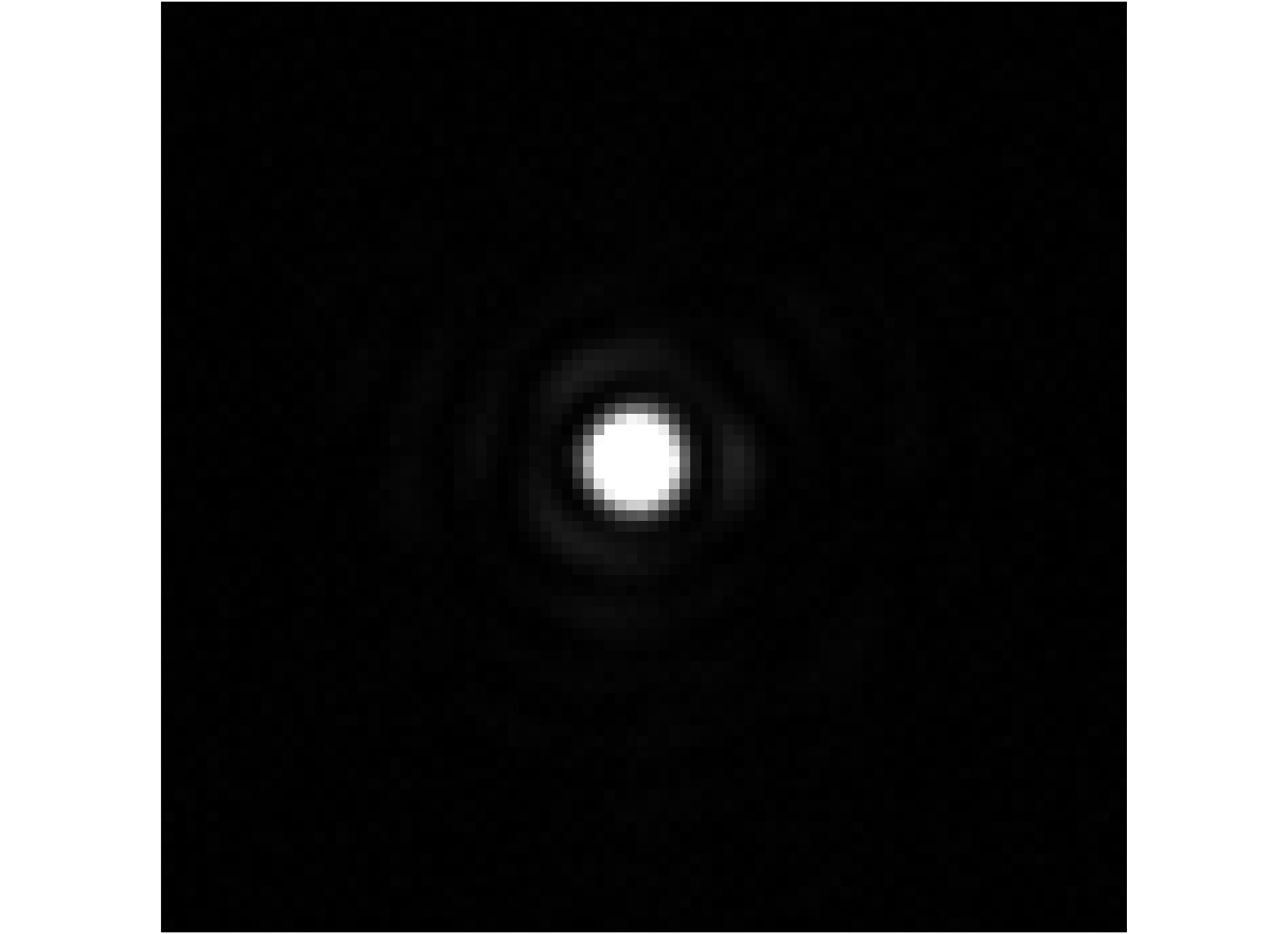
Figure 6.
PSF corrected by using Jo
-
Figure 7.
PSF corrected by using Jlg

 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: