| Citation: | Chen SR, Ha YL, Zhang F et al. Towards the performance limit of catenary meta-optics via field-driven optimization. Opto-Electron Adv 7, 230145 (2024). doi: 10.29026/oea.2024.230145 |
Towards the performance limit of catenary meta-optics via field-driven optimization
-
Abstract
Catenary optics enables metasurfaces with higher efficiency and wider bandwidth, and is highly anticipated in the imaging system, super-resolution lithography, and broadband absorbers. However, the periodic boundary approximation without considering aperiodic electromagnetic crosstalk poses challenges for catenary optical devices to reach their performance limits. Here, perfect control of both local geometric and propagation phases is realized through field-driven optimization, in which the field distribution is calculated under real boundary conditions. Different from other optimization methods requiring a mass of iterations, the proposed design method requires less than ten iterations to get the efficiency close to the optimal value. Based on the library of shape-optimized catenary structures, centimeter-scale devices can be designed in ten seconds, with the performance improved by ~15%. Furthermore, this method has the ability to extend catenary-like continuous structures to arbitrary polarization, including both linear and elliptical polarizations, which is difficult to achieve with traditional design methods. It provides a way for the development of catenary optics and serves as a potent tool for constructing high-performance optical devices.-
Keywords:
- catenary optics /
- catenary structures /
- field-driven optimization
-

-
References
[1] Xie X, Pu MB, Jin JJ, Xu MF, Guo YH et al. Generalized pancharatnam-berry phase in rotationally symmetric meta-atoms. Phys Rev Lett 126, 183902 (2021). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.126.183902 [2] Wang YX, Yuan YY, Liu Y, Ding XM, Ratni B et al. Extreme diffraction management in phase-corrected gradient metasurface by fourier harmonic component engineering. Laser Photonics Rev 17, 2300152 (2023). doi: 10.1002/lpor.202300152 [3] Liu MZ, Zhu WQ, Huo PC, Feng L, Song MW et al. Multifunctional metasurfaces enabled by simultaneous and independent control of phase and amplitude for orthogonal polarization states. Light Sci Appl 10, 107 (2021). doi: 10.1038/s41377-021-00552-3 [4] Wang EW, Yu SJ, Phan T, Dhuey S, Fan JA. Arbitrary achromatic polarization control with reconfigurable metasurface systems. Laser Photonics Rev 17, 2200926 (2023). doi: 10.1002/lpor.202200926 [5] Wang S, Wen S, Deng ZL, Li XP, Yang YM. Metasurface-based solid poincaré sphere polarizer. Phys Rev Lett 130, 123801 (2023). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.130.123801 [6] Xu YH, Xu Q, Zhang XQ, Feng X, Lu YC et al. Stereo metasurfaces for efficient and broadband terahertz polarization conversion. Adv Funct Mater 32, 2207269 (2022). doi: 10.1002/adfm.202207269 [7] Zhang YX, Pu MB, Jin JJ, Lu XJ, Guo YH et al. Crosstalk-free achromatic full Stokes imaging polarimetry metasurface enabled by polarization-dependent phase optimization. Opto-Electron Adv 5, 220058 (2022). doi: 10.29026/oea.2022.220058 [8] Miyata M, Nemoto N, Shikama K, Kobayashi F, Hashimoto T. Full-color-sorting metalenses for high-sensitivity image sensors. Optica 8, 1596–1604 (2021). doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.444255 [9] Xiao XJ, Zhao YW, Ye X, Chen C, Lu XM et al. Large-scale achromatic flat lens by light frequency-domain coherence optimization. Light Sci Appl 11, 323 (2022). doi: 10.1038/s41377-022-01024-y [10] Wei MG, Xu YH, Liu GG, Wu T, Liu WY et al. Extended metasurface spin functionalities from rotation of elements. Adv Opt Mater 10, 2201975 (2022). doi: 10.1002/adom.202201975 [11] Fu P, Ni PN, Wu B, Pei XZ, Wang QH et al. Metasurface enabled on-chip generation and manipulation of vector beams from vertical cavity surface-emitting lasers. Adv Mater 35, 2204286 (2023). doi: 10.1002/adma.202204286 [12] Dorrah AH, Rubin NA, Zaidi A, Tamagnone M, Capasso F. Metasurface optics for on-demand polarization transformations along the optical path. Nat Photonics 15, 287–296 (2021). doi: 10.1038/s41566-020-00750-2 [13] Gao S, Zhou CY, Liu WW, Yue WJ, Chen SQ et al. Dielectric polarization-filtering metasurface doublet for trifunctional control of full-space visible light. Laser Photonics Rev 16, 2100603 (2022). doi: 10.1002/lpor.202100603 [14] Yan JX, Wei QS, Liu Y, Geng GZ, Li JJ et al. Single pixel imaging key for holographic encryption based on spatial multiplexing metasurface. Small 18, 2203197 (2022). doi: 10.1002/smll.202203197 [15] Song MW, Feng L, Huo PC, Liu MZ, Huang CY et al. Versatile full-colour nanopainting enabled by a pixelated plasmonic metasurface. Nat Nanotechnol 18, 71–78 (2023). doi: 10.1038/s41565-022-01256-4 [16] Song MW, Wang D, Kudyshev ZA, Xuan Y, Wang ZX et al. Enabling optical steganography, data storage, and encryption with plasmonic colors. Laser Photonics Rev 15, 2000343 (2021). doi: 10.1002/lpor.202000343 [17] Zhang F, Pu MB, Gao P, Jin JJ, Li X et al. Simultaneous full-color printing and holography enabled by centimeter-scale plasmonic metasurfaces. Adv Sci 7, 1903156 (2020). doi: 10.1002/advs.201903156 [18] Huang YJ, Xiao TX, Chen S, Xie ZW, Zheng J et al. All-optical controlled-NOT logic gate achieving directional asymmetric transmission based on metasurface doublet. Opto-Electron Adv 6, 220073 (2023). doi: 10.29026/oea.2023.220073 [19] Tang DL, Shao ZL, Xie X, Zhou YJ, Zhang XH et al. Flat multifunctional liquid crystal elements through multi-dimensional information multiplexing. Opto-Electron Adv 6, 220063 (2023). doi: 10.29026/oea.2023.220063 [20] Hasman E, Kleiner V, Biener G, Niv A. Polarization dependent focusing lens by use of quantized Pancharatnam-Berry phase diffractive optics. Appl Phys Lett 82, 328–330 (2003). doi: 10.1063/1.1539300 [21] Pu MB, Li X, Ma XL, Wang YQ, Zhao ZY et al. Catenary optics for achromatic generation of perfect optical angular momentum. Sci Adv 1, e1500396 (2015). doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1500396 [22] Wen YF, Zhang Q, He Q, Zhang FF, Xiong LX et al. Shortening focal length of 100-mm aperture flat lens based on improved sagnac interferometer and bifacial liquid crystal. Adv Opt Mater 11, 2300127 (2023). doi: 10.1002/adom.202300127 [23] Zhang F, Zeng QY, Pu MB, Wang YQ, Guo YH et al. Broadband and high-efficiency accelerating beam generation by dielectric catenary metasurfaces. Nanophotonics 9, 2829–2837 (2020). doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2020-0057 [24] Huang YJ, Luo J, Pu MB, Guo YH, Zhao ZY et al. Catenary electromagnetics for ultra-broadband lightweight absorbers and large-scale flat antennas. Adv Sci 6, 1801691 (2019). doi: 10.1002/advs.201801691 [25] Luo XG, Pu MB, Guo YH, Li X, Zhang F et al. Catenary functions meet electromagnetic waves: opportunities and promises. Adv Opt Mater 8, 2001194 (2020). doi: 10.1002/adom.202001194 [26] Song RR, Deng QL, Zhou SL, Pu MB. Catenary-based phase change metasurfaces for mid-infrared switchable wavefront control. Opt Express 29, 23006–23018 (2021). doi: 10.1364/OE.434844 [27] Zhang F, Pu MB, Li X, Ma XL, Guo YH et al. Extreme-angle silicon infrared optics enabled by streamlined surfaces. Adv Mater 33, 2008157 (2021). doi: 10.1002/adma.202008157 [28] Zhang YX, Pu MB, Guo YH, Jin JJ, He Q et al. High-efficiency mid-infrared catenary metasurface for chiral spectrometer. Proc SPIE 12072, 120720F (2021). [29] Guo YH, Huang YJ, Li X, Pu MB, Gao P et al. Polarization-controlled broadband accelerating beams generation by single catenary‐shaped metasurface. Adv Opt Mater 7, 1900503 (2019). doi: 10.1002/adom.201900503 [30] Jin JJ, Li X, Guo YH, Pu MB, Gao P et al. Polarization-controlled unidirectional excitation of surface plasmon polaritons utilizing catenary apertures. Nanoscale 11, 3952–3957 (2019). doi: 10.1039/C8NR09383K [31] Luo XG, Zhang F, Pu MM, Xu MF. Catenary optics: a perspective of applications and challenges. J Phys Condens Matter 34, 381501 (2022). doi: 10.1088/1361-648X/ac808e [32] Xie X, Pu M, Liu K, Ma X, Li X et al. High-efficiency and tunable circular-polarization beam splitting with a liquid-filled all‐metallic catenary meta‐mirror. Adv Mater Technol 4, 1900334 (2019). doi: 10.1002/admt.201900334 [33] Xu MF, Pu MB, Sang D, Zheng YH, Li X et al. Topology-optimized catenary-like metasurface for wide-angle and high-efficiency deflection: from a discrete to continuous geometric phase. Opt Express 29, 10181–10191 (2021). doi: 10.1364/OE.422112 [34] Mansouree M, Kwon H, Arbabi E, McClung A, Faraon A et al. Multifunctional 2.5D metastructures enabled by adjoint optimization. Optica 7, 77–84 (2020). doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.374787 [35] Liu YJ, Zhang F, Xie T, Pu MB, Zhao ZY et al. Polarization-multiplexed metalens enabled by adjoint optimization. Chin Opt 14, 754–763 (2021). doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0035 [36] Mansouree M, McClung A, Samudrala S, Arbabi A. Large-scale parametrized metasurface design using adjoint optimization. ACS Photonics 8, 455–463 (2021). [37] Zhang F, Pu MB, Li X, Gao P, Ma XL et al. All-dielectric metasurfaces for simultaneous giant circular asymmetric transmission and wavefront shaping based on asymmetric photonic spin-orbit interactions. Adv Funct Mater 27, 1704295 (2017). doi: 10.1002/adfm.201704295 [38] Cai JX, Zhang F, Pu MB, Chen Y, Guo YH et al. Dispersion‐enabled symmetry switching of photonic angular‐momentum coupling. Adv Funct Mater 33, 2212147 (2023). doi: 10.1002/adfm.202212147 [39] Zhang F, Guo YH, Pu MB, Chen LW, Xu MF et al. Meta-optics empowered vector visual cryptography for high security and rapid decryption. Nat Commun 14, 1946 (2023). doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37510-z [40] Yu NF, Capasso F. Flat optics with designer metasurfaces. Nat Mater 13, 139–150 (2014). doi: 10.1038/nmat3839 [41] Li ZG, Stan L, Czaplewski DA, Yang XD, Gao J. Broadband infrared binary-pattern metasurface absorbers with micro-genetic algorithm optimization. Opt Lett 44, 114–117 (2019). doi: 10.1364/OL.44.000114 [42] Zhang JM, Wang GW, Wang T, Li FS. Genetic algorithms to automate the design of metasurfaces for absorption bandwidth broadening. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13, 7792–7800 (2021). doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c21984 [43] Hu JT, Liu CH, Ren XC, Lauhon LJ, Odom TW. Plasmonic lattice lenses for multiwavelength achromatic focusing. ACS Nano 10, 10275–10282 (2016). doi: 10.1021/acsnano.6b05855 [44] Nemat-Abad HM, Zareian-Jahromi E, Basiri R. Design of metasurface-based multi-layer THz filters utilizing optimization algorithm with distinct fitness function definitions. Plasmonics 16, 1865–1876 (2021). doi: 10.1007/s11468-021-01450-5 [45] Hojjati A, Soleimani M, Nayyeri V, Ramahi OM. Ternary optimization for designing metasurfaces. Sci Rep 11, 17110 (2021). doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-96564-5 [46] Ma TG, Tobah M, Wang HZ, Guo LJ. Benchmarking deep learning-based models on nanophotonic inverse design problems. Opto-Electron Sci 1, 210012 (2022). doi: 10.29026/oes.2022.210012 [47] Lalau-Keraly CM, Bhargava S, Miller OD, Yablonovitch E. Adjoint shape optimization applied to electromagnetic design. Opt Express 21, 21693–21701 (2013). doi: 10.1364/OE.21.021693 [48] Miller OD. Photonic Design: From Fundamental Solar Cell Physics to Computational Inverse Design (University of California, Berkeley, 2012). [49] Ciattoni A, Crosignani B, Di Porto P. Vectorial free-space optical propagation: a simple approach for generating all-order nonparaxial corrections. Opt Commun 177, 9–13 (2000). doi: 10.1016/S0030-4018(00)00569-1 [50] Li ZY, Pestourie R, Park JS, Huang YW, Johnson SG et al. Inverse design enables large-scale high-performance meta-optics reshaping virtual reality. Nat Commun 13, 2409 (2022). doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29973-3 -
Supplementary Information
Supplementary information for Towards the performance limit of catenary meta-optics via field-driven optimization 
-
Access History

Article Metrics
-
Figure 1.
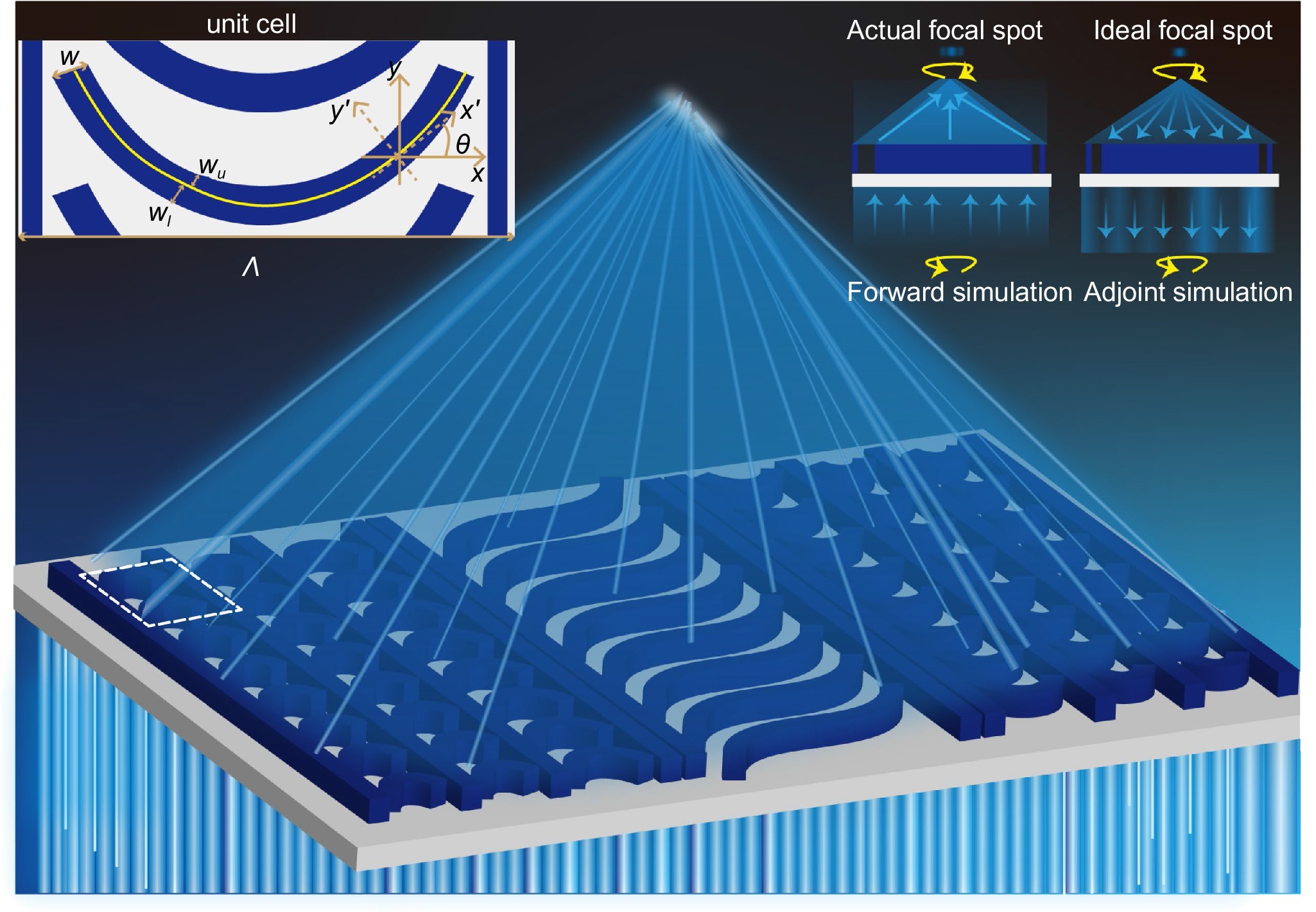
Schematic of a one-dimensional (1D) metalens composed of catenary-like structures. The metalens converges the incident light onto the focal spot. The FDO method is utilized to correct the propagation phases of the metalens.
-
Figure 2.
(a) Top views of the initial and optimized catenary and catenary-like optical devices with a diffraction angle of 45°. (b) Schematic of the diffraction efficiencies (Eff.) of the devices with diffraction angles of α = 45° and 75°.
-
Figure 3.
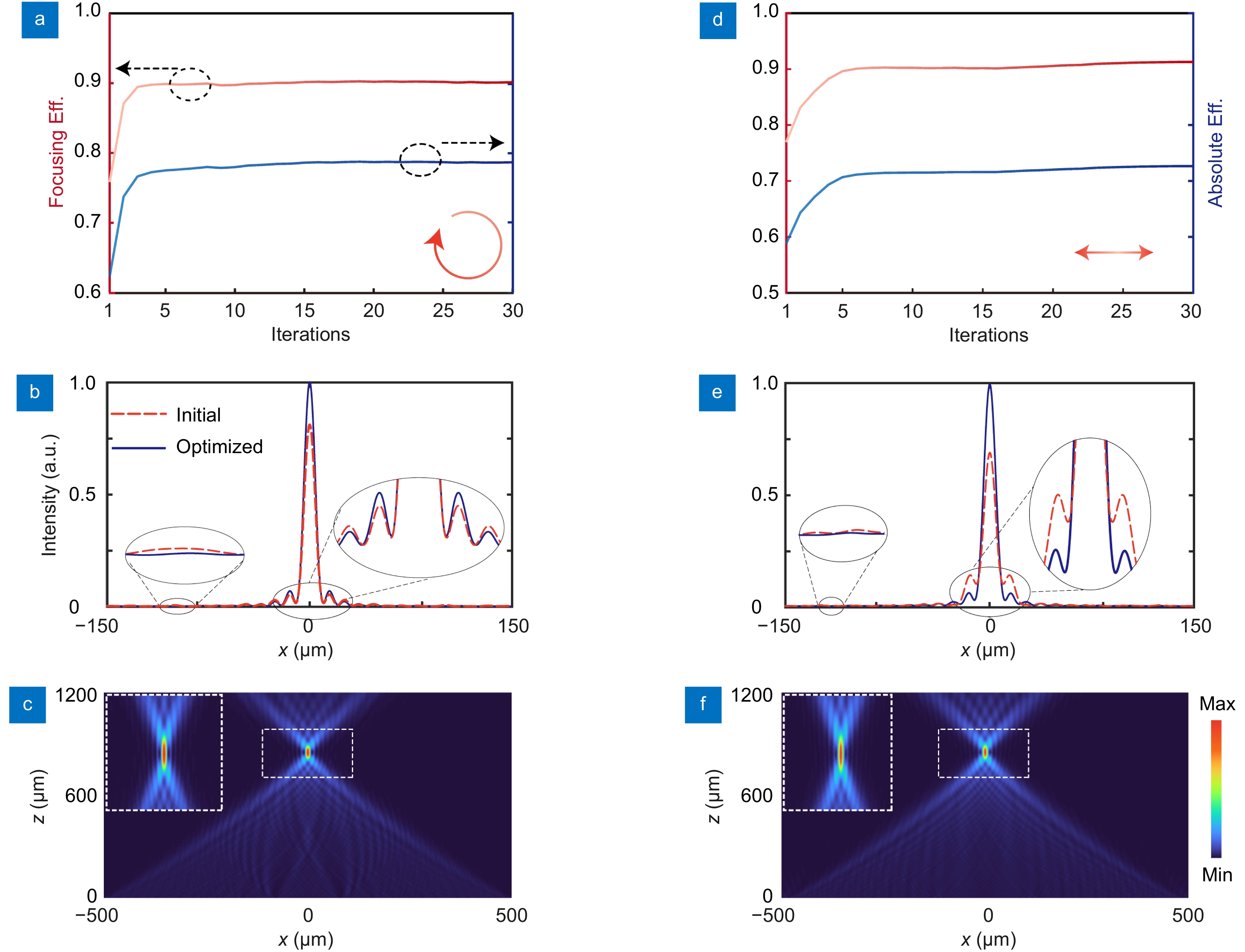
(a) Evolution of the efficiencies of the catenary-like 1D metalens with CP incidence. (b) The normalized light intensity distributions on the focal plane of the initial and optimized metalenses with CP incidence. (c) The distribution of light intensity on the XoZ plane with CP incidence. (d–f) The efficiencies and light intensity distributions of the metalenses with LP incidence.
-
Figure 4.
(a) Schematic of the catenary library. The inner dashed box part indicates the continuous part of the catenaries; the outer box part denotes the part of the rectangles. (b, c) The efficiencies of the equal-width catenary arrays (dashed lines), optimized catenary arrays via the FDO method (solid lines), and the predicted catenary arrays via the library (*). (d) The efficiencies of the catenary-like metalenses with equal width and predicted width, with NA ranging from 0.1 to 0.7.
-
Figure 5.
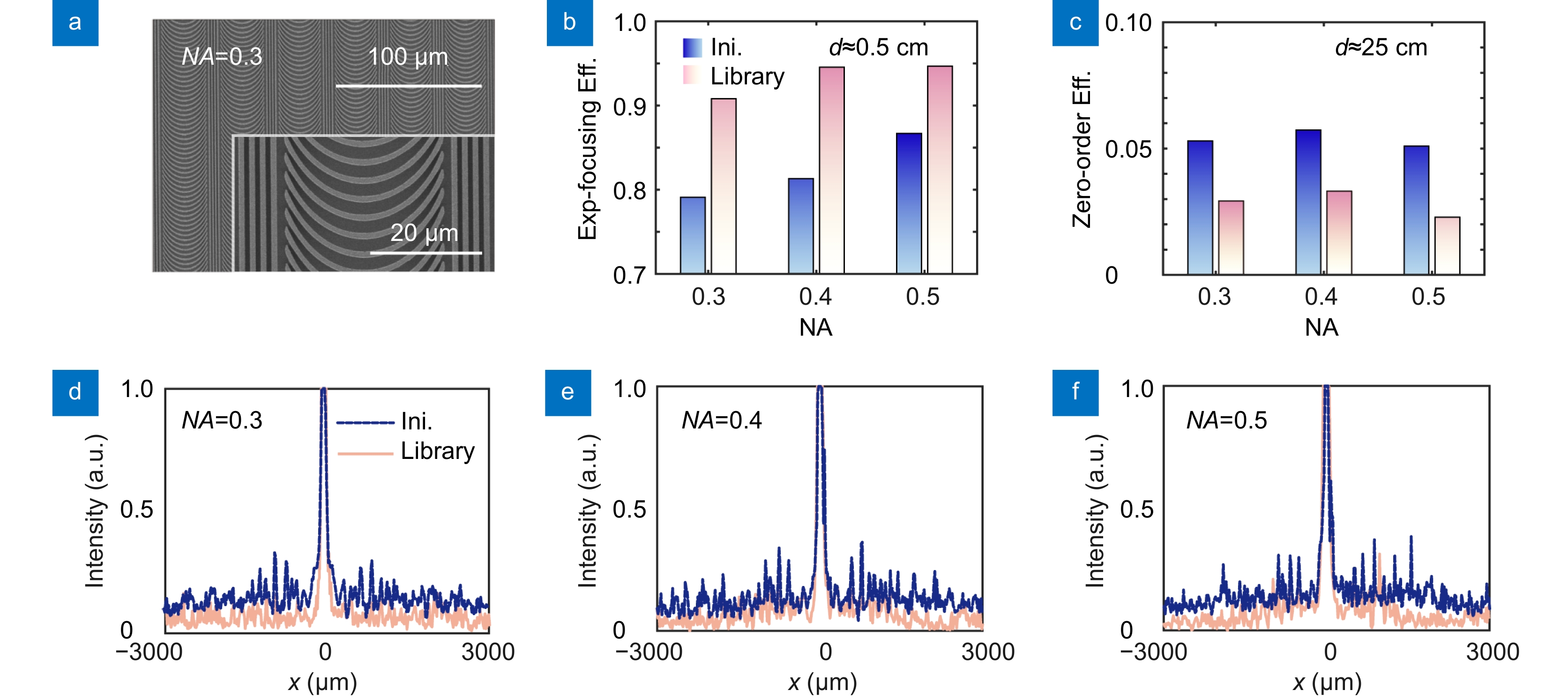
(a) The scanning electron microscope image of the metalens designed using the library with NA=0.3 and Dlens=6000 μm. (b) The experimental focusing efficiencies of the metalenses with NA=0.3, 0.4, and 0.5. (c) The experimental zero-order efficiencies. (d–f) Comparison of the background noise at the focal plane of the catenary-like metalenses with equal-width and predicted-width overexposure.

 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: