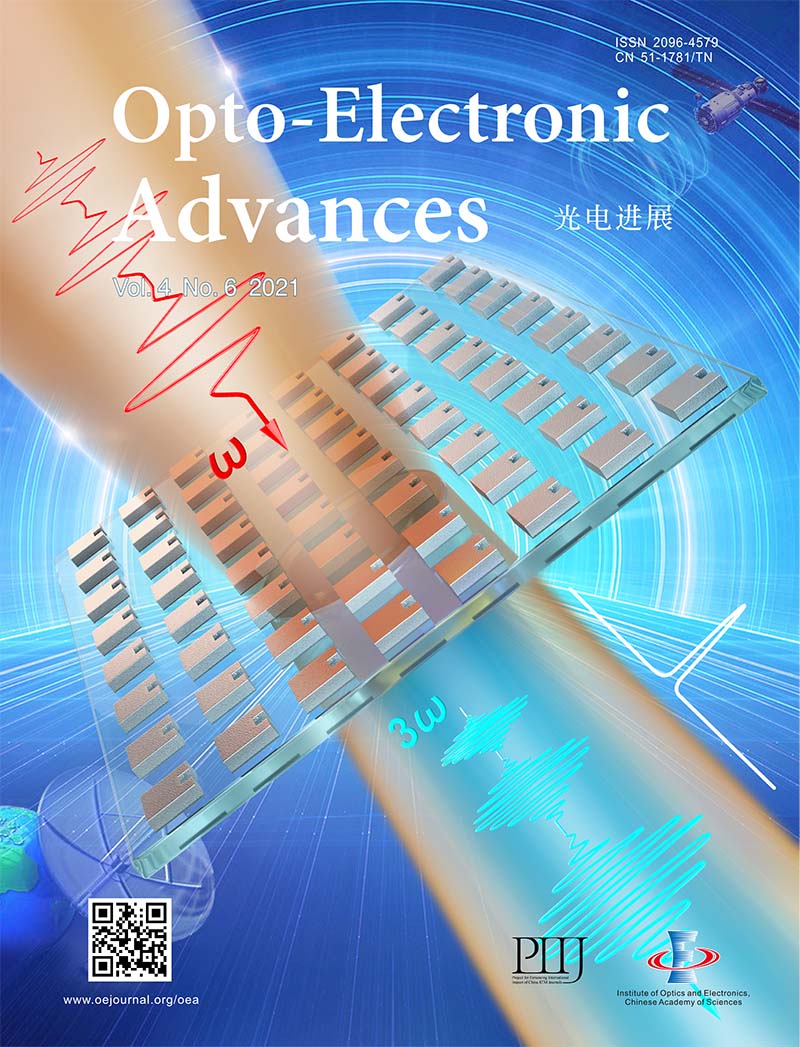
2021 Vol. 4, No. 6
The optical metasurface is a kind of special quasi-2D metamaterial consisting of ultrathin subwavelength resonators with different shapes and sizes. Due to the ability of efficient and flexible control of the electromagnetic wave, it shows a series of novel physical characteristics and application potentials. However, nanoresonators made of traditional materials (such as Si) can only support a relatively low Q factor, which limits the applications that require sharp spectral features. Recently, Professor Yan Liu and Professor Xuetao Gan at Xidian University and Northwestern Polytechnical University reported a method of realizing high-Q resonances in Si metasurfaces. By utilizing the mechanism of the bound states in the continuum, the Q factor of the resonance can be controlled by changing the size of the introduced defects and a high-Q resonance can be easily achieved by optimizing the dimensions of the nanostructures. In addition, the relationship between the Q factor and the size of the defect can be also adjusted by changing the design proposal. The experiment result indicates that the intensity of the third harmonic generation (THG) signal can be enhanced more than 368 times at the resonance. The proposed strategy and underlying theory can open up new avenues to realize ultrasharp resonances, which may promote the development of the potential meta-devices for nonlinearity, lasing action, and sensing.
-
{{article.year}}, {{article.volume}}({{article.issue}}): {{article.fpage | processPage:article.lpage:6}}. doi: {{article.doi}}{{article.articleStateNameEn}}, Published online {{article.preferredDate | date:'dd MMMM yyyy'}}, doi: {{article.doi}}{{article.articleStateNameEn}}, Accepted Date {{article.acceptedDate | date:'dd MMMM yyyy'}}CSTR: {{article.cstr}}
-
{{article.year}}, {{article.volume}}({{article.issue}}): {{article.fpage | processPage:article.lpage:6}}. doi: {{article.doi}}{{article.articleStateNameEn}}, Published online {{article.preferredDate | date:'dd MMMM yyyy'}}, doi: {{article.doi}}{{article.articleStateNameEn}}, Accepted Date {{article.acceptedDate | date:'dd MMMM yyyy'}}CSTR: {{article.cstr}}

 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS