| Citation: | Zhang D S, Sugioka K. Hierarchical microstructures with high spatial frequency laser induced periodic surface structures possessing different orientations created by femtosecond laser ablation of silicon in liquids. Opto-Electron Adv 2, 190002 (2019). doi: 10.29026/oea.2019.190002 |
Hierarchical microstructures with high spatial frequency laser induced periodic surface structures possessing different orientations created by femtosecond laser ablation of silicon in liquids
-
Abstract
High spatial frequency laser induced periodic surface structures (HSFLs) on silicon substrates are often developed on flat surfaces at low fluences near ablation threshold of 0.1 J/cm2, seldom on microstructures or microgrooves at relatively higher fluences above 1 J/cm2. This work aims to enrich the variety of HSFLs-containing hierarchical microstructures, by femtosecond laser (pulse duration: 457 fs, wavelength: 1045 nm, and repetition rate: 100 kHz) in liquids (water and acetone) at laser fluence of 1.7 J/cm2. The period of Si-HSFLs in the range of 110-200 nm is independent of the scanning speeds (0.1, 0.5, 1 and 2 mm/s), line intervals (5, 15 and 20 μm) of scanning lines and scanning directions (perpendicular or parallel to light polarization direction). It is interestingly found that besides normal HSFLs whose orientations are perpendicular to the direction of light polarization, both clockwise or anticlockwise randomly tilted HSFLs with a maximal deviation angle of 50° as compared to those of normal HSFLSs are found on the microstructures with height gradients. Raman spectra and SEM characterization jointly clarify that surface melting and nanocapillary waves play important roles in the formation of Si-HSFLs. The fact that no HSFLs are produced by laser ablation in air indicates that moderate melting facilitated with ultrafast liquid cooling is beneficial for the formation of HSFLs by LALs. On the basis of our findings and previous reports, a synergistic formation mechanism for HSFLs at high fluence was proposed and discussed, including thermal melting with the concomitance of ultrafast cooling in liquids, transformation of the molten layers into ripples and nanotips by surface plasmon polaritons (SPP) and second-harmonic generation (SHG), and modulation of Si-HSFLs direction by both nanocapillary waves and the localized electric field coming from the excited large Si particles. -

-
References
[1] Bonse J, H hm S, Kirner S V, Rosenfeld A, Krüger J. Laser-induced periodic surface structures—a scientific evergreen. IEEE J Sel Top Quantum Electron 23, 9000615 (2017). [2] Sugioka K. Progress in ultrafast laser processing and future prospects. Nanophotonics 6, 393-413 (2017). [3] Sugioka K, Cheng Y. Ultrafast lasers—reliable tools for advanced materials processing. Light: Sci Appl 3, e149 (2014). doi: 10.1038/lsa.2014.30 [4] Zeng H B, Du X W, Singh S C, Kulinich S A, Yang S K et al. Nanomaterials via laser ablation/irradiation in liquid: A review. Adv Funct Mater 22, 1333-1353 (2012). doi: 10.1002/adfm.v22.7 [5] Zhang D S, G kce B. Perspective of laser-prototyping nanoparticle-polymer composites. Appl Surf Sci 392, 991-1003 (2017). doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.09.150 [6] Zhang D S, G kce B, Barcikowski S. Laser synthesis and processing of colloids: Fundamentals and applications. Chem Rev 117, 3990-4103 (2017). doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00468 [7] Zhang D S, Liu J, Li P F, Tian Z F, Liang C H. Recent advances in surfactant-free, surface-charged, and defect-rich catalysts developed by laser ablation and processing in liquids. ChemNanoMat 3, 512-533 (2017). doi: 10.1002/cnma.v3.8 [8] Amendola V, Meneghetti M. What controls the composition and the structure of nanomaterials generated by laser ablation in liquid solution? Phys Chem Chem Phys 15, 3027-3046 (2013). doi: 10.1039/C2CP42895D [9] Yang G W. Laser ablation in liquids: Applications in the synthesis of nanocrystals. Prog Mater Sci 52, 648-698 (2007). doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2006.10.016 [10] Zhang D S, Zhang C, Liu J, Chen Q, Zhu X G et al. Carbon-encapsulated metal/metal carbide/metal oxide core-shell nanostructures generated by laser ablation of metals in organic solvents. ACS Appl Nano Mater 2, 28-39 (2019). doi: 10.1021/acsanm.8b01541 [11] Zhang D S, Choi W, Yazawa K, Numata K, Tateishi A et al. Two birds with one stone: Spontaneous size separation and growth inhibition of femtosecond laser-generated surfactant-free metallic nanoparticles via ex situ su-8 functionalization. ACS Omega 3, 10953-10966 (2018). doi: 10.1021/acsomega.8b01250 [12] Zhang D S, Liu J, Liang C H. Perspective on how laser-ablated particles grow in liquids. Sci China Phys, Mech Astron 60, 074201 (2017). doi: 10.1007/s11433-017-9035-8 [13] Zhang D S, Choi W, Jakobi J, Kalus M R, Barcikowski S et al. Spontaneous shape alteration and size separation of surfactant-free silver particles synthesized by laser ablation in acetone during long-period storage. Nanomaterials 8, 529 (2018). doi: 10.3390/nano8070529 [14] Zhang D S, Chen F, Yang Q, Yong J L, Bian H et al. A simple way to achieve pattern-dependent tunable adhesion in superhydrophobic surfaces by a femtosecond laser. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4, 4905-4912 (2012). doi: 10.1021/am3012388 [15] Zhang D S, Chen F, Fang G P, Yang Q, Xie D G et al. Wetting characteristics on hierarchical structures patterned by a femtosecond laser. J Micromech Microeng 20, 075029 (2010). doi: 10.1088/0960-1317/20/7/075029 [16] Zhang D S, Chen F, Yang Q, Si J H, Hou X. Mutual wetting transition between isotropic and anisotropic on directional structures fabricated by femotosecond laser. Soft Matter 7, 8337-8342 (2011). doi: 10.1039/c1sm05649b [17] Yong J L, Chen F, Yang Q, Jiang Z D, Hou X. A review of femtosecond-laser-induced underwater superoleophobic surfaces. Adv Mater Interfaces 5, 1701370 (2018). doi: 10.1002/admi.v5.7 [18] Intartaglia R, Barchanski A, Bagga K, Genovese A, Das G et al. Bioconjugated silicon quantum dots from one-step green synthesis. Nanoscale 4, 1271-1274 (2012). doi: 10.1039/c2nr11763k [19] Simitzi C, Efstathopoulos P, Kourgiantaki A, Ranella A, Charalampopoulos I et al. Laser fabricated discontinuous anisotropic microconical substrates as a new model scaffold to control the directionality of neuronal network outgrowth. Biomaterials 67, 115-128 (2015). doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.07.008 [20] Yiannakou C, Simitzi C, Manousaki A, Fotakis C, Ranella A et al. Cell patterning via laser micro/nano structured silicon surfaces. Biofabrication 9, 025024 (2017). doi: 10.1088/1758-5090/aa71c6 [21] Wang Z Y, Zhou R, Wen F, Zhang R K, Ren L et al. Reliable laser fabrication: The quest for responsive biomaterials surface. J Mater Chem B 6, 3612-3631 (2018). doi: 10.1039/C7TB02545A [22] Luo X, Zhang H J, Pan W, Gong J H, Khalid B et al. SiOx nanodandelion by laser ablation for anode of lithium-ion battery. Small 11, 6009-6012 (2015). doi: 10.1002/smll.201502539 [23] Xu K C, Zhang C T, Zhou R, Ji R, Hong M H. Hybrid micro/nano-structure formation by angular laser texturing of si surface for surface enhanced raman scattering. Opt Express 24, 10352-10358 (2016). doi: 10.1364/OE.24.010352 [24] Yang J, Li J B, Du Z R, Gong Q H, Teng J H et al. Laser hybrid micro/nano-structuring of si surfaces in air and its applications for sers detection. Sci Rep 4, 6657 (2014). [25] Sartori A F, Orlando S, Bellucci A, Trucchi D M, Abrahami S et al. Laser-induced periodic surface structures (LIPSS) on heavily boron-doped diamond for electrode applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10, 43236-43251 (2018). doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b15951 [26] Duan G B, Hu X L, Song X Y, Qiu Z W, Gong H B et al. Morphology evolution of zno submicroparticles induced by laser irradiation and their enhanced tribology properties by compositing with Al2O3 nanoparticles. Adv Eng Mater 17, 341-348 (2015). doi: 10.1002/adem.201400385 [27] Luo T, Wang P, Qiu Z W, Yang S H, Zeng H B et al. Smooth and solid WS2 submicrospheres grown by a new laser fragmentation and reshaping process with enhanced tribological properties. Chem Commun 52, 10147-10150 (2016). doi: 10.1039/C6CC04212K [28] Luo T, Chen X C, Li P S, Wang P, Li C C et al. Laser irradiation-induced laminated graphene/MoS2 composites with synergistically improved tribological properties. Nanotechnology 29, 265704 (2018). doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/aabcf5 [29] Bonse J, Kirner S, Griepentrog M, Spaltmann D, Krüger J. Femtosecond laser texturing of surfaces for tribological applications. Materials 11, 801 (2018). doi: 10.3390/ma11050801 [30] Serien D, Sugioka K. Fabrication of three-dimensional proteinaceous micro- and nano-structures by femtosecond laser cross-linking. Opto-Electron Adv 1, 180008 (2018). [31] Sugioka K, Cheng Y. Femtosecond laser three-dimensional micro- and nanofabrication. Appl Phys Rev 1, 041303 (2014). doi: 10.1063/1.4904320 [32] Birnbaum M. Semiconductor surface damage produced by ruby lasers. J Appl Phys 36, 3688-3689 (1965). doi: 10.1063/1.1703071 [33] Le Harzic R, D rr D, Sauer D, Stracke F, Zimmermann H. Generation of high spatial frequency ripples on silicon under ultrashort laser pulses irradiation. Appl Phys Lett 98, 211905 (2011). doi: 10.1063/1.3593493 [34] Huang M, Zhao F L, Cheng Y, Xu N S, Xu Z Z. Origin of laser-induced near-subwavelength ripples: Interference between surface plasmons and incident laser. ACS Nano 3, 4062-4070 (2009). doi: 10.1021/nn900654v [35] Tan B, Venkatakrishnan K. A femtosecond laser-induced periodical surface structure on crystalline silicon. J Micromech Microeng 16, 1080-1085 (2006). doi: 10.1088/0960-1317/16/5/029 [36] Costache F, Kouteva-Arguirova S, Reif J. Sub-damage-threshold femtosecond laser ablation from crystalline Si: Surface nanostructures and phase transformation. Appl Phys A 79, 1429-1432 (2004). doi: 10.1007/s00339-004-2803-y [37] Tsibidis G D, Barberoglou M, Loukakos P A, Stratakis E, Fotakis C. Dynamics of ripple formation on silicon surfaces by ultrashort laser pulses in subablation conditions. Phys Rev B 86, 115316 (2012). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.86.115316 [38] Wang C, Huo H B, Johnson M, Shen M Y, Mazur E. The thresholds of surface nano-/micro-morphology modifications with femtosecond laser pulse irradiations.Nanotechnology 21, 075304 (2010). doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/21/7/075304 [39] Le Harzic R, Schuck H, Sauer D, Anhut T, Riemann I, K nig K. Sub-100 nm nanostructuring of silicon by ultrashort laser pulses. Opt Express 13, 6651-6656 (2005). doi: 10.1364/OPEX.13.006651 [40] Derrien T J Y, Koter R, Krüger J, H hm S, Rosenfeld A et al. Plasmonic formation mechanism of periodic 100-nm-structures upon femtosecond laser irradiation of silicon in water. J Appl Phys 116, 074902 (2014). doi: 10.1063/1.4887808 [41] Daminelli G, Krüger J, Kautek W. Femtosecond laser interaction with silicon under water confinement. Thin Solid Films 467, 334-341 (2004). doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2004.04.043 [42] Le Harzic R, D rr D, Sauer D, Neumeier M, Epple M et al. Large-area, uniform, high-spatial-frequency ripples generated on silicon using a nanojoule-femtosecond laser at high repetition rate. Opt Lett 36, 229-231 (2011). doi: 10.1364/OL.36.000229 [43] Shen M Y, Carey J E, Crouch C H, Kandyla M, Stone H A et al. High-density regular arrays of nanometer-scale rods formed on silicon surfaces via femtosecond laser irradiation in water. Nano Lett 8, 2087-2091 (2008). doi: 10.1021/nl080291q [44] Kautek W, Rudolph P, Daminelli G, Krüger J. Physico-chemical aspects of femtosecond-pulse-laser-induced surface nanostructures. Appl Phys A 81, 65-70 (2005). [45] Jeschke H O, Garcia M E, Lenzner M, Bonse J, Krüger J et al. Laser ablation thresholds of silicon for different pulse durations: Theory and experiment. Appl Surf Sci 197-198, 839-844 (2002). doi: 10.1016/S0169-4332(02)00458-0 [46] Miyaji G, Miyazaki K, Zhang K F, Yoshifuji T, Fujita J. Mechanism of femtosecond-laser-induced periodic nanostructure formation on crystalline silicon surface immersed in water. Opt Express 20, 14848-14856 (2012). doi: 10.1364/OE.20.014848 [47] Miyazaki K, Miyaji G. Periodic nanostructure formation on silicon irradiated with multiple low-fluence femtosecond laser pulses in water. Phys Procedia 39, 674-682 (2012). doi: 10.1016/j.phpro.2012.10.088 [48] Crawford T H R, Borowiec A, Haugen H K. Femtosecond laser micromachining of grooves in silicon with 800 nm pulses. Appl Phys A 80, 1717-1724 (2005). doi: 10.1007/s00339-004-2941-2 [49] Lee S, Yang D F, Nikumb S. Femtosecond laser micromilling of Si wafers. Appl Surf Sci 254, 2996-3005 (2008). doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2007.10.063 [50] Hamad S, Podagatlapalli G K, Vendamani V S, Nageswara Rao S V S, Pathak A P et al. Femtosecond ablation of silicon in acetone: Tunable photoluminescence from generated nanoparticles and fabrication of surface nanostructures. J Phys Chem C 118, 7139-7151 (2014). [51] Meng G, Jiang L, Li X, Xu Y D, Shi X S et al. Dual-scale nanoripple/nanoparticle-covered microspikes on silicon by femtosecond double pulse train irradiation in water. Appl Surf Sci 410, 22-28 (2017). doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.03.079 [52] Ganeev R A, Lei D Y, Hutchison C, Witting T, Frank F et al. Extended homogeneous nanoripple formation during interaction of high-intensity few-cycle pulses with a moving silicon wafer. Appl Phys A 112, 457-462 (2013). [53] Ma Y C, Si J H, Sun X H, Chen T, Hou X. Progressive evolution of silicon surface microstructures via femtosecond laser irradiation in ambient air. Appl Surf Sci 313, 905-910 (2014). doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.06.105 [54] Barcikowski S, Menéndez-Manjón A, Chichkov B, Brikas M, Račiukaitis G. Generation of nanoparticle colloids by picosecond and femtosecond laser ablations in liquid flow. Appl Phys Lett 91, 083113 (2007). doi: 10.1063/1.2773937 [55] Zhang D S, Gökce B, Sommer S, Streubel R, Barcikowski S. Debris-free rear-side picosecond laser ablation of thin germanium wafers in water with ethanol. Appl Surf Sci 367, 222-230 (2016). doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.01.071 [56] Iqbal Z, Vepřek S, Webb A P, Capezzuto P. Raman scattering from small particle size polycrystalline silicon. Solid State Commun 37, 993-996 (1981). doi: 10.1016/0038-1098(81)91202-3 [57] Svrcek V, Mariotti D, Cvelbar U, Filipič G, Lozac'h M et al. Environmentally friendly processing technology for engineering silicon nanocrystals in water with laser pulses. J Phys Chem C 120, 18822-18830 (2016). doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b04405 [58] Meier C, Lüttjohann S, Kravets V G, Nienhaus H, Lorke A et al. Raman properties of silicon nanoparticles. Physica E: Low-dimens Syst Nanostruct 32, 155-158 (2006). doi: 10.1016/j.physe.2005.12.030 [59] Streubel R, Barcikowski S, G kce B. Continuous multigram nanoparticle synthesis by high-power, high-repetition-rate ultrafast laser ablation in liquids. Opt Lett 41, 1486-1489 (2016). doi: 10.1364/OL.41.001486 [60] Yoo J H, Jeong S H, Mao X L, Greif R, Russo R E. Evidence for phase-explosion and generation of large particles during high power nanosecond laser ablation of silicon. Appl Phys Lett 76, 783-785 (2000). doi: 10.1063/1.125894 [61] Zhang D S, Choi W, Oshima Y, Wiedwald U, Cho S H et al. Magnetic Fe@FeOx, Fe@C and α-Fe2O3 single-crystal nanoblends synthesized by femtosecond laser ablation of fe in acetone. Nanomaterials 8, 631 (2018). doi: 10.3390/nano8080631 [62] Sedao X, Shugaev M V, Wu C P, Douillard T, Esnouf C et al. Growth twinning and generation of high-frequency surface nanostructures in ultrafast laser-induced transient melting and resolidification. ACS Nano 10, 6995-7007 (2016). doi: 10.1021/acsnano.6b02970 [63] Zhang D S, Lau M, Lu S W, Barcikowski S, G kce B. Germanium sub-microspheres synthesized by picosecond pulsed laser melting in liquids: Educt size effects. Sci Rep 7, 40355 (2017). doi: 10.1038/srep40355 [64] Shih C Y, Streubel R, Heberle J, Letzel A, Shugaev M V et al. Two mechanisms of nanoparticle generation in picosecond laser ablation in liquids: The origin of the bimodal size distribution. Nanoscale 10, 6900-6910 (2018). doi: 10.1039/C7NR08614H [65] Abou-Saleh A, Karim E T, Maurice C, Reynaud S, Pigeon F et al. Spallation-induced roughness promoting high spatial frequency nanostructure formation on Cr. Appl Phys A 124, 308 (2018). doi: 10.1007/s00339-018-1716-0 [66] Miyaji G, Miyazaki K. Role of multiple shots of femtosecond laser pulses in periodic surface nanoablation. Appl Phys Lett 103, 071910 (2013). doi: 10.1063/1.4818818 [67] Cheng H C, Li P, Liu S, Chen P, Han L et al. Vortex-controlled morphology conversion of microstructures on silicon induced by femtosecond vector vortex beams. Appl Phys Lett 111, 141901 (2017). doi: 10.1063/1.4994926 [68] Fraggelakis F, Stratakis E, Loukakos P A. Control of periodic surface structures on silicon by combined temporal and polarization shaping of femtosecond laser pulses. Appl Surf Sci 444, 154-160 (2018). doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.02.258 [69] Zhang D S, Ma Z, Spasova M, Yelsukova A E, Lu S W et al. Formation mechanism of laser-synthesized iron-manganese alloy nanoparticles, manganese oxide nanosheets and nanofibers. Part Part Syst Char 34, 1600225 (2017). doi: 10.1002/ppsc.v34.3 [70] Shugaev M V, Gnilitskyi I, Bulgakova N M, Zhigilei L V. Mechanism of single-pulse ablative generation of laser-induced periodic surface structures. Phys Rev B 96, 205429 (2017). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.96.205429 [71] He X L, Datta A, Nam W, Traverso L M, Xu X F. Sub-diffraction limited writing based on laser induced periodic surface structures (LIPSS). Sci Rep 6, 35035 (2016). doi: 10.1038/srep35035 [72] Li H, Shi Z, Wang X W, Sui L Z, Li S Y et al. Influence of dopants on supercontinuum generation during the femtosecond laser filamentation in water. Chem Phys Lett 681, 86-89 (2017). doi: 10.1016/j.cplett.2017.05.029 [73] Potemkin F V, Mareev E I, Smetanina E O. Influence of wave-front curvature on supercontinuum energy during filamentation of femtosecond laser pulses in water. Phys Rev A 97, 033801 (2018). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.97.033801 [74] Besner S, Kabashin A V, Winnik F M, Meunier M. Synthesis of size-tunable polymer-protected gold nanoparticles by femtosecond laser-based ablation and seed growth. J Phys Chem C 113, 9526-9531 (2009). doi: 10.1021/jp809275v [75] Kaviany M. Principles of Heat Transfer (John Wiley & Sons, 2002). [76] Derrien T J Y, Krüger J, Bonse J. Properties of surface plasmon polaritons on lossy materials: Lifetimes, periods and excitation conditions. J Opt 18, 115007 (2016). doi: 10.1088/2040-8978/18/11/115007 [77] Ziemkiewicz D, Słowik K, Zielińska-Raczyńska S. Ultraslow long-living plasmons with electromagnetically induced transparency. Opt Lett 43, 490-493 (2018). doi: 10.1364/OL.43.000490 [78] Shen M Y, Crouch C H, Carey J E, Younkin R, Mazur E et al. Formation of regular arrays of silicon microspikes by femtosecond laser irradiation through a mask. Appl Phys Lett 82, 1715-1717 (2003). doi: 10.1063/1.1561162 [79] Medvedev N, Li Z, Ziaja B. Thermal and nonthermal melting of silicon under femtosecond x-ray irradiation. Phys Rev B 91, 054113 (2015). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.91.054113 [80] Tull B R, Carey J E, Mazur E, McDonald J P, Yalisove S M. Silicon surface morphologies after femtosecond laser irradiation. MRS Bull 31, 626-633 (2006). doi: 10.1557/mrs2006.160 [81] Xue H Y, Deng G L, Feng G Y, Chen L, Li J Q et al. Role of nanoparticles generation in the formation of femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structures on silicon. Opt Lett 42, 3315-3318 (2017). doi: 10.1364/OL.42.003315 -
Access History

Article Metrics
-
Figure 1.
SEM images of surface structures under different magnifications (a–f), and XRD (g) and Raman (h) spectra of the Si prepared by LAA with a laser fluence of 3.8 J/cm2, a line interval of 5 μm and a scanning speed of 1 mm/s.
-
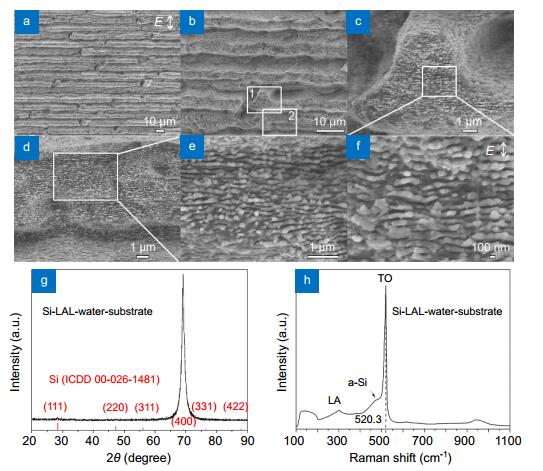
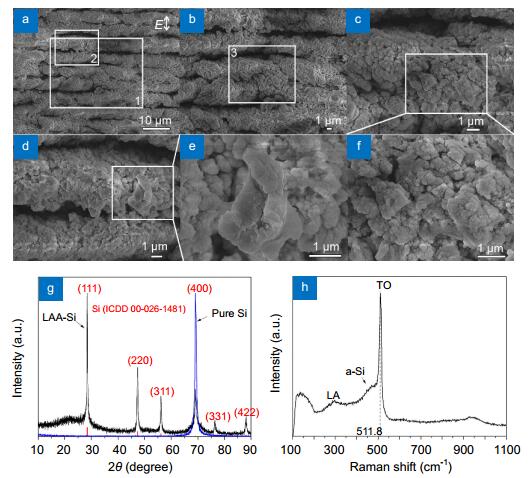
Figure 2.
SEM images (a–f), XRD (g) and Raman (h) spectra of Si surfaces prepared by laser ablation in water with a laser fluence of 1.7 J/cm2, a line interval of 5 μm and a scanning speed of 1 mm/s.
-
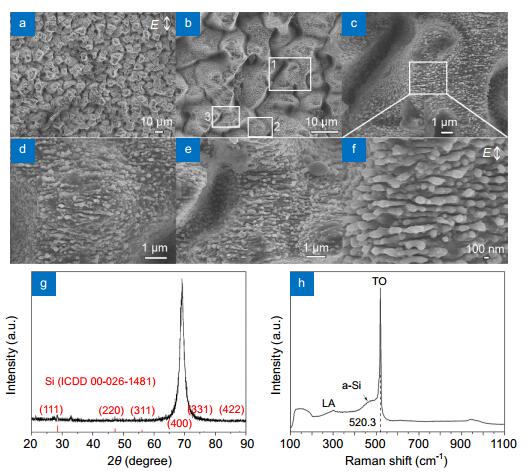
Figure 3.
SEM images (a–f), XRD (g) and Raman (h) spectra of Si surfaces prepared by laser ablation of Si in acetone with a laser fluence of 1.7 J/cm2, a line interval of 5 μm and a scanning speed of 1 mm/s.
-
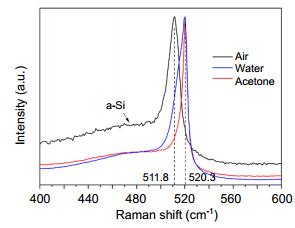
Figure 4.
Comparison of the Raman spectra of Si surfaces prepared by laser ablation in air, water and acetone.
-
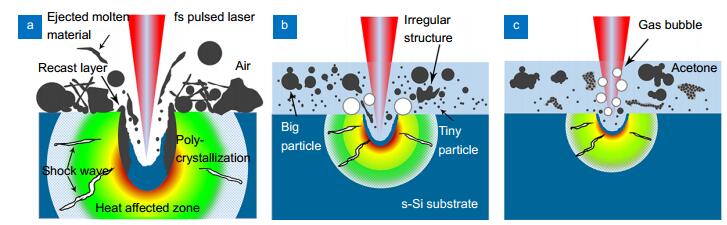
Figure 5.
(a–c) Schematics of the proposed ablation scenarios in air, water and acetone, respectively.
-
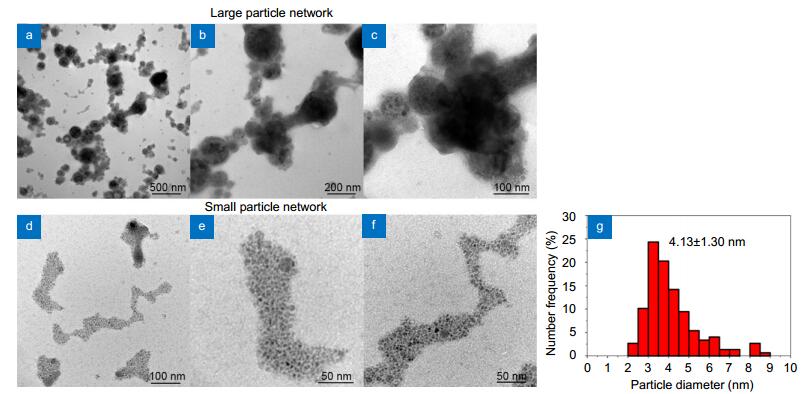
Figure 6.
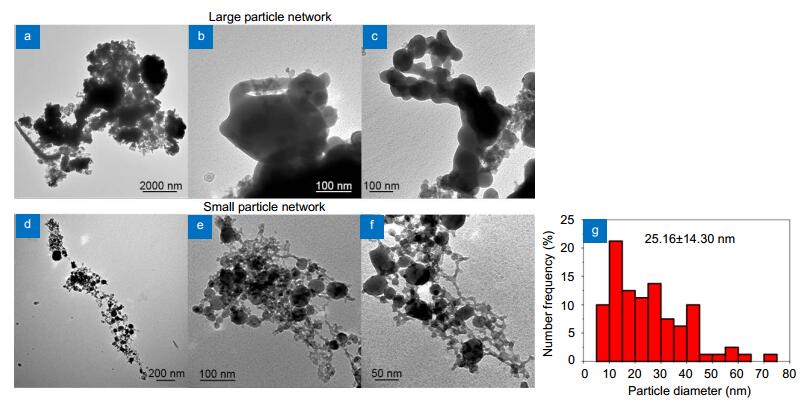
TEM images of (a–c) large and (d–f) small particle networks synthesized by LAA. (g) Size distribution of small particles.
-
Figure 7.
TEM images of (a–c) large particles and networks and (d–f) small particles synthesized by LAL in water. (g) Size distribution of small particles
-
Figure 8.
TEM images of (a–c) large and (d–f) small particle networks synthesized by LAL in acetone. (g) Size distribution of small particles.
-
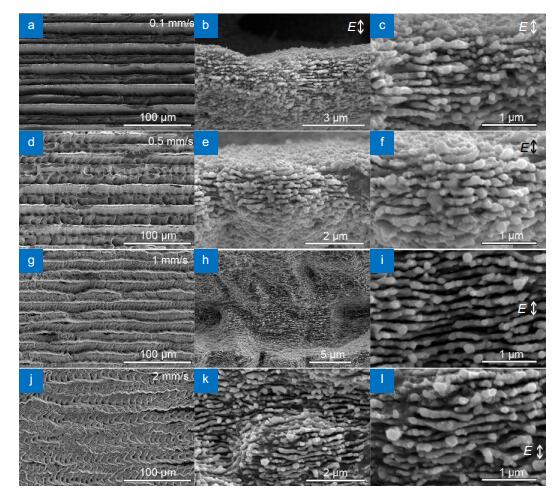
Figure 9.
SEM images of structures obtained by LAL of Si in water at scanning speed of (a–c) 0.1, (d–f) 0.5, (g–i) 1 and (j–l) 2 mm/s with a scanning line interval of 15 μm.
-
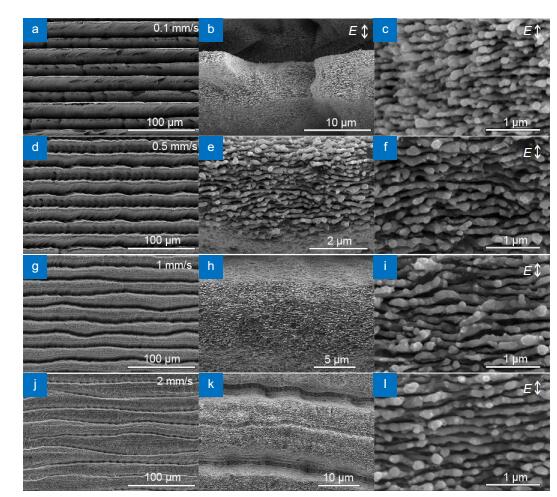
Figure 10.
SEM images of the structures obtained by LAL of Si in water at scanning speed of (a–c) 0.1, (d–f) 0.5, (g–i) 1 and (j–l) 2 mm/s with a scanning line interval of 20 μm.
-
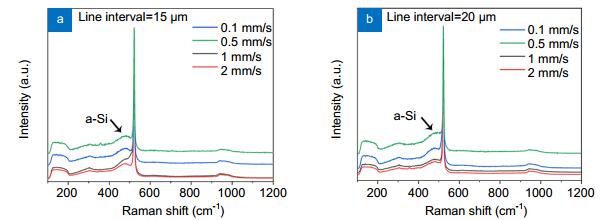
Figure 11.
Raman spectra of Si substrates ablated with line intervals of 15 μm (a) and 20 μm (b) at scanning speeds of 0.1, 0.5, 1 and 2 mm/s.
-
Figure 12.
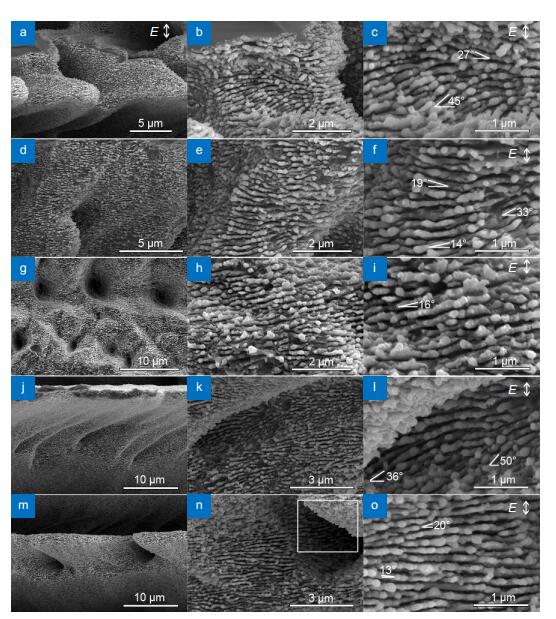
SEM images of micro-structures obtained by LAL of Si in water with a line interval of 15 μm (a–f) at scanning speeds of 0.1 mm/s (a–c), 0.5 mm/s (d–f), 2 mm/s (g–i) and a line interval of 20 μm at a scanning speed of 0.1 mm/s (j–o).
-
Figure 13.
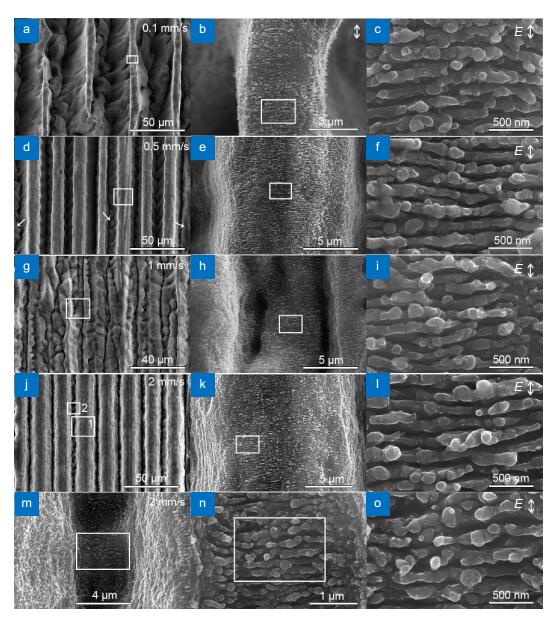
SEM images of the hierarchical micro/nanostructures obtained by LAL of Si in water with a line interval of 20 μm at scanning speeds of 0.1 (a–c), 0.5 (d–f), 1 mm/s (g–i) and 2 mm/s (j–o).
-
Figure 14.
SEM images of micro/nano structures obtained by LAL of Si in water with a line interval of 20 μm at scanning speeds of 0.1 (a–f) and 1 mm/s (g–l).

 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: