| Citation: | Nie QX, Peng YB, Chen QH et al. Agile cavity ringdown spectroscopy enabled by moderate optical feedback to a quantum cascade laser. Opto-Electron Adv 7, 240077 (2024). doi: 10.29026/oea.2024.240077 |
Agile cavity ringdown spectroscopy enabled by moderate optical feedback to a quantum cascade laser
-
Abstract
Cavity ringdown spectroscopy (CRDS), relying on measuring the decay time of photons inside a high-finesse optical cavity, offers an important analytical tool for chemistry, physics, environmental science, and biology. Through the reflection of a slight amount of phase-coherent light back to the laser source, the resonant optical feedback approach effectively couples the laser beam into the optical cavity and achieves a high signal-to-noise ratio. However, the need for active phase-locking mechanisms complicates the spectroscopic system, limiting its primarily laboratory-based use. Here, we report how passive optical feedback can be implemented in a quantum cascade laser (QCL) based CRDS system to address this issue. Without using any phase-locking loops, we reflect a moderate amount of light (–18.2 dB) to a continuous-wave QCL simply using a fixed flat mirror, narrowing the QCL linewidth from 1.2 MHz to 170 kHz and significantly increasing the laser-cavity coupling efficiency. To validate the method’s feasibility and effectiveness, we measured the absorption line (P(18e), 2207.62 cm−1) of N2O in a Fabry–Perot cavity with a high finesse of ~52000 and an inter-mirror distance of 33 cm. This agile approach paves the way for revolutionizing existing analytical tools by offering compact and high-fidelity mid-infrared CRDS systems.-
Keywords:
- cavity ringdown spectroscopy /
- optical feedback /
- quantum cascade laser /
- gas sensing
-

-
References
[1] O’Keefe A, Deacon DAG. Cavity ring-down optical spectrometer for absorption measurements using pulsed laser sources. Rev Sci Instrum 59, 2544–2551 (1988). doi: 10.1063/1.1139895 [2] Romanini D, Kachanov AA, Sadeghi N et al. CW cavity ring down spectroscopy. Chem Phys Lett 264, 316–322 (1997). doi: 10.1016/S0009-2614(96)01351-6 [3] Berden G, Peeters R, Meijer G. Cavity ring-down spectroscopy: experimental schemes and applications. Int Rev Phys Chem 19, 565–607 (2000). doi: 10.1080/014423500750040627 [4] Truong GW, Douglass KO, Maxwell SE et al. Frequency-agile, rapid scanning spectroscopy. Nat Photonics 7, 532–534 (2013). doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2013.98 [5] Giusfredi G, Bartalini S, Borri S et al. Saturated-absorption cavity ring-down spectroscopy. Phys Rev Lett 104, 110801 (2010). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.104.110801 [6] Gagliardi G, Loock HP. Cavity-Enhanced Spectroscopy and Sensing (Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, 2014). [7] Goldenstein CS, Spearrin RM, Jeffries JB et al. Infrared laser-absorption sensing for combustion gases. Prog Energy Combust Sci 60, 132–176 (2017). doi: 10.1016/j.pecs.2016.12.002 [8] Farooq A, Alquaity ABS, Raza M et al. Laser sensors for energy systems and process industries: perspectives and directions. Prog Energy Combust Sci 91, 100997 (2022). doi: 10.1016/j.pecs.2022.100997 [9] Chen Q, Liang L, Zheng QL et al. On-chip readout plasmonic mid-IR gas sensor. Opto-Electron Adv 3, 190040 (2020). doi: 10.29026/oea.2020.190040 [10] Liu YH, Qiao SD, Fang C et al. A highly sensitive LITES sensor based on a multi-pass cell with dense spot pattern and a novel quartz tuning fork with low frequency. Opto-Electron Adv 7, 230230 (2024). doi: 10.29026/oea.2024.230230 [11] Mondelain D, Vasilchenko S, Čermák P et al. The self- and foreign-absorption continua of water vapor by cavity ring-down spectroscopy near 2.35 μm. Phys Chem Chem Phys 17, 17762–17770 (2015). doi: 10.1039/C5CP01238D [12] Vogler DE, Sigrist MW. Near-infrared laser based cavity ringdown spectroscopy for applications in petrochemical industry. Appl Phys B 85, 349–354 (2006). doi: 10.1007/s00340-006-2313-z [13] Galli I, Bartalini S, Ballerini R et al. Spectroscopic detection of radiocarbon dioxide at parts-per-quadrillion sensitivity. Optica 3, 385–388 (2016). doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.3.000385 [14] McCartt AD, Jiang J. Room-temperature optical detection of 14CO2 below the natural abundance with two-color cavity ring-down spectroscopy. ACS Sens 7, 3258–3264 (2022). doi: 10.1021/acssensors.2c01253 [15] Chen Y, Lehmann KK, Kessler J et al. Measurement of the 13C/12C of atmospheric CH4 using near-infrared (NIR) cavity ring-down spectroscopy. Anal Chem 85, 11250–11257 (2013). doi: 10.1021/ac401605s [16] Cone MT, Mason JD, Figueroa E et al. Measuring the absorption coefficient of biological materials using integrating cavity ring-down spectroscopy. Optica 2, 162–168 (2015). doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.2.000162 [17] Long DA, Fleisher AJ, Liu Q et al. Ultra-sensitive cavity ring-down spectroscopy in the mid-infrared spectral region. Opt Lett 41, 1612–1615 (2016). doi: 10.1364/OL.41.001612 [18] Baran SG, Hancock G, Peverall R et al. Optical feedback cavity enhanced absorption spectroscopy with diode lasers. Analyst 134, 243–249 (2009). doi: 10.1039/B811793D [19] Argence B, Chanteau B, Lopez O et al. Quantum cascade laser frequency stabilization at the sub-Hz level. Nat Photonics 9, 456–460 (2015). doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2015.93 [20] Zhao G, Tian JF, Hodges JT et al. Frequency stabilization of a quantum cascade laser by weak resonant feedback from a Fabry-Perot cavity. Opt Lett 46, 3057–3060 (2021). doi: 10.1364/OL.427083 [21] Ohtsubo J. Semiconductor Lasers: Stability, Instability and Chaos 3rd ed (Springer, New York, 2013). [22] Schunk N, Petermann K. Numerical analysis of the feedback regimes for a single-mode semiconductor laser with external feedback. IEEE J Quantum Electron 24, 1242–1247 (1988). doi: 10.1109/3.960 [23] Morville J, Kassi S, Chenevier M et al. Fast, low-noise, mode-by-mode, cavity-enhanced absorption spectroscopy by diode-laser self-locking. Appl Phys B 80, 1027–1038 (2005). doi: 10.1007/s00340-005-1828-z [24] Kassi S, Stoltmann T, Casado M et al. Lamb dip CRDS of highly saturated transitions of water near 1.4 μm. J Chem Phys 148, 054201 (2018). doi: 10.1063/1.5010957 [25] Burkart J, Romanini D, Kassi S. Optical feedback frequency stabilized cavity ring-down spectroscopy. Opt Lett 39, 4695–4698 (2014). doi: 10.1364/OL.39.004695 [26] Zhao G, Bailey DM, Fleisher AJ et al. Doppler-free two-photon cavity ring-down spectroscopy of a nitrous oxide (N2O) vibrational overtone transition. Phys Rev A 101, 062509 (2020). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.101.062509 [27] Motto-Ros V, Morville J, Rairoux P. Mode-by-mode optical feedback: cavity ringdown spectroscopy. Appl Phys B 87, 531–538 (2007). [28] Maity A, Maithani S, Pradhan M. Cavity ring-down spectroscopy: recent technological advancements, techniques, and applications. Anal Chem 93, 388–416 (2021). doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.0c04329 [29] Coldren LA, Corzine SW, Mašanović ML. Dynamic effects. In Coldren LA, Corzine SW, Mašanović ML. Diode Lasers and Photonic Integrated Circuits (John Wiley & Sons, Inc. , Hoboken, USA, 2012). [30] Capasso F, Gmachl C, Sivco DL et al. Quantum cascade lasers. Phys Today 55, 34–40 (2002). [31] Mezzapesa FP, Columbo LL, Brambilla M et al. Intrinsic stability of quantum cascade lasers against optical feedback. Opt Express 21, 13748–13757 (2013). doi: 10.1364/OE.21.013748 [32] Zhao BB, Wang XG, Wang C. Strong optical feedback stabilized quantum cascade laser. ACS Photonics 7, 1255–1261 (2020). doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.0c00189 [33] Orr BJ, He YB. Rapidly swept continuous-wave cavity-ringdown spectroscopy. Chem Phys Lett 512, 1–20 (2011). doi: 10.1016/j.cplett.2011.05.052 [34] Truong GW, Perner LW, Bailey DM et al. Mid-infrared supermirrors with finesse exceeding 400000. Nat Commun 14, 7846 (2023). doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-43367-z [35] Li XY, Fan ZF, Deng Y et al. 30-kHz linewidth interband cascade laser with optical feedback. Appl Phys Lett 120, 171109 (2022). doi: 10.1063/5.0090937 [36] Yang M, Wang Z, Nie QX et al. Mid-infrared cavity-enhanced absorption sensor for ppb-level N2O detection using an injection-current-modulated quantum cascade laser. Opt Express 29, 41634–41642 (2021). doi: 10.1364/OE.444286 [37] Foltynowicz A, Schmidt FM, Ma W et al. Noise-immune cavity-enhanced optical heterodyne molecular spectroscopy: Current status and future potential. Appl Phys B 92, 313–326 (2008). [38] Nie QX, Wang Z, Borri S et al. Mid-infrared swept cavity-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy using a quartz tuning fork. Appl Phys Lett 123, 054102 (2023). doi: 10.1063/5.0159131 [39] Jin W, Cao YC, Yang F et al. Ultra-sensitive all-fibre photothermal spectroscopy with large dynamic range. Nat Commun 6, 6767 (2015). doi: 10.1038/ncomms7767 [40] Liao XY, Wang XG, Zhou K et al. Terahertz quantum cascade laser frequency combs with optical feedback. Opt Express 30, 35937–35950 (2022). doi: 10.1364/OE.467992 [41] Guan W, Li ZP, Wu SM et al. Relative phase locking of a terahertz laser system configured with a frequency comb and a single-mode laser. Adv Photonics Nexus 2, 026006 (2023). -
Supplementary Information
Supplementary information for Agile cavity ringdown spectroscopy enabled by moderate optical feedback to a quantum cascade laser 
-
Access History

Article Metrics
-
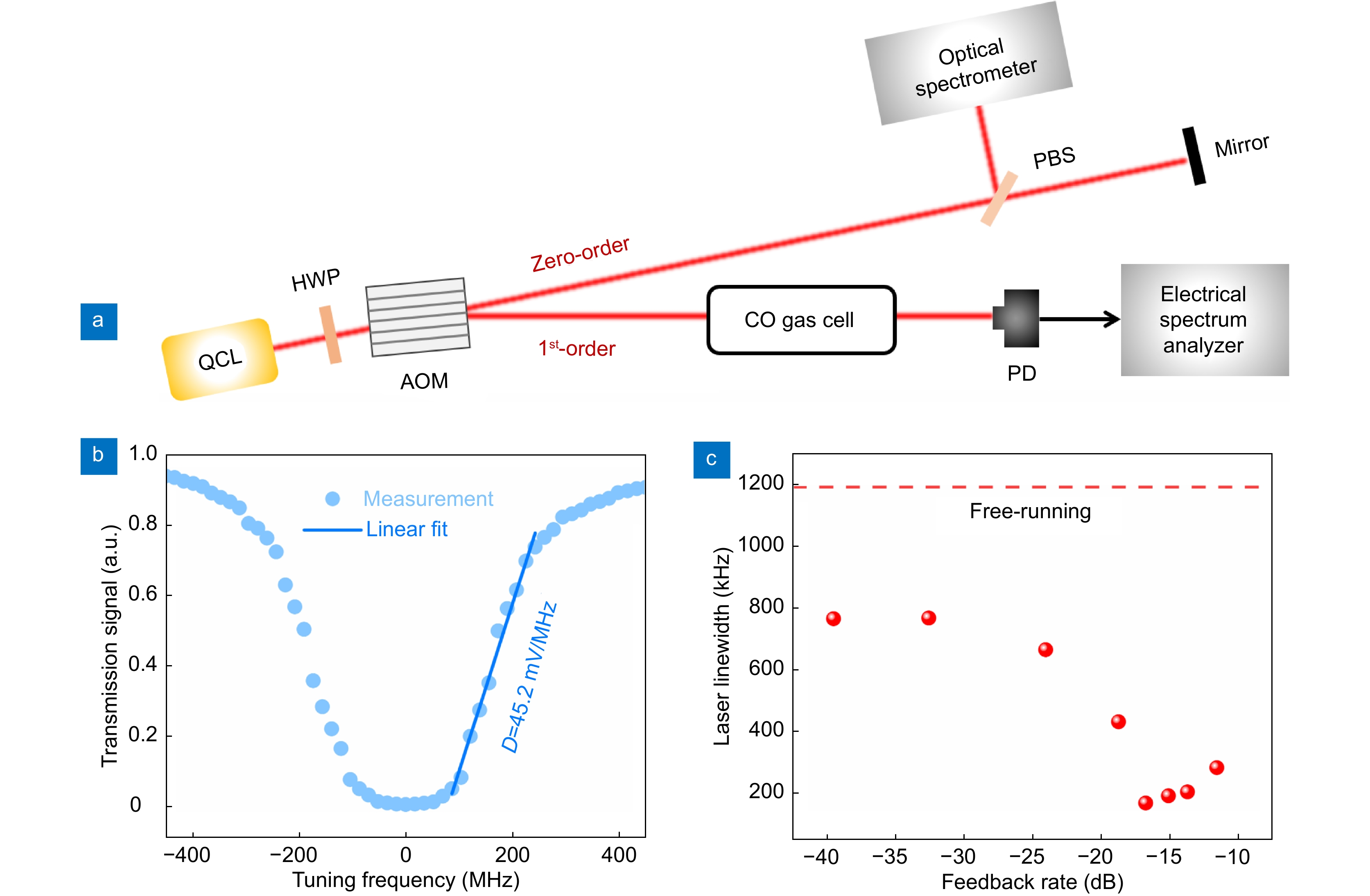
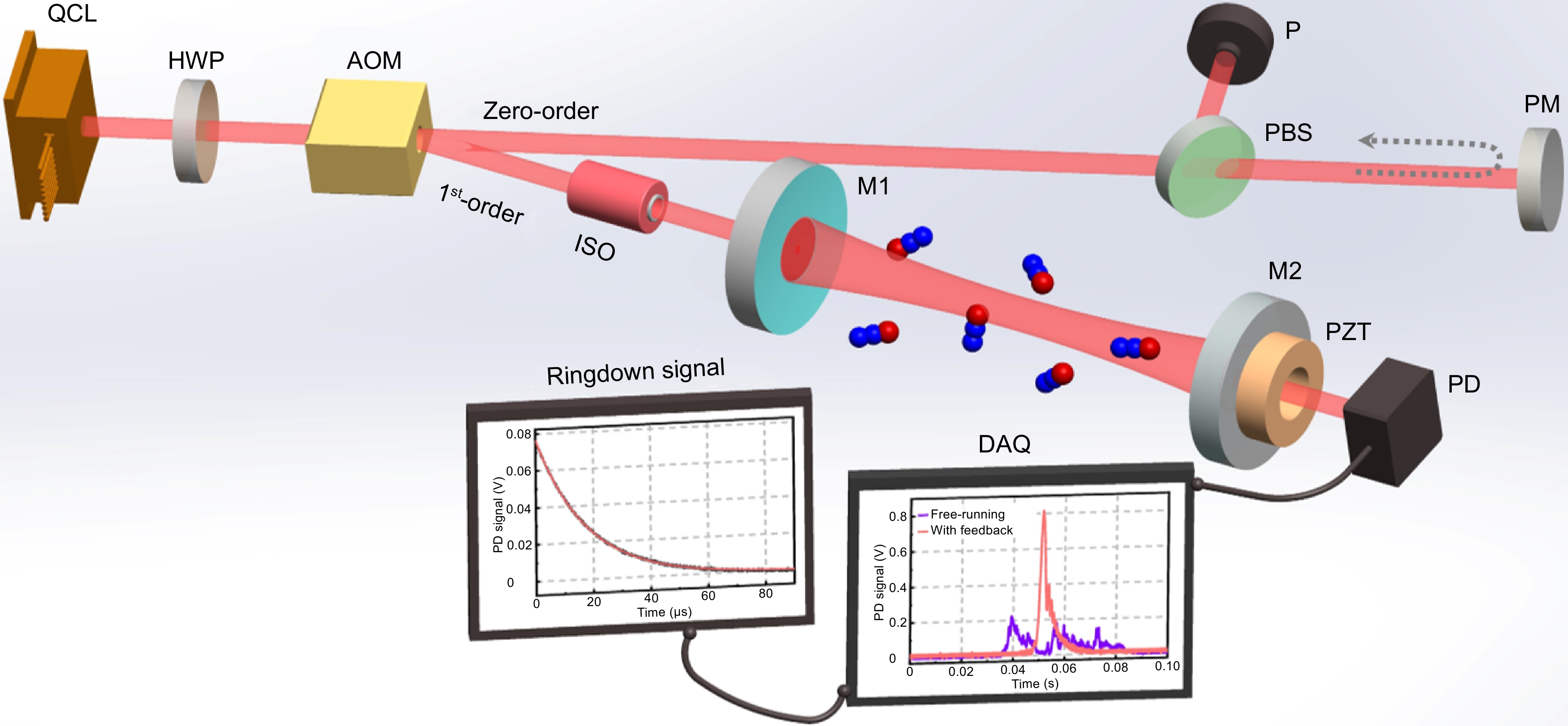
Figure 1.
Principle of the agile CRDS with moderate optical feedback to a QCL. HWP: half-wave plate; AOM: acousto-optic modulator; PBS: polarizing beamsplitter; PM: plane mirror; P: power meter; ISO: optical isolator; M1, M2: cavity mirrors; PZT: piezoelectric actuator; PD: photodetector; DAQ: data acquisition card.
-
Figure 2.
Characterization of QCL linewidth. (a) Experimental setup. The absorption line of CO sealed in a gas cell (15 Torr) is used as a frequency discriminator. (b) Typical transmission signal of the QCL through the CO reference cell. (c) Variation of QCL linewidth with the feedback rate. The dashed line indicates the linewidth of the free-running QCL.
-
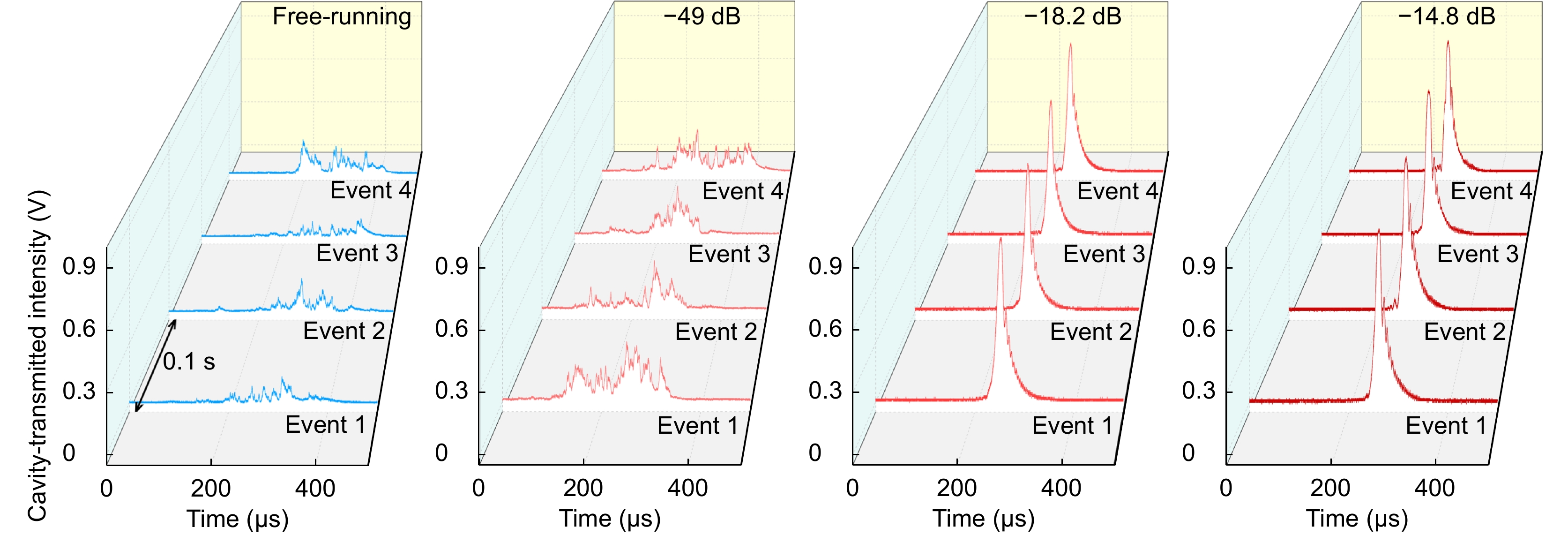
Figure 3.
Comparison of the cavity-transmitted signals with different levels of optical feedback. Four ringdown events obtained by scanning the cavity length with a triangle waveform (5 Hz) are shown in each figure. The QCL is operating either at the free-running state or with optical feedback (from −49 dB to −14.8 dB).
-
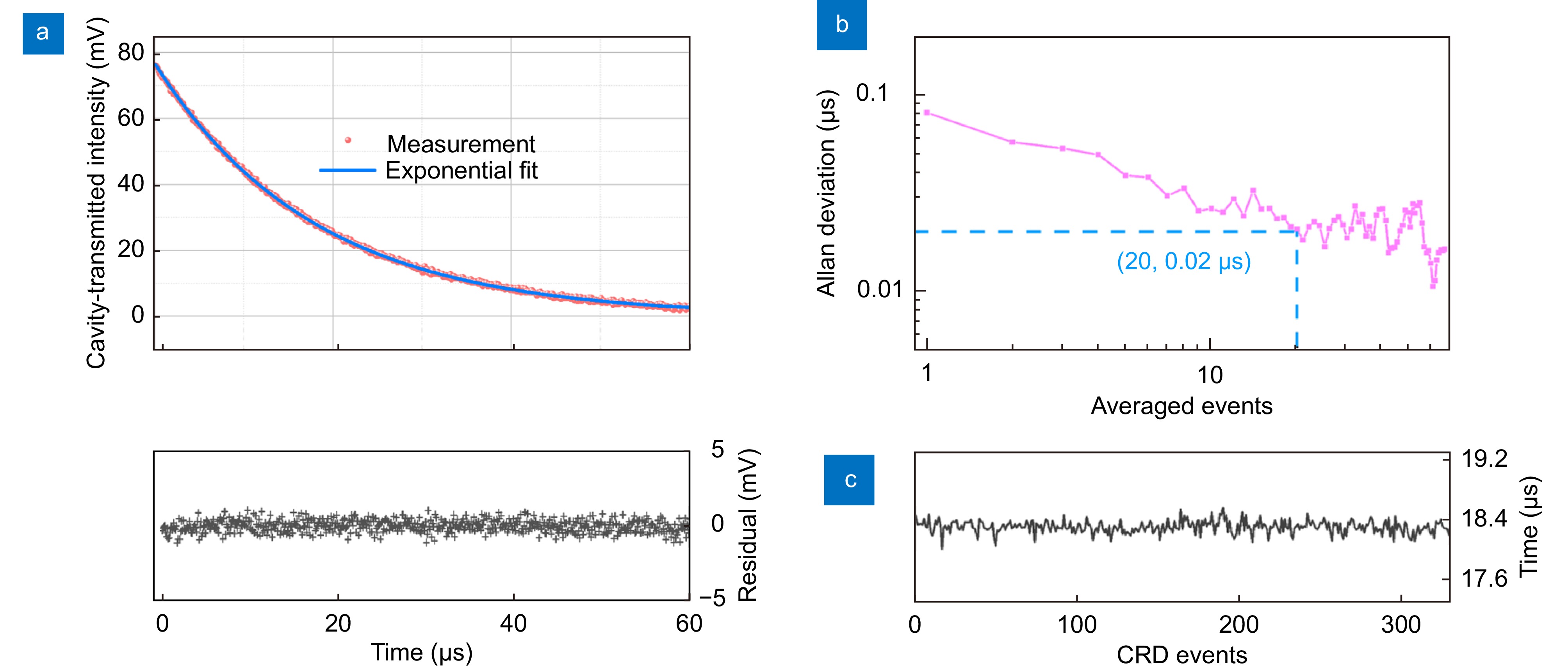
Figure 4.
Cavity ringdown measurement with a feedback rate of −18.2 dB. The cavity is in a vacuum. (a) Characterization of a single cavity ringdown event with an incident optical power of 0.4 mW. The residual between the measurement and exponential fit is plotted in the bottom panel, and the SNR of the ringdown signal is 162. (b) Allan deviation analysis of the ringdown time measurement. (c) Continuous measurement of more than 300 ringdown events.
-
Figure 5.
High-resolution and high-sensitivity molecular spectroscopy of trace amount of N2O. (a) Measured absorption spectrum of 10 ppb N2O. The residual of the spectral fitting by the Lorentzian function is plotted in the bottom panel. (b) Comparison of the CRDS measurements with the nominal concentrations of N2O (1–10 ppb). The horizontal error bar represents the uncertainty in the nominal gas concentration, while the vertical error bar (too small to be visible) represents the 1−σ standard deviation of 300 CRDS measurements.

 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: